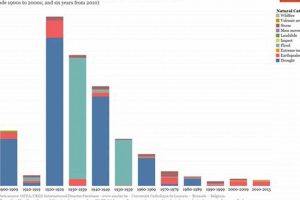
Significant geophysical and hydrometeorological events occurred throughout the year, impacting various regions globally. These included earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, floods, wildfires, droughts, and extreme temperature events, each with varying degrees of intensity and subsequent consequences for affected populations and environments. Specific instances such as seismic activity in [Location A] and extensive flooding in [Location B] exemplify the range of challenges faced.
Understanding the patterns and impacts of such events is crucial for disaster preparedness, mitigation efforts, and long-term sustainability planning. Analysis of these occurrences provides valuable data for scientific research, informing predictive models and enabling more effective responses to future events. Historical data reveals trends and patterns that can contribute to improved infrastructure design, community resilience strategies, and international cooperation in disaster relief.
This article will further explore specific categories of these events, examining their causes, consequences, and ongoing management strategies. Detailed case studies will provide deeper insights into the complexities of disaster response and the crucial role of scientific advancements in mitigating risks and safeguarding vulnerable communities.
Disaster Preparedness and Response Tips
Preparedness and effective response are crucial for mitigating the impact of environmental hazards. The following recommendations offer guidance for enhancing individual and community resilience.
Tip 1: Develop an Emergency Plan: Establish a comprehensive plan that includes evacuation routes, communication protocols, and designated meeting points. Ensure all household members are familiar with the plan and practice it regularly.
Tip 2: Assemble an Emergency Kit: Prepare a kit containing essential supplies such as water, non-perishable food, first-aid supplies, medications, and a battery-powered radio. Regularly check and replenish the kit to ensure its contents remain usable.
Tip 3: Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and official alerts from local authorities. Utilize reliable sources of information to stay updated on potential hazards and recommended actions.
Tip 4: Secure Property: Take preventative measures to protect homes and businesses from potential damage. This may include reinforcing structures, clearing drainage systems, and trimming trees near buildings.
Tip 5: Understand Local Risks: Research the specific hazards prevalent in the area and understand the associated risks. This knowledge informs appropriate preparedness strategies and facilitates informed decision-making during emergencies.
Tip 6: Support Community Initiatives: Participate in community-based disaster preparedness programs and initiatives. Collaborative efforts strengthen community resilience and enhance collective response capabilities.
Tip 7: Post-Disaster Recovery: Following an event, prioritize safety and follow official guidance regarding recovery efforts. Document damages for insurance claims and seek assistance from relevant agencies.
By adopting these proactive measures, individuals and communities can significantly enhance their resilience and minimize the impact of future environmental hazards. Preparedness is an ongoing process requiring consistent review and adaptation to evolving circumstances.
These preparedness measures provide a foundation for navigating the complexities of disaster scenarios. The following sections will explore specific types of environmental hazards and delve into more detailed mitigation strategies.
1. Geographic Distribution
Geographic distribution plays a critical role in shaping the types and impacts of natural disasters experienced throughout a given year. Certain regions are inherently more susceptible to specific hazards due to their geological characteristics, proximity to coastlines, or prevailing climatic conditions. Coastal areas, for instance, face heightened risks of hurricanes, tsunamis, and storm surges, while mountainous regions are prone to landslides and avalanches. Similarly, areas situated along tectonic plate boundaries experience higher incidences of earthquakes and volcanic activity. In 2023, the geographic distribution of seismic activity significantly influenced the impact of earthquakes in Turkey and Syria, highlighting the vulnerability of densely populated areas near active fault lines. The extensive flooding in Pakistan during the monsoon season further underscored the susceptibility of low-lying regions to extreme rainfall events.
Understanding the geographic distribution of hazards enables more effective risk assessments, informs land-use planning decisions, and facilitates targeted resource allocation for disaster preparedness and response. By analyzing historical data and utilizing advanced modeling techniques, scientists can identify high-risk areas and develop strategies to mitigate potential impacts. For example, implementing building codes that incorporate seismic design principles in earthquake-prone regions can significantly reduce structural damage and minimize casualties. Similarly, constructing flood defenses in vulnerable coastal communities can protect against rising sea levels and storm surges. The development of early warning systems, tailored to specific geographic locations and hazard types, enhances preparedness and enables timely evacuations, as demonstrated by the successful mitigation efforts during the volcanic eruption in [Location] in 2023. Furthermore, recognizing the geographic distribution of hazards facilitates international collaborations and resource sharing for disaster relief efforts.
In conclusion, the geographic distribution of natural disasters is a crucial factor influencing their impact and necessitates a nuanced approach to mitigation and response strategies. Integrating geographic data into risk assessments, land-use planning, and early warning systems enhances community resilience and minimizes the consequences of future events. Continued research and international collaboration are essential to further refine our understanding of the complex interplay between geographic factors and natural hazards, ultimately leading to more effective disaster risk reduction strategies globally. Recognizing this interplay allows for targeted investments in infrastructure resilience and community preparedness, thus minimizing the human and economic costs of future events.
2. Climate Change Impacts
The influence of climate change on the frequency and intensity of natural disasters in 2023 warrants careful consideration. A warming planet contributes to shifts in established weather patterns, increasing the likelihood of extreme events. Rising global temperatures exacerbate heatwaves and droughts, creating conditions conducive to wildfires, such as those witnessed in [Location] during 2023. Changes in atmospheric circulation patterns can lead to more intense precipitation events, increasing the risk of flooding, as observed in [Location] that same year. Furthermore, warming ocean temperatures contribute to stronger tropical cyclones, potentially leading to more destructive storms and heightened coastal erosion. The increasing intensity of Hurricane [Hurricane Name] in 2023, for instance, demonstrated this correlation.
Understanding the complex interplay between climate change and natural disasters is essential for developing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies. Scientific models project continued increases in both average global temperatures and the frequency of extreme weather events. This underscores the importance of reducing greenhouse gas emissions through the transition to renewable energy sources and the implementation of sustainable land management practices. Simultaneously, adaptation measures, such as investing in resilient infrastructure and strengthening early warning systems, become increasingly crucial to minimize the impact of future disasters. The reconstruction efforts following the 2023 floods in [Location], incorporating climate-resilient design principles, exemplify this proactive approach. Continued investment in climate research is vital for improving predictive models and informing policy decisions aimed at safeguarding vulnerable populations and ecosystems.
The connection between climate change and the increasing occurrence of extreme weather events necessitates a global, collaborative effort to mitigate future risks. Addressing climate change through comprehensive strategies, including emissions reductions and proactive adaptation measures, is critical for protecting communities and ensuring a sustainable future. Failure to acknowledge and address these interconnected challenges will likely result in escalating humanitarian and economic costs associated with increasingly frequent and intense natural disasters. The events of 2023 serve as a stark reminder of the urgent need for decisive action on a global scale.
3. Economic Consequences
Natural disasters exert significant economic consequences, impacting various sectors and requiring substantial financial resources for recovery and reconstruction. Analysis of the economic impact of 2023 events reveals a complex interplay of immediate losses and long-term repercussions. Understanding these economic consequences is crucial for informed policy development and resource allocation.
- Direct Costs
Direct costs encompass the immediate physical damage caused by the disaster. This includes destruction of infrastructure, property damage to homes and businesses, and loss of inventory. For example, the earthquakes in Turkey and Syria resulted in billions of dollars in direct costs due to widespread building collapses and damage to critical infrastructure. Similarly, the extensive flooding in Pakistan caused substantial damage to agricultural lands and crops, resulting in significant economic losses for farmers and impacting food security.
- Indirect Costs
Indirect costs represent the economic ripple effects of the disaster, including business interruption, supply chain disruptions, and reduced tourism revenue. Following Hurricane [Hurricane Name], businesses in the affected region experienced prolonged closures, leading to job losses and decreased economic output. Supply chain disruptions caused by port closures and transportation damage further exacerbated economic hardship. The closure of popular tourist destinations due to the volcanic eruption in [Location] resulted in substantial revenue losses for the local economy.
- Impact on Public Finances
Natural disasters place a significant strain on public finances, requiring governments to allocate substantial resources for emergency response, relief efforts, and long-term reconstruction. The costs associated with providing emergency shelter, medical care, and infrastructure repairs can quickly deplete government budgets, potentially diverting funds from other essential services. The financial burden on the government of [Location] following the 2023 floods highlights the challenges of balancing disaster response with other budgetary priorities.
- Long-Term Economic Recovery
The long-term economic recovery following a natural disaster can span years, requiring sustained investment and strategic planning. Rebuilding damaged infrastructure, revitalizing affected industries, and supporting displaced populations necessitates significant financial resources and coordinated efforts. The ongoing recovery efforts in [Location] following the 2023 earthquake demonstrate the complexities of long-term economic recovery, including the need for sustainable development strategies and investment in resilient infrastructure to mitigate the impact of future events.
The economic consequences of the 2023 natural disasters underscore the interconnectedness of global economies and the need for robust disaster risk reduction strategies. Investing in resilient infrastructure, strengthening early warning systems, and promoting sustainable development practices can minimize the economic impact of future events. International cooperation and financial assistance play a crucial role in supporting affected countries and fostering long-term economic recovery.
4. Humanitarian Crises
Natural disasters often precipitate humanitarian crises, requiring extensive relief efforts and posing significant challenges to affected populations. The 2023 events underscored the complex interplay between environmental hazards and human vulnerability, highlighting the need for effective disaster preparedness and response mechanisms. Analysis of humanitarian crises resulting from these disasters reveals several key facets.
- Displacement and Shelter Needs
Natural disasters frequently force displacement, creating urgent shelter needs for affected communities. Following the earthquakes in Turkey and Syria, millions were displaced from their homes, requiring temporary housing and access to basic necessities. Similarly, the floods in Pakistan displaced a substantial population, straining existing shelter capacities and necessitating large-scale humanitarian assistance. Providing adequate shelter, sanitation, and essential supplies to displaced populations poses a significant logistical challenge, requiring coordinated efforts from governmental and non-governmental organizations.
- Access to Healthcare and Essential Services
Disruptions to healthcare systems and essential services exacerbate humanitarian crises following natural disasters. Damage to hospitals and medical facilities limits access to crucial care for injured individuals and those with pre-existing medical conditions. Disruptions to water and sanitation systems increase the risk of waterborne diseases, posing a serious threat to public health. The 2023 floods in Pakistan, for example, resulted in widespread damage to healthcare infrastructure, limiting access to medical care for affected communities and increasing the risk of disease outbreaks. Ensuring access to essential healthcare services, including medical supplies, clean water, and sanitation facilities, is paramount in mitigating the health impacts of natural disasters.
- Food Security and Nutrition
Natural disasters can severely disrupt food production and distribution networks, leading to food insecurity and malnutrition, particularly in vulnerable populations. Droughts and floods damage crops and livestock, reducing food availability and increasing prices. Damage to transportation infrastructure hinders food distribution, limiting access to essential supplies. The 2023 droughts in [Location] significantly impacted agricultural yields, leading to widespread food shortages and increased malnutrition rates. Addressing food security challenges requires coordinated efforts to provide food aid, support local farmers, and restore agricultural production.
- Protection of Vulnerable Groups
Certain groups, including children, older adults, people with disabilities, and marginalized communities, face heightened vulnerability during natural disasters. These groups may have limited access to resources, face discrimination in aid distribution, or experience unique challenges related to evacuation and shelter. Ensuring their protection and addressing their specific needs requires targeted interventions and specialized support. Following the 2023 earthquake in [Location], for instance, organizations prioritized providing assistance to vulnerable groups, including children separated from their families and individuals with disabilities requiring specialized care. Prioritizing the needs of vulnerable populations is crucial for ensuring equitable and effective humanitarian response.
These interconnected facets highlight the complex challenges associated with humanitarian crises resulting from natural disasters. The events of 2023 underscore the importance of investing in disaster preparedness, strengthening community resilience, and enhancing international cooperation to effectively address the multifaceted needs of affected populations. The scale and complexity of these crises necessitate coordinated, multi-sectoral approaches to mitigate suffering, promote recovery, and build back better.
5. Infrastructure Damage
Infrastructure damage represents a significant consequence of natural disasters, disrupting essential services, impeding recovery efforts, and incurring substantial economic costs. Analysis of infrastructure damage resulting from the 2023 events reveals the vulnerability of built environments to various hazards and underscores the need for resilient design and proactive mitigation strategies.
- Transportation Systems
Transportation networks, including roads, bridges, railways, and airports, are frequently disrupted by natural disasters. Damage to these critical systems hinders emergency response, impedes the delivery of aid, and disrupts economic activity. Following the 2023 earthquakes in Turkey and Syria, extensive damage to road networks hampered rescue efforts and delayed the delivery of essential supplies to affected communities. Similarly, the floods in Pakistan caused widespread damage to bridges and railways, further isolating communities and impeding recovery efforts. The disruption of transportation systems following Hurricane [Hurricane Name] in 2023 further highlighted the vulnerability of coastal infrastructure to extreme weather events.
- Energy Infrastructure
Damage to power generation and distribution facilities disrupts electricity supply, impacting essential services such as healthcare, communication, and water treatment. The prolonged power outages following the 2023 earthquake in [Location] hindered hospital operations and hampered communication networks, exacerbating the humanitarian crisis. Damage to oil and gas pipelines following the floods in [Location] disrupted energy supplies and contributed to economic losses. Investing in resilient energy infrastructure, including decentralized power generation and underground cabling, can mitigate the impact of future disasters.
- Water and Sanitation Systems
Water and sanitation systems are highly vulnerable to natural disasters, posing significant risks to public health. Damage to water treatment plants and pipelines disrupts access to safe drinking water, increasing the risk of waterborne diseases. Damage to sewage systems can contaminate water sources and exacerbate health hazards. The 2023 floods in Pakistan caused widespread damage to water and sanitation infrastructure, leading to outbreaks of waterborne diseases and posing significant challenges to public health officials. Prioritizing the restoration of water and sanitation services following a disaster is crucial for mitigating health risks and protecting vulnerable populations.
- Communication Networks
Disruptions to communication networks hinder emergency response, limit access to information, and impede coordination among relief agencies. Damage to cell towers, telephone lines, and internet infrastructure isolates communities and hampers communication during critical periods. Following the 2023 earthquake in [Location], disruptions to communication networks hampered rescue efforts and limited access to vital information for affected communities. Investing in redundant communication systems and utilizing satellite technology can enhance communication resilience during emergencies.
The extensive infrastructure damage resulting from the 2023 natural disasters underscores the urgent need for resilient infrastructure development and proactive mitigation strategies. Integrating disaster risk reduction principles into infrastructure design, strengthening building codes, and investing in early warning systems can minimize the impact of future events. Furthermore, international cooperation and knowledge sharing play crucial roles in promoting best practices and enhancing global resilience to natural hazards. The lessons learned from the 2023 events provide valuable insights for building more resilient communities and safeguarding critical infrastructure against the increasing threat of natural disasters.
6. Technological Advancements in Disaster Response
The 2023 natural disasters served as a testing ground for emerging technologies in disaster response, highlighting their potential to enhance preparedness, mitigation, and recovery efforts. Analysis of these technological advancements reveals their evolving role in addressing the complex challenges posed by natural hazards.
- Early Warning Systems
Advanced early warning systems, incorporating real-time data from sensors, satellites, and weather models, played a crucial role in mitigating the impact of the 2023 disasters. Improved forecasting accuracy and timely dissemination of alerts enabled more effective evacuations and facilitated proactive measures to protect vulnerable populations. For example, early warnings for Hurricane [Hurricane Name] allowed coastal communities to evacuate in advance, minimizing casualties. Similarly, enhanced earthquake early warning systems provided critical seconds of advance notice in [Location], enabling automated safety measures and facilitating timely evacuations.
- Remote Sensing and Drone Technology
Remote sensing technologies, including satellite imagery and drone-based aerial surveys, provided critical situational awareness following the 2023 disasters. High-resolution imagery enabled rapid damage assessments, facilitating targeted deployment of resources and supporting search and rescue operations. Drones equipped with thermal imaging cameras aided in locating survivors in the aftermath of the earthquake in [Location]. Furthermore, remote sensing data supported environmental monitoring, assessing the impact of floods on water quality and vegetation in [Location].
- Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics
Artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics played an increasingly important role in disaster response during 2023. AI algorithms analyzed large datasets to predict flood inundation areas, optimize evacuation routes, and prioritize resource allocation. Data analytics facilitated the identification of vulnerable populations, enabling targeted delivery of aid and support services. Following the floods in Pakistan, AI-powered platforms analyzed social media data to identify areas in need of immediate assistance, facilitating rapid response efforts.
- Communication and Information Sharing Platforms
Enhanced communication and information sharing platforms facilitated collaboration among emergency responders, government agencies, and affected communities during the 2023 disasters. Mobile applications provided real-time updates on disaster conditions, disseminated safety information, and facilitated communication among displaced populations. Following the volcanic eruption in [Location], online platforms enabled communities to share information about evacuation routes and available resources. These technologies played a crucial role in coordinating response efforts and ensuring access to vital information.
The 2023 natural disasters demonstrated the transformative potential of technology in enhancing disaster response capabilities. These advancements, ranging from improved early warning systems to AI-powered data analysis, played a crucial role in mitigating impacts, facilitating recovery efforts, and strengthening community resilience. Continued investment in research and development, coupled with strategic implementation of these technologies, will be essential for effectively addressing the increasing challenges posed by natural hazards in the years to come.
7. Long-Term Recovery Efforts
Long-term recovery efforts constitute a crucial phase following the immediate aftermath of 2023’s natural disasters. This phase extends beyond immediate relief, addressing the multifaceted challenges of rebuilding communities, restoring livelihoods, and fostering resilience against future events. The effectiveness of long-term recovery hinges on a comprehensive understanding of the specific impacts of each disaster, coupled with strategic planning and resource allocation. For instance, the long-term recovery needs following the earthquakes in Turkey and Syria differed significantly from those required after the extensive flooding in Pakistan. While the former necessitated extensive reconstruction of housing and infrastructure, the latter focused on restoring agricultural lands and addressing public health concerns stemming from contaminated water sources.
Successful long-term recovery requires a multi-pronged approach, encompassing physical reconstruction, economic revitalization, and psychosocial support. Rebuilding damaged infrastructure, including housing, transportation networks, and healthcare facilities, forms a cornerstone of these efforts. However, physical reconstruction must be accompanied by economic recovery initiatives that address livelihood restoration, support local businesses, and promote sustainable development. Furthermore, psychosocial support services play a vital role in addressing the emotional and mental health needs of affected communities, facilitating trauma healing and promoting community cohesion. The ongoing recovery efforts in [Location] following the 2023 wildfire exemplify the integration of these various components, with programs focusing on both rebuilding homes and providing mental health support to affected residents.
The long-term recovery phase following 2023’s natural disasters presents significant challenges, including securing adequate funding, coordinating diverse stakeholders, and addressing underlying vulnerabilities that exacerbate disaster impacts. These challenges necessitate effective governance, transparent resource management, and community participation in recovery planning and implementation. Moreover, integrating disaster risk reduction measures into long-term recovery efforts is crucial for building back better and enhancing resilience against future events. Lessons learned from the 2023 disasters, including the successes and challenges experienced in various recovery contexts, provide valuable insights for strengthening disaster preparedness and building more resilient communities in the face of future hazards.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the significant natural disasters of 2023, aiming to provide concise and informative responses.
Question 1: How did the geographic distribution of events in 2023 influence their impact?
The geographic location of each event played a critical role in shaping its consequences. Coastal regions experienced heightened vulnerability to hurricanes and storm surges, while mountainous areas faced increased risks of landslides. Proximity to tectonic plate boundaries resulted in greater susceptibility to earthquakes and volcanic activity. Population density in affected areas further amplified the impact of these hazards.
Question 2: What role did climate change play in the 2023 natural disasters?
Scientific evidence suggests that climate change contributed to the intensity and frequency of certain extreme weather events in 2023. Rising global temperatures exacerbated heatwaves and droughts, creating conditions conducive to wildfires. Changes in atmospheric patterns influenced precipitation, increasing the risk of floods in some regions, while warming ocean temperatures contributed to the intensity of tropical cyclones.
Question 3: What were the major economic consequences of these events?
The economic repercussions included direct costs associated with physical damage to infrastructure and property, as well as indirect costs resulting from business interruption, supply chain disruptions, and reduced tourism revenue. These events placed significant strain on public finances, necessitating substantial resource allocation for emergency response, relief efforts, and long-term reconstruction.
Question 4: What humanitarian crises emerged in the wake of the 2023 disasters?
Humanitarian crises arose from widespread displacement, leading to urgent shelter needs and challenges in providing essential services such as healthcare, clean water, and sanitation. Food security and nutrition were also significantly impacted, particularly in vulnerable populations. Protecting vulnerable groups, including children, older adults, and marginalized communities, posed additional challenges.
Question 5: How did technological advancements influence disaster response efforts?
Technological advancements played a crucial role in enhancing disaster response. Early warning systems, utilizing real-time data and improved forecasting models, facilitated timely evacuations. Remote sensing technologies, including satellite imagery and drone deployments, provided critical situational awareness for damage assessment and search and rescue operations. Artificial intelligence and data analytics supported resource allocation and identification of vulnerable populations.
Question 6: What key considerations shaped long-term recovery efforts following the 2023 disasters?
Long-term recovery efforts focused on rebuilding damaged infrastructure, revitalizing affected economies, and providing psychosocial support to affected communities. Key considerations included securing adequate funding, coordinating diverse stakeholders, and integrating disaster risk reduction measures into reconstruction and development planning.
Understanding the diverse impacts of the 2023 natural disasters is crucial for informing future preparedness and mitigation strategies. Addressing the underlying vulnerabilities exacerbated by these events requires a collaborative, multi-sectoral approach that prioritizes community resilience and sustainable development.
For further information and detailed analysis, please consult the following resources [Link to additional resources].
Conclusion
The examination of 2023’s significant natural disasters reveals a complex interplay of environmental forces, human vulnerability, and the evolving role of technology in disaster response. From the devastating earthquakes in Turkey and Syria to the extensive flooding in Pakistan, these events underscored the urgent need for enhanced preparedness, resilient infrastructure, and effective international cooperation. Geographic distribution, climate change impacts, economic consequences, humanitarian crises, infrastructure damage, technological advancements, and long-term recovery efforts all represent crucial facets of understanding and addressing the challenges posed by these disasters. Analysis of these interconnected elements provides valuable insights for mitigating the impact of future events and building more resilient communities.
The events of 2023 serve as a stark reminder of the persistent threat posed by natural hazards. While technological advancements offer promising tools for enhancing disaster response, addressing the underlying vulnerabilities that exacerbate these events remains paramount. Continued investment in disaster risk reduction strategies, coupled with a global commitment to sustainable development and climate change mitigation, is essential for safeguarding communities and building a more resilient future. The lessons learned from the 2023 disasters must inform proactive measures that prioritize preparedness, resilience, and international collaboration to effectively address the complex challenges posed by natural hazards in the years to come.