
Catastrophic events originating from natural processes, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, and asteroid impacts, can cause widespread devastation and significantly alter landscapes. An example includes the Chicxulub impact, believed to have... Read more »

Catastrophic events stemming from natural processes, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, floods, wildfires, and severe storms, have always posed significant challenges to human populations. The immediacy of these events and their potential... Read more »
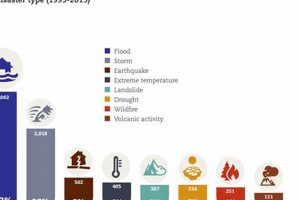
Globally, frequently occurring devastating events include floods, earthquakes, wildfires, volcanic eruptions, droughts, and severe storms such as hurricanes, cyclones, and tornadoes. These phenomena, arising from natural processes within the Earth’s systems or... Read more »
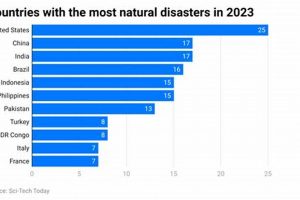
Determining which nation experiences the highest frequency of natural disasters involves analyzing various factors, including the types of disasters considered (e.g., geophysical, hydrological, meteorological, climatological, biological) and the timeframe of assessment. Vulnerability... Read more »
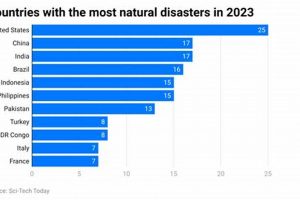
Analyzing the frequency of natural hazard events across different nations provides crucial insights into global risk profiles. For instance, comparing the incidence of earthquakes in Japan with the occurrence of floods in... Read more »
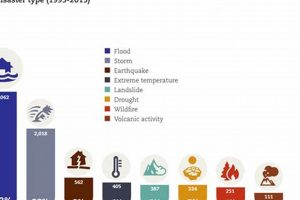
Floods are the most frequently occurring natural hazard. These events, characterized by overflowing water submerging normally dry land, can arise from various sources, including heavy rainfall, rapid snowmelt, dam failures, and coastal... Read more »

Catastrophic natural events, encompassing geophysical occurrences like earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis, as well as climate-related phenomena such as floods, droughts, wildfires, and storms, represent a significant threat to human populations and... Read more »
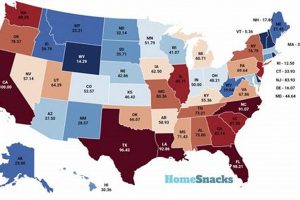
Geographic locations experiencing a high frequency of naturally occurring hazardous events, such as floods, wildfires, hurricanes, tornadoes, and earthquakes, are often subject to significant societal and economic impacts. For example, coastal regions... Read more »
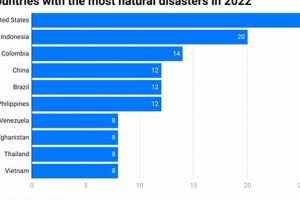
Determining nations most susceptible to natural hazards involves analyzing the frequency, intensity, and impact of events like earthquakes, floods, droughts, volcanic eruptions, and storms. For example, a nation situated on a major... Read more »

A calamity, catastrophe, or emergency of significant magnitude that has occurred closest to the present time defines the concept. For example, an earthquake that struck last week would be considered more current... Read more »


