Positions within this field encompass providing medical care in the wake of natural disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods, as well as during public health emergencies such as pandemics or large-scale accidents. These specialized roles may involve triage, emergency treatment, public health outreach, and coordinating medical resources within challenging and often resource-constrained environments.
These critical roles contribute significantly to saving lives and mitigating suffering during crises. The ability to provide timely and effective medical care amidst chaos and devastation is paramount. Historically, the need for such specialized personnel became increasingly apparent as the impact of large-scale disasters grew, leading to the development of dedicated training programs and response teams.
The following sections will explore key aspects of careers in disaster relief nursing, including required skills, typical responsibilities, educational pathways, and potential career paths.
Tips for Pursuing a Career in Disaster Relief Nursing
This section offers practical guidance for those interested in pursuing a career in disaster nursing.
Tip 1: Develop Strong Foundational Nursing Skills: A solid background in core nursing principles and practices is crucial. Experience in areas like emergency room, critical care, or trauma nursing provides invaluable preparation for the demanding environment of disaster response.
Tip 2: Seek Specialized Training and Certifications: Certifications in areas such as disaster nursing, emergency management, or public health can enhance professional qualifications and demonstrate a commitment to this specialized field. Training programs often cover topics like triage, mass casualty management, and field medicine.
Tip 3: Cultivate Adaptability and Resilience: Disaster settings are inherently unpredictable and challenging. The ability to adapt to rapidly changing situations, work under pressure, and cope with emotionally demanding circumstances is essential.
Tip 4: Enhance Physical and Mental Stamina: Disaster response can involve long hours, physically demanding tasks, and exposure to stressful environments. Maintaining physical fitness and developing strategies for managing stress are critical.
Tip 5: Network with Professionals in the Field: Connecting with experienced disaster nurses and other professionals in emergency management can provide valuable insights, mentorship, and potential career opportunities. Attending conferences and joining professional organizations can facilitate networking.
Tip 6: Research and Understand Different Organizations: Various organizations, including governmental agencies, non-profits, and international bodies, employ disaster nurses. Understanding the different roles, missions, and deployment opportunities within each organization is important for career planning.
Tip 7: Be Prepared for Deployment Challenges: Deployment to disaster zones can involve travel to remote locations, working in austere conditions, and being separated from family and support networks. Realistic expectations and preparation for these challenges are vital.
By focusing on these key areas, aspiring disaster nurses can gain the necessary skills, knowledge, and resilience to thrive in this demanding but rewarding field.
The following section will provide a comprehensive overview of the typical career paths available within disaster nursing.
1. Emergency Response
Emergency response is a critical component of disaster nursing, encompassing the immediate actions taken to provide medical care and support to those affected by a catastrophic event. The effectiveness of emergency response directly impacts the survival and recovery of disaster victims, highlighting the crucial role of disaster nurses in these situations.
- Initial Assessment and Triage
Disaster nurses play a vital role in the initial assessment of the scene and the triage of patients. They rapidly evaluate the severity of injuries and prioritize care based on need, ensuring that those with the most life-threatening conditions receive immediate attention. For example, following a building collapse, nurses might utilize triage tags to categorize victims based on injury severity, facilitating efficient allocation of limited medical resources.
- Providing Emergency Medical Care
Delivering essential medical care in often chaotic and resource-limited environments is a core function. This includes stabilizing injuries, administering medications, and providing basic life support. In the aftermath of a hurricane, for instance, disaster nurses might establish temporary medical facilities to treat injuries, manage chronic conditions exacerbated by the disaster, and provide preventative care for emerging health threats.
- Coordination and Communication
Effective communication and coordination are paramount in emergency response. Disaster nurses collaborate with other first responders, medical personnel, and emergency management agencies to ensure a streamlined and efficient response. During a widespread wildfire, this might involve coordinating patient evacuations, communicating resource needs to command centers, and relaying critical information to incoming medical teams.
- Adaptability and Problem-Solving
Emergency response requires adaptability and quick thinking. Disaster nurses often face unexpected challenges and must improvise solutions with limited resources. In a remote area affected by an earthquake, a nurse might need to adapt treatment protocols based on available supplies, utilize unconventional methods for pain management, or create makeshift shelters for displaced individuals.
These interconnected facets of emergency response highlight the demanding and dynamic nature of disaster nursing. The ability to effectively assess, treat, coordinate, and adapt in high-pressure situations underscores the essential contribution of disaster nurses to mitigating the impact of catastrophic events and facilitating recovery efforts.
2. Triage and stabilization
Triage and stabilization are fundamental aspects of disaster nursing, directly impacting patient outcomes and the effective allocation of resources during mass casualty events. Triage involves rapidly assessing patients to categorize them based on the severity of their injuries and the urgency of required medical intervention. Stabilization focuses on delivering essential life-saving care to critically injured individuals, aiming to prevent further deterioration and prepare them for definitive treatment. The interconnectedness of these two processes is crucial for maximizing survival rates and efficiently utilizing limited resources within the chaotic environment of a disaster.
In a mass casualty incident resulting from a natural disaster or a large-scale accident, the number of casualties often overwhelms available medical resources. Disaster nurses play a critical role in implementing triage systems, such as the Simple Triage and Rapid Treatment (START) method, which utilizes easily observable parameters like respiration, perfusion, and mental status to categorize patients. Those with immediately life-threatening injuries are prioritized for treatment, while individuals with less severe conditions may receive delayed care. For instance, following an earthquake, a nurse might triage a patient with a significant head injury as immediate (red tag), while an individual with a minor fracture might be categorized as delayed (yellow tag). This prioritization system ensures that limited resources are directed toward those with the highest chance of survival.
Stabilization efforts focus on addressing immediate life threats, such as airway compromise, hemorrhage, and shock. Disaster nurses utilize their advanced skills and training to perform interventions like airway management, hemorrhage control, and fluid resuscitation. These immediate actions can significantly improve patient outcomes and increase the likelihood of survival until definitive care can be provided. The effective execution of triage and stabilization processes hinges on disaster nurses’ expertise, adaptability, and ability to function effectively under extreme pressure. These skills are essential for maximizing patient survival and minimizing the overall impact of a disaster.
3. Public health outreach
Public health outreach is an integral component of disaster nursing, extending beyond immediate medical care to address the broader health needs of affected populations. It focuses on preventative measures, health education, and community engagement to mitigate the spread of disease, promote long-term recovery, and build community resilience in the wake of disasters.
- Disease Prevention and Health Promotion
Disaster-stricken populations are often vulnerable to infectious diseases due to compromised sanitation, limited access to clean water, and overcrowded living conditions. Disaster nurses implement public health interventions to prevent disease outbreaks, including promoting hygiene practices, providing vaccinations, and distributing essential supplies like mosquito nets and water purification tablets. After a hurricane, for instance, nurses might educate displaced communities about waterborne illnesses and demonstrate safe water handling techniques.
- Community Health Assessments and Surveillance
Conducting rapid health assessments and establishing surveillance systems are crucial for identifying emerging health threats and tracking the spread of disease within affected populations. Disaster nurses collect data on morbidity, mortality, and risk factors, enabling public health authorities to allocate resources effectively and implement targeted interventions. Following a flood, nurses might conduct door-to-door surveys to assess the prevalence of respiratory infections and identify areas with high rates of water contamination.
- Health Education and Risk Communication
Empowering affected communities with accurate and timely health information is essential for promoting self-care and preventing the spread of misinformation. Disaster nurses educate individuals about potential health risks, preventative measures, and available resources. They also play a vital role in addressing community concerns and dispelling rumors, building trust and fostering community participation in recovery efforts. In the aftermath of a chemical spill, nurses might provide clear instructions on decontamination procedures and address public anxieties regarding long-term health effects.
- Collaboration and Advocacy
Effective public health outreach requires collaboration with various stakeholders, including local health authorities, community organizations, and international aid agencies. Disaster nurses act as advocates for affected populations, ensuring that their health needs are addressed in recovery planning and resource allocation. They might work with community leaders to establish temporary health clinics, advocate for increased access to mental health services, or collaborate with NGOs to distribute essential supplies.
These interconnected aspects of public health outreach demonstrate the vital role disaster nurses play in safeguarding the well-being of communities impacted by disasters. Their expertise in disease prevention, health promotion, and community engagement contributes significantly to mitigating long-term health consequences and building resilience in the face of future challenges.
4. Trauma Care Expertise
Proficiency in trauma care is paramount in disaster nursing, where nurses frequently encounter severe and complex injuries resulting from a range of catastrophic events. This expertise enables effective management of immediate life threats, stabilization of patients, and preparation for definitive medical treatment. The ability to rapidly assess injuries, prioritize interventions, and provide specialized care significantly impacts patient outcomes in disaster settings.
- Rapid Assessment and Triage
Disaster nurses with trauma expertise possess the skills to quickly assess the extent of injuries in mass casualty situations. They employ advanced triage techniques to prioritize patients based on injury severity, ensuring that those with the most critical conditions receive immediate attention. For example, in the aftermath of a building collapse, a nurse might utilize the START triage system to categorize victims based on respiration, perfusion, and mental status, rapidly identifying those requiring immediate intervention.
- Hemorrhage Control and Wound Management
Controlling severe bleeding and managing complex wounds are essential skills in disaster trauma care. Nurses skilled in trauma management utilize techniques like tourniquet application, wound packing, and pressure dressings to stabilize patients and prevent further blood loss. In scenarios like bomb blasts or industrial accidents, where penetrating injuries and traumatic amputations are common, this expertise is crucial for saving lives.
- Airway Management and Respiratory Support
Maintaining airway patency and providing respiratory support are critical in trauma situations. Disaster nurses proficient in trauma care are trained to manage complex airways, administer oxygen therapy, and utilize mechanical ventilation when necessary. Following a natural disaster like a tsunami, where victims might experience near-drowning or inhalation injuries, these skills are essential for preserving respiratory function.
- Pain Management and Comfort Care
Providing pain relief and comfort care is an integral part of trauma management in disaster settings. Disaster nurses utilize pharmacological and non-pharmacological methods to alleviate pain, reduce anxiety, and provide emotional support to injured individuals. In situations where access to advanced pain management resources is limited, nurses must adapt and utilize available resources effectively to minimize suffering and promote patient comfort.
These interconnected aspects of trauma care expertise highlight the essential role of skilled disaster nurses in mitigating the impact of catastrophic events. Their ability to rapidly assess, stabilize, and manage complex injuries significantly contributes to improved patient outcomes and increased survival rates in disaster settings. The specialized knowledge and skills in trauma care are not only crucial for immediate response but also contribute to long-term recovery and rehabilitation efforts within affected communities.
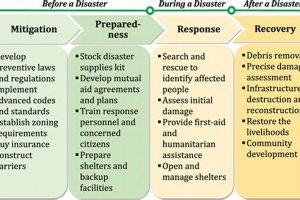
5. Disaster Preparedness
Disaster preparedness is inextricably linked to the effectiveness of disaster nursing. It represents the proactive planning and preparation undertaken to mitigate the impact of disasters and ensure a coordinated and efficient response. For disaster nurses, preparedness translates into a range of activities, from developing emergency plans and participating in drills to acquiring specialized training and pre-positioning essential supplies. This proactive approach is crucial for minimizing casualties, reducing suffering, and facilitating a swift and effective recovery process. For example, nurses involved in disaster preparedness might develop protocols for triage and patient management in the event of a chemical spill, ensuring a coordinated and timely response that minimizes the health consequences of such an incident. A well-defined disaster preparedness plan, outlining roles, responsibilities, and communication channels, is fundamental to a successful disaster response.
The practical significance of disaster preparedness for disaster nurses is evident in its impact on real-world scenarios. Nurses who have undergone comprehensive disaster training and participated in realistic simulations are better equipped to handle the chaotic and demanding environment of a disaster zone. They can confidently implement triage protocols, manage mass casualties, and deliver critical medical care under pressure. Furthermore, disaster preparedness includes establishing robust communication systems, pre-positioning medical supplies and equipment, and identifying potential evacuation routes. These logistical preparations are crucial for ensuring a timely and effective response, minimizing delays in providing essential medical services to affected populations. For example, nurses involved in preparing for a potential hurricane might coordinate with local authorities to establish temporary shelters equipped with essential medical supplies, enabling them to provide immediate care to displaced individuals.
In conclusion, disaster preparedness forms the cornerstone of effective disaster nursing. It equips nurses with the knowledge, skills, and resources necessary to navigate the complexities of disaster response, ultimately saving lives and mitigating suffering within affected communities. Addressing the ongoing challenges of evolving disaster threats requires continuous refinement of preparedness strategies, incorporating lessons learned from past events and integrating innovative approaches to enhance response capabilities. This proactive approach to disaster management ensures that nurses are prepared to effectively address the multifaceted health needs of populations impacted by disasters.
6. Crisis Communication
Effective crisis communication is integral to disaster nursing, serving as a lifeline connecting healthcare providers, affected populations, and supporting organizations. It facilitates coordinated responses, reduces confusion and anxiety, and ultimately contributes to improved outcomes in disaster scenarios. Clear, accurate, and timely communication enables efficient resource allocation, facilitates informed decision-making, and strengthens community resilience. For example, during a widespread wildfire, timely communication between disaster nurses, evacuation centers, and hospitals ensures efficient patient transfer and continuity of care. Conversely, communication breakdowns can hinder rescue efforts, exacerbate existing challenges, and compromise patient safety.
The practical significance of crisis communication for disaster nurses manifests in several ways. It enables them to relay critical information about patient conditions, resource needs, and evolving hazards to relevant stakeholders. Effective communication with affected communities provides vital health information, dispels rumors, and fosters trust, empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their safety and well-being. In a public health emergency like a pandemic, clear and consistent communication from disaster nurses can educate the public about preventative measures, address concerns about vaccine safety, and promote adherence to public health guidelines. Furthermore, robust communication channels facilitate coordination among various response teams, ensuring that efforts are aligned and resources are utilized efficiently. Utilizing established protocols and standardized terminology enhances clarity and minimizes misinterpretations, especially in high-stress environments.
In summary, proficient crisis communication is not merely a desirable skill but a fundamental requirement for effective disaster nursing. It underpins coordinated responses, empowers informed decision-making, and fosters community resilience in the face of adversity. Recognizing the critical role of communication in disaster scenarios reinforces the need for continuous training and refinement of communication strategies within disaster preparedness plans. Addressing challenges such as language barriers, technological limitations, and misinformation requires adaptable communication strategies, ensuring that vital information reaches all segments of the affected population. This proactive approach strengthens the overall effectiveness of disaster response, contributing to improved outcomes and fostering greater community resilience in the aftermath of disasters.
7. Collaboration and Teamwork
Effective disaster response hinges on seamless collaboration and teamwork. Disaster nursing, operating within complex and high-pressure environments, requires coordinated efforts from diverse teams. From immediate medical care to long-term recovery efforts, collaborative partnerships significantly influence the success of disaster management. The following facets illustrate the integral role of teamwork in disaster nursing:
- Interprofessional Collaboration
Disaster nurses collaborate with a wide range of professionals, including physicians, paramedics, emergency medical technicians, mental health professionals, and logisticians. This interprofessional approach ensures comprehensive patient care, addresses diverse needs within affected populations, and facilitates efficient resource allocation. For example, following a hurricane, nurses might work with paramedics to triage patients, coordinate with mental health professionals to provide psychological support, and collaborate with logisticians to ensure adequate medical supplies reach affected areas.
- Communication and Coordination
Clear and concise communication is crucial for effective teamwork in disaster settings. Disaster nurses utilize established communication protocols to share critical information about patient conditions, resource availability, and evolving hazards. Effective communication minimizes misunderstandings, facilitates informed decision-making, and ensures coordinated responses. During a large-scale industrial accident, clear communication between nurses, emergency responders, and hospital staff streamlines patient transport, facilitates appropriate medical interventions, and minimizes delays in care.
- Shared Leadership and Decision-Making
Disaster response often requires distributed leadership and shared decision-making. Disaster nurses collaborate with other team members to assess situations, develop action plans, and adapt to rapidly changing circumstances. This collaborative approach fosters flexibility, enhances problem-solving capabilities, and empowers team members to take initiative. In a remote area affected by an earthquake, nurses might collaborate with community leaders to establish temporary medical facilities, coordinate resource distribution, and make decisions about evacuation strategies based on available information and local expertise.
- Mutual Support and Resilience
Disaster response can be physically and emotionally demanding. Teamwork provides essential emotional support, fosters resilience, and enables individuals to cope with challenging circumstances. Disaster nurses support each other, share experiences, and provide encouragement, contributing to overall team well-being and sustained effectiveness during prolonged disaster operations. Following a mass casualty event, team debriefings and peer support networks can help nurses process traumatic experiences, mitigate the risk of burnout, and maintain their emotional well-being.
These interconnected facets of collaboration and teamwork underscore their vital importance in disaster nursing. The ability to work effectively within interdisciplinary teams, communicate clearly, share leadership, and provide mutual support directly contributes to successful disaster response and improved outcomes for affected populations. Investing in team-building activities, establishing clear communication protocols, and fostering a culture of mutual respect strengthens disaster preparedness and enhances the resilience of healthcare systems in the face of future challenges. The effectiveness of disaster nursing hinges on recognizing the inherent value of teamwork and fostering strong collaborative partnerships across all levels of disaster response.
Frequently Asked Questions about Disaster Relief Nursing
This section addresses common inquiries regarding careers in disaster relief nursing, providing concise and informative responses.
Question 1: What specific skills are essential for success in disaster nursing?
Essential skills include advanced clinical proficiency, adaptability to unpredictable environments, strong decision-making capabilities under pressure, and excellent communication and teamwork skills. Experience in areas such as emergency, trauma, or critical care nursing provides a valuable foundation.
Question 2: How does one become a disaster relief nurse?
A registered nursing license is required. Pursuing further education, such as a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) or advanced certifications in areas like disaster nursing, public health, or emergency management, strengthens qualifications. Gaining experience in relevant clinical settings is highly recommended.
Question 3: What types of organizations employ disaster relief nurses?
Opportunities exist within governmental agencies (e.g., FEMA, public health departments), non-governmental organizations (e.g., Red Cross, Doctors Without Borders), international organizations (e.g., WHO), and private companies specializing in disaster response.
Question 4: What are the typical working conditions in disaster relief settings?
Working conditions can be challenging and unpredictable, involving long hours, physically demanding tasks, exposure to hazardous environments, and emotional stress. Deployment locations can range from remote areas to urban disaster zones.
Question 5: What are the potential career paths within disaster relief nursing?
Career paths can include specializing in areas like disaster management, emergency preparedness, public health, or international aid. Experienced nurses may progress to leadership roles within disaster response teams or organizations.
Question 6: What are the personal rewards and challenges of this career?
While emotionally and physically demanding, disaster relief nursing offers the profound reward of making a tangible difference in the lives of those affected by crises. The challenges include exposure to trauma, demanding work conditions, and time spent away from family and support networks.
Disaster nursing requires dedication, resilience, and a commitment to serving others in times of need. The information provided here offers a starting point for further exploration of this unique and vital field within healthcare.
The next section will offer resources for further exploration of disaster nursing careers.
Disaster Nurse Jobs
Exploration of disaster nursing positions reveals a multifaceted field demanding specialized skills, unwavering commitment, and profound resilience. From providing immediate medical care in the chaotic aftermath of natural disasters to implementing public health measures that mitigate long-term consequences, these professionals operate on the front lines of crisis response. Their expertise in triage, trauma care, and crisis communication is crucial for maximizing survival rates and minimizing suffering within affected communities. Moreover, their dedication to disaster preparedness and community resilience building contributes significantly to mitigating the impact of future catastrophic events.
The increasing frequency and intensity of global disasters underscore the growing importance of skilled disaster nursing professionals. Investment in training, resources, and ongoing support for these individuals is not merely a matter of healthcare infrastructure but a critical investment in safeguarding communities worldwide. The future of disaster response hinges on the continued development and empowerment of these dedicated professionals who stand ready to serve in times of greatest need. The demanding nature of these positions is undeniable, yet the profound impact they have on individual lives and community recovery underscores the vital role disaster nurses play in navigating the complexities of crisis response and building a more resilient future.