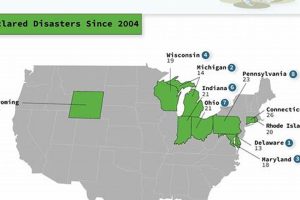
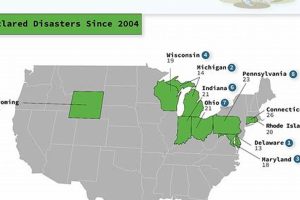
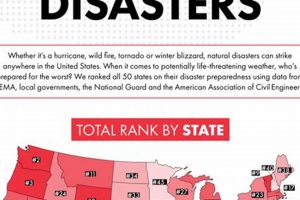
Mississippi’s geographic location and subtropical climate render it vulnerable to a range of severe weather events. These include hurricanes originating in the Gulf of Mexico, tornadoes frequently occurring during spring and fall, and river flooding, particularly along the Mississippi River and its tributaries. Less frequent but still impactful events include severe thunderstorms, hailstorms, wildfires, and occasional winter storms producing ice and snow.
Understanding the specific threats posed by these phenomena is crucial for effective disaster preparedness and mitigation. Historical records document significant impacts from such events, shaping building codes, evacuation procedures, and emergency response protocols. Preparedness measures minimize loss of life, reduce economic damage, and contribute to faster community recovery. Effective disaster response relies heavily on accurate forecasting, timely public warnings, and the coordinated efforts of local, state, and federal agencies.
This information serves as a foundation for exploring specific hazard types, their historical impact on the state, and the ongoing efforts to improve community resilience in the face of future events. Subsequent sections will delve into detailed analyses of individual disaster types, outlining their unique characteristics, mitigation strategies, and the role of public awareness in minimizing their impact.
Disaster Preparedness Tips for Mississippi Residents
Preparation is crucial for mitigating the impact of severe weather events. The following recommendations offer guidance for enhancing individual and community resilience.
Tip 1: Develop a Family Emergency Plan: Establish a communication plan, designate meeting points, and outline evacuation routes. Include provisions for pets and individuals with special needs.
Tip 2: Assemble an Emergency Kit: Stock a kit with essential supplies, including water, non-perishable food, first-aid supplies, medications, flashlights, and a battery-powered radio. Ensure the kit is readily accessible and regularly updated.
Tip 3: Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts through reliable sources like the National Weather Service. Sign up for local emergency alerts and heed warnings promptly.
Tip 4: Secure Your Property: Trim trees and shrubs around homes. Reinforce windows and doors to protect against wind damage. Elevate critical utilities and appliances in flood-prone areas.
Tip 5: Understand Evacuation Procedures: Familiarize oneself with local evacuation routes and designated shelters. Prepare transportation and accommodation arrangements in advance.
Tip 6: Review Insurance Coverage: Ensure adequate insurance coverage for relevant hazards, including flood insurance, even in areas not designated as high-risk.
Tip 7: Participate in Community Preparedness Activities: Engage in local initiatives such as volunteer training programs and community drills to foster collective resilience.
Proactive planning and preparation minimize the impact of disasters, protecting life and property. Implementing these strategies enhances community resilience and contributes to a faster recovery process following a severe weather event.
By understanding the risks and taking appropriate precautions, Mississippi residents can better navigate the challenges posed by severe weather and contribute to a safer and more resilient community. The following section provides further resources and contact information for accessing additional support and guidance.
1. Hurricanes
Hurricanes represent a significant natural disaster threat to Mississippi, particularly for coastal regions. The state’s location along the Gulf of Mexico exposes it to these powerful storms, which bring high winds, storm surge, and heavy rainfall. Hurricane Camille in 1969 and Hurricane Katrina in 2005 serve as stark reminders of the devastating impact these events can have. Camille, a Category 5 hurricane, caused widespread destruction along the Mississippi coast, while Katrina brought catastrophic flooding to coastal communities due to levee failures and storm surge. These events highlight the vulnerability of coastal infrastructure and the importance of robust building codes and evacuation plans.
The impact of hurricanes extends beyond immediate wind and water damage. Power outages, disruptions to transportation networks, and damage to essential services like hospitals and communication systems often follow in a hurricane’s wake. Economic losses due to business closures and property damage can be substantial, impacting communities for years after the initial event. Furthermore, saltwater intrusion from storm surge can contaminate freshwater sources and damage agricultural lands, posing long-term challenges for recovery. The complex interplay of these factors necessitates comprehensive disaster preparedness strategies that address both immediate response and long-term recovery needs.
Understanding the historical impact of hurricanes in Mississippi and the evolving science of hurricane prediction are crucial for mitigating future risks. Improved forecasting models, coupled with effective communication and evacuation procedures, can minimize loss of life and property. Investing in resilient infrastructure, including strengthened building codes and coastal protection measures, is essential for reducing vulnerability to these powerful storms. Continued research into hurricane behavior and the development of community-based adaptation strategies are vital for fostering long-term resilience in the face of this persistent threat.
2. Tornadoes
Tornadoes represent a significant threat within the spectrum of natural disasters affecting Mississippi. The state’s location in the southeastern United States places it within the “Dixie Alley,” a region known for frequent and often intense tornado activity. Atmospheric conditions conducive to tornado formation, such as warm, moist air colliding with cooler, drier air masses, occur frequently, particularly during the spring and fall months. These conditions can lead to the development of supercell thunderstorms, capable of producing violent tornadoes. The flat terrain of much of Mississippi offers few natural barriers to impede tornado strength or path, increasing the potential for widespread damage.
Historical records document numerous significant tornado outbreaks in Mississippi. The Tupelo-Gainesville tornado outbreak of 1936, which caused widespread devastation and numerous fatalities across multiple states including Mississippi, stands as a grim reminder of the destructive power of these events. More recently, the 2011 Super Outbreak, a series of violent tornadoes affecting several southeastern states, resulted in significant damage and loss of life in Mississippi. These events underscore the importance of advanced warning systems, community preparedness, and robust building codes in mitigating tornado risks.
Understanding the specific meteorological conditions that contribute to tornado formation in Mississippi is crucial for effective forecasting and warning dissemination. Continued research into tornado dynamics and improved detection technologies enhance the ability to provide timely warnings, allowing residents to seek shelter and minimize casualties. Community education programs focused on tornado safety procedures, coupled with investments in storm shelters and resilient infrastructure, are essential for enhancing community preparedness and reducing the impact of these devastating events.
3. Flooding
Flooding constitutes a recurring natural hazard in Mississippi, impacting communities across the state. The convergence of several factors contributes to the state’s vulnerability. The extensive network of rivers and tributaries, including the Mississippi River itself, creates pathways for widespread inundation during periods of heavy rainfall. The relatively flat terrain, especially in the Delta region, exacerbates the issue, allowing floodwaters to spread extensively. Coastal areas face additional risks from storm surge associated with hurricanes and tropical storms, which can overwhelm natural and man-made defenses. The interaction of these factors makes flooding a complex and pervasive challenge.
Historical flood events illustrate the significant impact on communities and infrastructure. The Great Mississippi Flood of 1927, one of the most destructive floods in U.S. history, inundated vast areas of the Mississippi Delta, displacing hundreds of thousands of residents and causing widespread economic devastation. More recently, heavy rainfall in 2011 led to significant flooding along the Mississippi River and its tributaries, again impacting homes, businesses, and agricultural lands. These events demonstrate the disruptive potential of flooding, highlighting the need for comprehensive flood management strategies.
Addressing flood risks in Mississippi requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing infrastructure improvements, land management practices, and community preparedness. Investing in levee systems, flood control reservoirs, and improved drainage infrastructure can mitigate the impact of heavy rainfall and riverine flooding. Promoting responsible land use practices, such as preserving wetlands and implementing floodplain management regulations, can help absorb excess water and reduce flood risks. Educating residents about flood safety and encouraging the development of community-based emergency response plans are essential for minimizing the impact of future flood events. The ongoing challenge lies in balancing the need for development with the preservation of natural floodplains and the implementation of sustainable flood management practices.
4. Severe thunderstorms
Severe thunderstorms pose a substantial threat as a component of natural disasters in Mississippi. The state’s climate and geographical location create favorable conditions for the development of these storms, characterized by damaging winds, large hail, frequent lightning, and heavy rainfall. The warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico interacting with cooler, drier air masses from the north creates atmospheric instability, fueling the formation of powerful thunderstorms, especially during the spring and summer months. These storms can produce localized flooding due to intense rainfall, and strong winds can down trees and power lines, causing widespread damage and disruption to essential services.
The impact of severe thunderstorms in Mississippi is exemplified by numerous events. Frequent occurrences of hailstorms damage crops and property, and intense lightning strikes ignite wildfires, particularly during dry periods. The combination of strong winds and saturated soil can lead to downed trees, further exacerbating damage and posing risks to public safety. While individual thunderstorms may be localized, their cumulative impact across the state contributes significantly to annual disaster-related costs and necessitates robust preparedness measures. Understanding the specific atmospheric dynamics that lead to severe thunderstorm development in Mississippi is crucial for accurate forecasting and timely warnings, enabling residents to take appropriate safety precautions.
Mitigating the impact of severe thunderstorms requires a multi-pronged approach. Enhanced weather forecasting and public awareness campaigns play a vital role in communicating risks and promoting preparedness. Investing in resilient infrastructure, such as reinforced power lines and robust drainage systems, can minimize damage from high winds and heavy rainfall. Community-based emergency response plans, coupled with readily accessible storm shelters, provide crucial safeguards for residents during severe weather events. The ongoing challenge lies in balancing the need for development with the implementation of sustainable land management practices that minimize the impact of severe thunderstorms and enhance community resilience.
5. Wildfires
While less frequent than hurricanes, tornadoes, or floods, wildfires constitute a notable component of natural disasters in Mississippi. The state’s warm, dry climate, particularly during the fall months, coupled with abundant flammable vegetation, creates conditions conducive to wildfire ignition and spread. Although often smaller in scale than wildfires in western states, Mississippi wildfires pose significant threats to forests, property, and air quality. Human activities, such as debris burning and discarded cigarettes, are primary ignition sources, underscoring the importance of public awareness and responsible land management practices. Drought conditions exacerbate wildfire risks by increasing fuel dryness and susceptibility to ignition.
The Leaf River Fire of 2008, which burned over 18,000 acres in southeastern Mississippi, exemplifies the destructive potential of wildfires in the state. This event highlighted the challenges of containing wildfires in remote areas with limited access and the significant strain on firefighting resources. Smoke from wildfires can degrade air quality, posing respiratory hazards to vulnerable populations. Furthermore, wildfires can disrupt ecosystems, damage timber resources, and impact wildlife habitats. Understanding the factors that contribute to wildfire risk in Mississippi, including climate patterns, vegetation types, and human activities, is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies.
Addressing wildfire risks requires a comprehensive approach encompassing public education, preventative measures, and effective suppression strategies. Public awareness campaigns focused on fire safety and responsible land management practices, such as prescribed burns and creating defensible space around structures, can reduce wildfire ignition risks. Investing in firefighting resources, including training and equipment, enhances the capacity to suppress wildfires effectively. Collaboration among local, state, and federal agencies is crucial for coordinating response efforts and resource allocation during large-scale wildfire events. Continued research into wildfire behavior and the development of community-based wildfire protection plans are vital for minimizing the impact of these events and protecting Mississippi’s natural resources.
Frequently Asked Questions about Natural Disasters in Mississippi
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the various natural hazards affecting Mississippi, providing concise and informative responses.
Question 1: What is the most common natural disaster in Mississippi?
Severe thunderstorms are the most frequent natural hazard, occurring throughout the year. However, tornadoes, floods, and hurricanes pose more significant risks in terms of potential damage and loss of life.
Question 2: When is hurricane season in Mississippi?
The official Atlantic hurricane season runs from June 1st to November 30th, with the peak activity typically occurring between August and October.
Question 3: What areas of Mississippi are most susceptible to flooding?
Areas along the Mississippi River, its tributaries, and coastal regions are particularly vulnerable to flooding due to storm surge, heavy rainfall, and river overflow.
Question 4: How can I receive emergency alerts and warnings?
Residents are encouraged to sign up for local emergency alert systems, monitor weather forecasts from the National Weather Service, and utilize weather radio broadcasts.
Question 5: Does standard homeowners insurance cover flood damage?
Standard homeowners insurance policies typically do not cover flood damage. Separate flood insurance policies are available through the National Flood Insurance Program.
Question 6: What resources are available for disaster assistance in Mississippi?
The Mississippi Emergency Management Agency (MEMA) and the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) provide resources and assistance following disaster events. Local community organizations also offer support services.
Understanding the specific risks associated with various natural hazards and taking proactive steps to prepare can significantly enhance individual and community resilience. Being informed and prepared remains the most effective strategy for mitigating the impact of future events.
The subsequent section provides further resources and contact information for disaster preparedness and recovery assistance within the state of Mississippi.
Conclusion
Mississippi’s vulnerability to a range of natural hazards, including hurricanes, tornadoes, floods, severe thunderstorms, and wildfires, necessitates a comprehensive and proactive approach to disaster preparedness and mitigation. Understanding the unique characteristics of each hazard type, coupled with historical context and ongoing research, informs effective strategies for minimizing impacts. From robust building codes and infrastructure improvements to advanced warning systems and community-based emergency response plans, a multi-faceted approach is crucial for building resilience.
Continued investment in research, improved forecasting capabilities, and public awareness campaigns remain essential for strengthening community preparedness and reducing the impact of future events. Promoting individual responsibility, fostering collaboration among stakeholders, and prioritizing sustainable land management practices are vital for creating a more resilient Mississippi, capable of weathering the inevitable challenges posed by natural disasters.