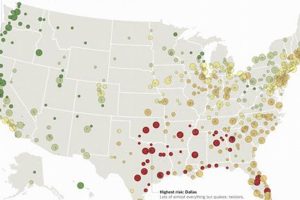
Determining areas with minimal natural hazard risk involves analyzing various factors, including seismic activity, hurricane and tornado frequency, wildfire susceptibility, flood plains, drought prevalence, and extreme temperature variations. A region’s infrastructure and... Read more »
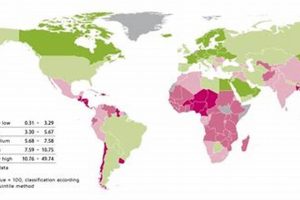
Regions with minimal exposure to geological hazards like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, as well as hydrological and meteorological events such as floods, cyclones, and wildfires, are generally considered low-risk. Factors like robust... Read more »
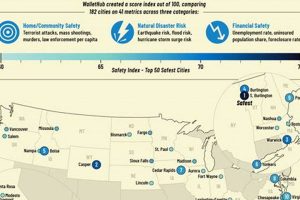
Determining areas with minimal risk from environmental hazards involves considering the likelihood of earthquakes, hurricanes, wildfires, tornadoes, floods, and droughts. For example, a region might be relatively safe from hurricanes but susceptible... Read more »
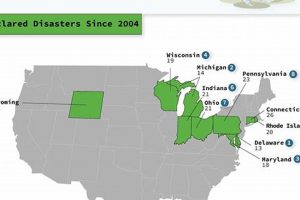
Determining regions with minimal risk from natural hazards involves assessing geological stability, climate patterns, and historical disaster data. For example, areas less prone to earthquakes, hurricanes, wildfires, and flooding are generally considered... Read more »

Minimizing exposure to natural hazards is a critical factor in determining optimal locations for human settlement. Vulnerability to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, floods, wildfires, and extreme weather events varies significantly across the... Read more »

Regions experiencing minimal geological and meteorological events, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, floods, wildfires, and cyclones, offer enhanced safety and stability. These areas often exhibit specific geological and climatic characteristics, like stable... Read more »

Determining areas with minimal risk from natural hazards involves analyzing historical data on events like hurricanes, floods, wildfires, tornadoes, and droughts. Factors such as elevation, proximity to fault lines, and building codes... Read more »
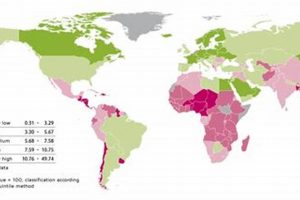
Regions with minimal exposure to geological hazards like earthquakes, volcanoes, and tsunamis, as well as meteorological events such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts, are often considered desirable locations for settlement and infrastructure... Read more »

The concept of a region with minimal vulnerability to geophysical and hydrometeorological hazards is a complex one. No location is entirely immune to the forces of nature. However, certain areas exhibit statistically... Read more »
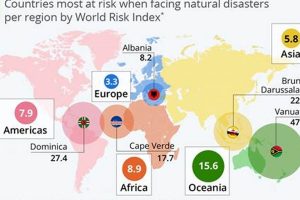
Regions with minimal exposure to geological hazards like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, hydrological events such as floods and tsunamis, and climatological threats like hurricanes and droughts are considered prime candidates for human... Read more »


