Restoring critical IT systems and operations following disruptive events involves establishing predetermined procedures and infrastructure. These might include failing over to a backup data center in another geographic location when the primary... Read more »

The process of evaluating applications and systems designed to restore data and functionality after unforeseen events like natural disasters, cyberattacks, or hardware failures is critical for business continuity. For example, a simulated... Read more »
A robust plan for business continuity and data protection in the cloud involves establishing resilient systems capable of withstanding outages and quickly restoring services. This typically encompasses a combination of infrastructure and... Read more »

A structured evaluation of processes designed to restore critical IT infrastructure and data following an unforeseen disruptive event is essential for any organization. This evaluation simulates various scenarios, from natural disasters to... Read more »
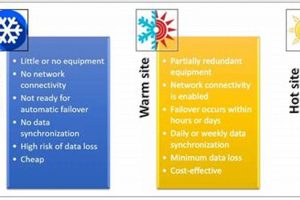
A facility designated for business continuity purposes provides basic infrastructure but lacks active equipment. This setup involves customers providing and installing their own hardware and software after a disruptive event. For instance,... Read more »

Protecting digital assets and ensuring business continuity are paramount in today’s interconnected world. This involves implementing strategies that safeguard data against loss from hardware failures, cyberattacks, natural disasters, and human error. For... Read more »

The ability of an organization to resume vital IT operations following an unplanned outage or disruption affecting its data center constitutes a critical business function. This involves a range of strategies and... Read more »
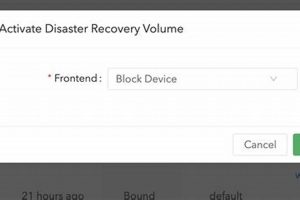
In the realm of data protection, a persistent storage entity dedicated to safeguarding critical information and ensuring business continuity in the event of system failures plays a vital role. This dedicated storage... Read more »

The process of restoring critical data and applications housed on a failed server is essential for business continuity. For example, a company might replicate its server data to a secondary location, enabling... Read more »

Restoring vital IT infrastructure and operations in England’s second-largest city following unforeseen events like natural disasters, cyberattacks, or hardware failures is a critical aspect of business continuity. Imagine a scenario where a... Read more »


