
The Hindenburg disaster refers to the catastrophic fire that consumed the German passenger airship LZ 129 Hindenburg on May 6, 1937, in Lakehurst, New Jersey. Moored at the Naval Air Station Lakehurst... Read more »

The catastrophic destruction of the German passenger airship LZ 129 Hindenburg occurred on May 6, 1937, at Naval Air Station Lakehurst in Manchester Township, New Jersey. Thirty-six passengers and crew members aboard... Read more »

Calamities stemming from human actions, negligence, or mismanagement, rather than natural processes, encompass a broad spectrum of events. Examples include technological accidents like industrial explosions or nuclear meltdowns, environmental degradation such as... Read more »
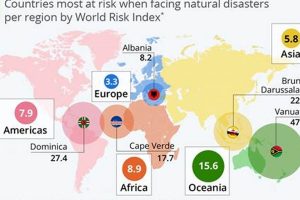
A catastrophic event with atmospheric, geological, or hydrological origins is generally classified as a natural disaster. Examples include earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, floods, wildfires, hurricanes, droughts, and landslides. These events are characterized... Read more »
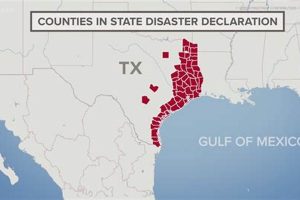
A presidential disaster declaration allows counties in Texas affected by specific events to receive federal assistance. This aid can include grants for temporary housing and home repairs, low-cost loans to cover uninsured... Read more »

New York State, while not typically associated with widespread catastrophic events, faces a range of potential natural hazards. These include severe winter storms featuring heavy snow, freezing rain, and blizzards; flooding from... Read more »
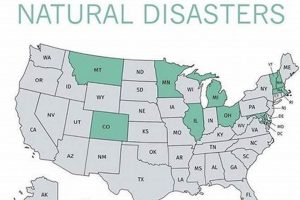
No state is entirely free from the risk of natural hazards. While some regions experience certain hazards more frequently or intensely than others, all areas of the United States are susceptible to... Read more »

This phrase signifies a search for information regarding a specific unfortunate event that occurred in Pismo Beach, California. It suggests a desire to understand the nature of the incident, its causes, and... Read more »
Hardship withdrawals from retirement accounts, specifically permitted under IRS regulations, allow access to funds before retirement age without the usual penalties in specific circumstances. These qualifying events typically encompass sudden, unexpected, and... Read more »

Catastrophic natural events pose significant threats to human life and infrastructure. These events encompass a range of phenomena, including geophysical events like earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions, as well as climate-related hazards... Read more »


