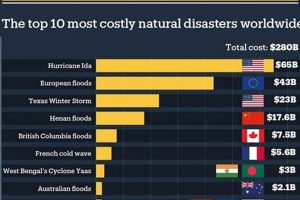
North Carolina’s geographic location makes it vulnerable to a variety of severe weather events, including hurricanes, floods, tornadoes, winter storms, and wildfires. These events can cause significant damage to infrastructure, property, and the environment, posing substantial risks to human life and economic stability. For instance, hurricanes bringing torrential rainfall can lead to widespread flooding in coastal and inland regions, while powerful winds can down trees and power lines, disrupting essential services. Similarly, tornadoes can carve paths of destruction, damaging homes and businesses, while winter storms can bring heavy snow and ice, leading to power outages and hazardous travel conditions.
Understanding the patterns and impacts of these events is crucial for effective disaster preparedness and mitigation. Historical data provides valuable insights into the frequency, intensity, and geographical distribution of past disasters, enabling communities to better anticipate future risks and develop strategies to minimize potential damage. This historical context also informs the development of building codes, land-use planning, and emergency response protocols, ultimately enhancing community resilience and safeguarding public safety. Analysis of past events also highlights the social and economic vulnerabilities that exacerbate the impact of these disasters, allowing for targeted interventions to support vulnerable populations.
This information will further explore specific instances of severe weather events that have impacted North Carolina, examining their causes, consequences, and the ongoing efforts to enhance resilience and preparedness. Subsequent sections will address the role of meteorological forecasting, emergency management agencies, and community involvement in mitigating the impact of future disasters.
Disaster Preparedness Tips for North Carolina Residents
Given North Carolina’s vulnerability to various natural hazards, preparedness is crucial for minimizing potential impacts on life and property. The following tips offer guidance for enhancing individual and community resilience.
Tip 1: Develop a Family Emergency Plan: Establish a communication plan that includes designated meeting points and out-of-state contacts. Outline evacuation routes and ensure all family members understand their roles and responsibilities.
Tip 2: Assemble an Emergency Kit: Prepare a kit containing essential supplies such as non-perishable food, water, first-aid supplies, medications, flashlights, batteries, a radio, and important documents. This kit should sustain each family member for at least 72 hours.
Tip 3: Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and heed warnings issued by the National Weather Service and local authorities. Sign up for emergency alerts through local government channels.
Tip 4: Secure Your Property: Trim trees and shrubs around your home to minimize wind damage. Reinforce windows and doors and secure loose objects that could become projectiles during high winds.
Tip 5: Know Your Evacuation Zone: Identify your evacuation zone and plan evacuation routes in advance. Ensure your vehicle is well-maintained and has a full tank of gas.
Tip 6: Protect Important Documents: Store important documents, such as insurance policies, medical records, and identification, in a waterproof and fireproof container. Create digital copies and store them securely online.
Tip 7: Review Insurance Coverage: Regularly review insurance policies to ensure adequate coverage for potential disaster-related damages, including flood insurance, which is typically separate from standard homeowner’s insurance.
By taking these proactive steps, individuals and communities can significantly mitigate the impact of future disasters, safeguarding lives, protecting property, and fostering a culture of preparedness.
These preparedness measures provide a foundation for individual and community resilience in the face of natural hazards. Continued engagement with local resources and emergency management agencies further strengthens preparedness efforts.
1. Hurricane Florence
Hurricane Florence stands as a stark example of the devastating impact of recent natural disasters in North Carolina. This 2018 storm significantly reshaped the landscape and underscored the state’s vulnerability to powerful hurricanes and subsequent flooding. Analyzing Florence provides critical insights into effective disaster preparedness, response, and long-term recovery strategies.
- Record Rainfall and Flooding:
Florence produced record-breaking rainfall across North Carolina, resulting in catastrophic flooding in both coastal and inland regions. Rivers overflowed their banks, inundating communities and causing widespread damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure. This extreme rainfall highlighted the interconnectedness of river systems and the need for comprehensive flood mitigation strategies across entire watersheds.
- Storm Surge and Coastal Erosion:
The storm’s powerful surge inundated coastal communities, causing significant erosion and damage to beachfront properties and infrastructure. This highlighted the vulnerability of coastal areas to rising sea levels and the increasing intensity of hurricanes, underscoring the need for robust coastal protection measures and resilient building practices.
- Economic and Social Impacts:
Florence’s impact extended beyond immediate physical damage, causing substantial economic disruption and long-term social consequences. Businesses were forced to close, agricultural production suffered significant losses, and communities faced prolonged displacement and recovery challenges. This emphasized the need for comprehensive disaster recovery planning that addresses both immediate relief efforts and long-term economic and social recovery.
- Lessons Learned and Future Preparedness:
Hurricane Florence served as a critical learning experience, prompting a reevaluation of emergency preparedness and response protocols. The storm highlighted the importance of accurate forecasting, timely evacuations, effective communication, and robust infrastructure investments to mitigate the impacts of future hurricanes. The experience gained from Florence continues to shape disaster planning and community resilience initiatives across North Carolina.
Hurricane Florence serves as a crucial case study for understanding the complexities of recent natural disasters in North Carolina. Its multifaceted impacts, ranging from record flooding to long-term economic consequences, underscore the necessity of comprehensive disaster preparedness strategies that encompass mitigation, response, and long-term recovery. Florences legacy continues to shape policy discussions and inform ongoing efforts to enhance the states resilience to future extreme weather events.
2. Coastal Flooding
Coastal flooding represents a significant and recurring threat among recent natural disasters in North Carolina. The state’s extensive coastline, coupled with low-lying terrain and the increasing impacts of climate change, renders coastal communities particularly vulnerable to inundation from storm surge, sea-level rise, and heavy rainfall. Understanding the multifaceted nature of coastal flooding is crucial for effective mitigation and adaptation strategies.
- Storm Surge:
Storm surge, the temporary rise in sea level caused by the strong winds and low atmospheric pressure of tropical storms and hurricanes, poses a significant threat to North Carolina’s coastal regions. Hurricane Florence in 2018 demonstrated the devastating impact of storm surge, inundating coastal communities and causing widespread damage. The intensity and reach of storm surge are exacerbated by factors such as the storm’s size, forward speed, and the shape of the coastline.
- Sea-Level Rise:
The gradual increase in global sea levels due to climate change presents a long-term challenge for North Carolina’s coastal communities. Rising sea levels exacerbate the impacts of storm surge and high tides, increasing the frequency and severity of coastal flooding events. This poses a significant threat to infrastructure, property, and ecosystems along the coast.
- Heavy Rainfall and Drainage Issues:
Heavy rainfall events, often associated with tropical storms and hurricanes, can overwhelm drainage systems and contribute to coastal flooding. When combined with storm surge and high tides, heavy rainfall can lead to compound flooding events, significantly increasing the extent and severity of inundation in coastal areas. Urbanization and land development can further exacerbate drainage issues, increasing the risk of flooding.
- Erosion and Land Loss:
Coastal flooding contributes to erosion and land loss, further increasing the vulnerability of coastal communities to future flooding events. Erosion undermines infrastructure, damages property, and degrades natural habitats, compounding the long-term impacts of coastal flooding. Protecting and restoring coastal ecosystems, such as dunes and wetlands, can help mitigate erosion and enhance coastal resilience.
These interconnected factors contribute to the complex challenge of coastal flooding in North Carolina. Addressing this challenge requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates strategies such as improved forecasting, strengthened building codes, enhanced drainage systems, and nature-based solutions for coastal protection. Recognizing the dynamic interplay between these factors is crucial for developing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies that enhance the resilience of North Carolina’s coastal communities in the face of future extreme weather events.
3. Inland Flooding
Inland flooding poses a significant threat in North Carolina, often exacerbated by recent natural disasters. While coastal regions face risks from storm surge and sea-level rise, inland areas are susceptible to overflowing rivers, saturated ground, and inadequate drainage systems, particularly during periods of intense or prolonged rainfall. Understanding the dynamics of inland flooding is crucial for effective disaster preparedness and mitigation across the state.
- Excessive Rainfall:
Prolonged or heavy rainfall can overwhelm rivers and streams, leading to widespread flooding in inland areas. Hurricane Florence in 2018 demonstrated the devastating impact of excessive rainfall, as rivers across the state reached record levels, inundating communities and causing widespread damage. The topography of North Carolina, with its varying elevations and river basins, influences the flow of floodwaters and determines which areas are most vulnerable.
- Dam and Levee Failures:
Aging or poorly maintained dams and levees can fail during periods of heavy rainfall, releasing large volumes of water into surrounding areas and exacerbating inland flooding. These failures can have catastrophic consequences, leading to rapid inundation and significant damage to property and infrastructure. Regular inspections and maintenance of dams and levees are critical for mitigating the risk of failure and protecting downstream communities.
- Urban Development and Impervious Surfaces:
Urban development and the increasing prevalence of impervious surfaces, such as roads and parking lots, reduce the ground’s ability to absorb rainwater. This increased runoff contributes to higher flood peaks and more rapid flooding in urbanized areas. Implementing green infrastructure solutions, such as permeable pavements and green roofs, can help mitigate the impacts of urbanization on inland flooding.
- Mountainous Terrain and Flash Flooding:
The mountainous terrain of western North Carolina is particularly susceptible to flash flooding. Heavy rainfall in these areas can quickly generate fast-moving floodwaters that surge down steep slopes, carrying debris and posing a significant threat to life and property. Effective early warning systems and public awareness campaigns are crucial for mitigating the risks associated with flash flooding in mountainous regions.
These factors contribute to the complex nature of inland flooding in North Carolina. Addressing this challenge requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates strategies such as improved watershed management, enhanced infrastructure design, and community-based flood preparedness programs. By understanding the specific drivers of inland flooding and their interplay with recent natural disasters, communities can develop targeted mitigation and adaptation strategies to minimize the risks and enhance resilience in the face of future extreme weather events.
4. Tornado Outbreaks
Tornado outbreaks represent a significant threat within the broader context of recent natural disasters in North Carolina. While hurricanes often dominate headlines, tornadoes pose a distinct and recurring danger, capable of producing localized devastation and impacting communities across the state. Understanding the characteristics and patterns of tornado outbreaks is crucial for effective preparedness and mitigation efforts.
- Seasonal Patterns and Atmospheric Conditions:
North Carolina experiences tornadoes throughout the year, but the peak season typically occurs during the spring and fall months. These periods are characterized by the convergence of warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico and cool, dry air from the north, creating unstable atmospheric conditions conducive to tornado development. The interaction of these air masses can generate powerful thunderstorms capable of producing tornadoes.
- Tornado Alley and Dixie Alley:
While North Carolina is not situated within the traditional “Tornado Alley” of the Great Plains, it lies within a region known as “Dixie Alley,” which experiences a significant number of tornado outbreaks. Dixie Alley tornadoes often occur in more heavily populated areas and can be particularly dangerous due to factors such as longer tracks, nocturnal occurrences, and the presence of more complex terrain.
- Impact on Communities and Infrastructure:
Tornadoes can produce devastating impacts on communities and infrastructure. High winds can destroy homes and businesses, down power lines, and disrupt transportation networks. The localized nature of tornado damage can create significant challenges for emergency response and recovery efforts. Investing in resilient infrastructure and developing effective community warning systems are crucial for mitigating the impacts of tornadoes.
- Predictability and Warning Systems:
While predicting the exact location and timing of tornadoes remains challenging, advancements in meteorological forecasting and warning systems have significantly improved the ability to provide timely alerts to communities. These warnings provide crucial time for residents to seek shelter and take protective actions, reducing the risk of injury and loss of life. Continued investment in weather forecasting technologies and public awareness campaigns is essential for enhancing tornado preparedness.
Tornado outbreaks contribute significantly to the overall picture of recent natural disasters in North Carolina. Understanding the specific risks associated with tornadoes, including their seasonal patterns, potential impact, and the effectiveness of warning systems, is crucial for developing comprehensive disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies across the state. By integrating tornado preparedness into broader disaster planning efforts, communities can enhance their resilience and minimize the impact of these powerful and destructive weather events.
5. Wildfires
While hurricanes and floods often dominate discussions of natural disasters in North Carolina, wildfires represent a growing and significant threat, particularly in the western part of the state. The increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires, often fueled by drought conditions and changing weather patterns, contribute substantially to recent natural disaster trends. Understanding the unique characteristics and impacts of wildfires is crucial for effective mitigation and response strategies.
- Drought Conditions and Fuel Loads:
Prolonged periods of drought create dry vegetation, increasing the availability of fuel for wildfires. This elevated fuel load, combined with low humidity and high winds, can create conditions ripe for rapid fire spread. Climate change projections suggest that drought conditions may become more frequent and severe in the future, further exacerbating the risk of wildfires.
- Mountainous Terrain and Fire Behavior:
The mountainous terrain of western North Carolina influences wildfire behavior. Steep slopes can accelerate fire spread uphill, while narrow valleys can channel winds and create unpredictable fire patterns. This complex terrain presents challenges for firefighters and can make containment efforts more difficult.
- Impact on Air Quality and Public Health:
Wildfires produce significant amounts of smoke and particulate matter, degrading air quality and posing risks to public health. Smoke inhalation can exacerbate respiratory conditions and cardiovascular problems, particularly among vulnerable populations. The widespread nature of wildfire smoke can impact air quality across large regions, extending far beyond the immediate fire zone.
- Forest Management and Mitigation Strategies:
Forest management practices, including prescribed burns and the removal of dead vegetation, play a crucial role in mitigating wildfire risks. These practices reduce fuel loads and create breaks that can slow or stop the spread of wildfires. Community-based wildfire protection programs, such as Firewise USA, empower residents to take proactive steps to reduce wildfire risks around their homes.
Wildfires represent a complex and evolving challenge within the context of recent natural disasters in North Carolina. Their increasing frequency and intensity, coupled with their potential for widespread impacts on air quality and public health, necessitate a comprehensive approach to mitigation and response. By integrating wildfire preparedness into broader disaster planning efforts and investing in proactive forest management strategies, communities can enhance their resilience and minimize the risks associated with these increasingly prevalent natural hazards.
6. Winter Storms
Winter storms constitute a significant category within recent natural disasters in North Carolina, posing unique challenges and requiring specialized preparedness measures. While often overshadowed by hurricanes and other warmer-weather events, winter storms can produce widespread disruption and significant impacts, particularly in the western and central regions of the state. Understanding the specific hazards associated with winter storms is crucial for ensuring community resilience and minimizing disruptions to daily life.
- Heavy Snow and Ice Accumulation:
Heavy snowfall can accumulate rapidly during winter storms, blanketing roads, disrupting transportation networks, and isolating communities. Ice accumulation adds another layer of complexity, creating hazardous driving conditions and potentially downing power lines due to the added weight. The weight of snow and ice can also damage structures, posing risks to homes and businesses. The amount of snowfall and ice accumulation varies across the state, with mountainous regions generally experiencing higher totals.
- Power Outages and Infrastructure Disruptions:
Winter storms frequently cause power outages, disrupting essential services such as heating, communication, and access to information. Downed power lines due to heavy snow or ice accumulation can leave communities without electricity for extended periods, particularly in remote or mountainous areas. These outages can create dangerous situations, especially for vulnerable populations who rely on electricity for medical equipment or heating. The restoration of power after a winter storm can be a complex and time-consuming process, requiring significant coordination among utility companies and emergency management agencies.
- Dangerous Travel Conditions and Transportation Impacts:
Snow and ice accumulation create hazardous road conditions, increasing the risk of traffic accidents and hindering transportation networks. Roads can become impassable, making it difficult for emergency responders to reach those in need and disrupting the delivery of essential goods and services. School closures and business disruptions are common during winter storms, impacting daily routines and economic activity. Transportation agencies play a critical role in clearing roads and ensuring the safe movement of people and goods during and after winter storms.
- Hypothermia and Cold-Related Health Risks:
Exposure to extreme cold temperatures during winter storms can lead to hypothermia and other cold-related health problems. Prolonged exposure to freezing temperatures, particularly without adequate shelter or warm clothing, can be life-threatening. Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly and those experiencing homelessness, are at increased risk during winter storms. Public health campaigns and emergency shelters play a vital role in protecting vulnerable individuals during these events.
Winter storms, while distinct in their characteristics, contribute significantly to the overall picture of recent natural disasters in North Carolina. The combined impacts of heavy snow and ice, power outages, hazardous travel conditions, and cold-related health risks underscore the need for comprehensive preparedness strategies specific to winter weather. Integrating winter storm preparedness into broader disaster planning efforts, including public awareness campaigns, infrastructure improvements, and effective emergency response protocols, is crucial for enhancing community resilience and minimizing the disruptions caused by these recurring natural hazards.
Frequently Asked Questions about Natural Disasters in North Carolina
This section addresses common questions regarding the diverse range of natural hazards impacting North Carolina. Understanding these frequently asked questions provides valuable context for effective preparedness and informed decision-making.
Question 1: How frequently does North Carolina experience hurricanes?
North Carolina’s coastal location makes it susceptible to hurricanes, particularly during the Atlantic hurricane season, which runs from June 1st to November 30th. While the frequency of hurricane landfalls varies from year to year, historical data indicates a significant risk, with major hurricanes impacting the state approximately every 20-25 years. However, less intense tropical storms and hurricanes can affect the state more frequently.
Question 2: What are the primary causes of flooding in North Carolina?
Flooding in North Carolina can result from various factors, including hurricanes, tropical storms, heavy rainfall, and overflowing rivers and streams. Coastal regions are particularly vulnerable to storm surge, while inland areas are susceptible to riverine flooding. Urban development and inadequate drainage systems can exacerbate flooding in both coastal and inland areas.
Question 3: How can residents prepare for a natural disaster?
Residents can take several proactive steps to prepare for natural disasters, including developing a family emergency plan, assembling an emergency kit with essential supplies, staying informed about weather forecasts and warnings, securing their property, and understanding evacuation routes and procedures. Learning basic first aid and CPR skills is also recommended.
Question 4: What resources are available to assist with disaster recovery?
Various resources are available to assist with disaster recovery, including federal, state, and local government agencies, as well as non-profit organizations such as the American Red Cross. The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) provides financial assistance and resources for individuals and communities affected by disasters. State and local governments offer support through emergency management agencies and social service programs.
Question 5: What role does climate change play in North Carolina’s natural disasters?
Climate change contributes to an increased risk of certain natural hazards in North Carolina. Rising sea levels exacerbate coastal flooding, while changes in precipitation patterns can lead to more frequent and intense heavy rainfall events. Warmer temperatures can also influence the intensity and duration of heat waves and drought conditions, increasing wildfire risk. Understanding the influence of climate change is crucial for developing effective long-term mitigation and adaptation strategies.
Question 6: How can I stay informed about potential hazards and warnings?
Staying informed about potential hazards is crucial for personal safety and effective preparedness. Reliable sources of information include the National Weather Service, which provides weather forecasts, watches, and warnings. Local emergency management agencies disseminate information specific to your community. Signing up for emergency alerts through local government channels is highly recommended. Utilizing NOAA Weather Radio and reliable news sources also provides valuable updates during hazardous weather events.
Preparedness through understanding local risks and available resources significantly enhances community resilience in the face of natural hazards. Continued engagement with official sources of information promotes informed decision-making and fosters a culture of safety.
The next section offers a deeper exploration into specific recent events, providing detailed accounts of their impact and the ongoing recovery efforts.
Conclusion
North Carolina’s vulnerability to a diverse range of natural hazards, from hurricanes and floods to tornadoes, wildfires, and winter storms, presents significant challenges. This exploration has highlighted the multifaceted nature of these events, examining their distinct characteristics, potential impacts, and the complex interplay of contributing factors. Understanding the specific vulnerabilities within different regions of the state, whether coastal erosion, inland flooding, or wildfire risk, is crucial for developing targeted mitigation and adaptation strategies. Effective disaster preparedness necessitates not only individual actions but also community-wide collaboration, infrastructure investments, and robust emergency response protocols. The analysis of recent events, such as Hurricane Florence, underscores the importance of learning from past experiences to enhance future resilience.
Continued vigilance, informed decision-making, and proactive planning are essential for navigating the realities of natural disasters in North Carolina. Investing in resilient infrastructure, strengthening community preparedness programs, and promoting a culture of disaster awareness are crucial for minimizing the impacts of future events and fostering a safer, more resilient future for all residents. The ongoing pursuit of scientific understanding, coupled with community engagement and policy action, remains paramount in effectively addressing the evolving challenges posed by natural hazards in North Carolina’s dynamic environment.