Applications designed for mitigating risks, responding to crises, and facilitating recovery operations form a crucial part of modern emergency preparedness. These tools can track resources, manage personnel, analyze data, and streamline communication during emergencies, ranging from natural disasters like earthquakes and hurricanes to human-caused incidents such as industrial accidents or pandemics. For example, such a system might integrate geographical information systems (GIS) to visualize affected areas, track evacuation routes, and pinpoint the location of emergency resources.
Effective crisis response relies on coordinated efforts and accurate information. Historically, disaster response often relied on fragmented communication and manual processes, hindering effective resource allocation and timely decision-making. Modern technological solutions help overcome these challenges by providing a centralized platform for information sharing, situational awareness, and collaborative planning. This enhances efficiency, improves coordination among various stakeholders, and ultimately minimizes the impact of disruptive events on communities and organizations.
This discussion will further explore the key features, functionalities, and practical applications of these critical tools, examining their role in diverse scenarios and highlighting best practices for implementation and utilization.
Tips for Effective Utilization
Optimizing the value derived from emergency preparedness and response platforms requires careful planning and execution. The following tips offer guidance for maximizing effectiveness and ensuring successful implementation.
Tip 1: Comprehensive Needs Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of organizational needs and potential risks before selecting a platform. Consider the specific types of disasters relevant to the organization’s location and operations.
Tip 2: Stakeholder Collaboration: Involve all relevant stakeholders, including emergency responders, government agencies, and community organizations, in the selection and implementation process. This collaborative approach ensures the chosen system meets the needs of everyone involved.
Tip 3: Data Integration and Interoperability: Prioritize systems that can seamlessly integrate with existing data sources and communicate effectively with other platforms. This interoperability is crucial for sharing information and maintaining situational awareness during emergencies.
Tip 4: Robust Training and Exercises: Regular training and simulated exercises are essential for familiarizing personnel with the platform’s functionalities and ensuring they can effectively use the system under pressure.
Tip 5: Secure Data Management: Implement strong data security measures to protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
Tip 6: Scalability and Flexibility: Select a system that can scale to accommodate changing needs and adapt to evolving threats. A flexible platform allows organizations to respond effectively to a wide range of scenarios.
Tip 7: Regular System Maintenance and Updates: Ensure the platform remains current and functional through regular maintenance and updates. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of technical issues during critical situations.
By adhering to these guidelines, organizations can leverage these powerful tools to enhance preparedness, streamline response efforts, and facilitate efficient recovery in the face of disruptive events. These practical measures contribute significantly to minimizing the impact of disasters and fostering greater resilience.
These strategies form a foundation for successful implementation and contribute to overall organizational resilience.
1. Mitigation
Mitigation, a critical component of disaster management, focuses on reducing the potential impact of disasters before they occur. Software solutions play a vital role in supporting mitigation efforts by providing tools for risk assessment, vulnerability analysis, and planning preventative measures. Effective mitigation strategies lessen the severity of disasters and enhance community resilience.
- Risk Assessment and Analysis
Software facilitates comprehensive risk assessments by enabling the identification, analysis, and prioritization of potential hazards. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) integration allows for visualizing risks on maps, identifying vulnerable populations, and modeling the potential impact of various disaster scenarios. For instance, flood risk assessments can identify areas prone to inundation, enabling proactive infrastructure improvements or land-use planning decisions.
- Vulnerability Reduction
Mitigation efforts aim to reduce vulnerabilities within communities and infrastructure. Software assists in this process by enabling the development and implementation of mitigation plans, tracking progress on vulnerability reduction projects, and managing resources allocated to these initiatives. For example, software can track the progress of retrofitting buildings to withstand seismic activity or implementing erosion control measures in coastal areas.
- Land-Use Planning and Zoning
Informed land-use planning and zoning decisions are crucial for minimizing disaster risk. Software supports these efforts by providing data and tools for analyzing land suitability, modeling development scenarios, and ensuring compliance with building codes and regulations. Restricting development in floodplains or enforcing stringent building codes in earthquake-prone areas exemplifies this approach.
- Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about disaster risks and preparedness measures is essential for effective mitigation. Software can facilitate public education campaigns by providing platforms for disseminating information, developing educational materials, and engaging with communities. This might include creating online resources about evacuation procedures or developing mobile applications that provide real-time alerts and safety tips.
By supporting these key facets of mitigation, disaster management software empowers communities and organizations to proactively reduce disaster risks, minimize potential losses, and build greater resilience in the face of future events. Integrating mitigation strategies into broader disaster management plans enhances overall preparedness and contributes to more sustainable and disaster-resistant communities.
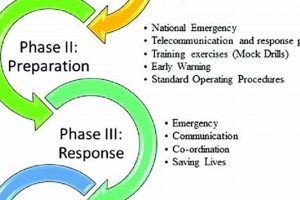
2. Preparedness
Preparedness, a crucial phase in disaster management, focuses on proactively planning and preparing for potential disasters. Disaster management software plays a vital role in supporting preparedness efforts by providing tools for developing response plans, managing resources, conducting training exercises, and establishing communication protocols. Robust preparedness measures significantly enhance an organization’s ability to respond effectively and minimize the impact of disasters.
- Emergency Planning and Response Plans
Developing comprehensive emergency plans is fundamental to preparedness. Software facilitates this process by providing templates, checklists, and collaborative tools for creating, reviewing, and updating response plans. These plans outline procedures for evacuations, resource allocation, communication protocols, and post-disaster recovery. For instance, a hospital’s emergency plan might detail procedures for patient evacuation during a flood, ensuring continuity of care in a temporary location.
- Resource Management and Tracking
Effective resource management is essential for a timely and coordinated response. Software enables organizations to inventory and track resources, including personnel, equipment, supplies, and facilities. This real-time visibility into available resources streamlines logistics, facilitates efficient deployment, and optimizes resource allocation during emergencies. For example, software can track the availability of ambulances, fire trucks, and medical supplies, ensuring they are readily accessible when needed.
- Training and Exercises
Regular training and exercises are crucial for preparing personnel to respond effectively during a disaster. Software supports training efforts by providing simulations, scenario planning tools, and platforms for conducting virtual exercises. These tools enable personnel to practice procedures, familiarize themselves with emergency protocols, and improve their decision-making skills under pressure. For instance, virtual exercises can simulate a chemical spill, allowing emergency responders to practice containment and decontamination procedures.
- Communication and Coordination
Effective communication is paramount during a disaster. Software enhances communication by providing secure messaging platforms, real-time alerts, and centralized information repositories. These tools facilitate seamless communication between emergency responders, government agencies, and affected communities, ensuring everyone has access to the latest information and updates. For instance, software can send automated alerts to residents about impending storms or provide updates on evacuation routes and shelter locations.
By supporting these key aspects of preparedness, disaster management software empowers organizations to proactively prepare for potential disasters, ensuring a more coordinated, efficient, and effective response. Integrating preparedness measures into broader disaster management strategies strengthens overall resilience and minimizes the impact of disruptive events.
3. Response
Effective response is the critical execution phase of disaster management plans, focusing on immediate actions taken during and immediately following a disaster. Disaster management software plays a crucial role in supporting response efforts by providing real-time information, facilitating communication and coordination, and streamlining resource allocation. Rapid and well-coordinated responses are essential for minimizing casualties, mitigating damage, and initiating recovery efforts.
- Real-time Situational Awareness
Maintaining accurate and up-to-date situational awareness is paramount during a disaster. Software integrates data from various sources, including sensors, social media, and emergency reports, to provide a comprehensive view of the evolving situation. This real-time information enables responders to make informed decisions, prioritize actions, and deploy resources effectively. For instance, real-time tracking of a wildfire’s perimeter allows firefighters to direct resources to the most critical areas and plan evacuation routes.
- Communication and Coordination
Effective communication and coordination are essential for a successful disaster response. Software facilitates communication among emergency responders, government agencies, and affected communities through secure messaging platforms, real-time alerts, and collaborative tools. This streamlined communication ensures everyone has access to the latest information, minimizing confusion and enabling coordinated action. For example, software can be used to coordinate the deployment of search and rescue teams following an earthquake, ensuring efficient coverage of affected areas.
- Resource Allocation and Deployment
Efficient resource allocation and deployment are critical for maximizing the impact of response efforts. Software enables organizations to track resource availability, manage logistics, and optimize deployment strategies. This real-time visibility into resources ensures that essential equipment, personnel, and supplies reach those who need them most. For instance, during a hurricane, software can track the location and availability of generators, enabling their rapid deployment to critical infrastructure such as hospitals and emergency shelters.
- Damage Assessment and Reporting
Rapid and accurate damage assessments are crucial for informing response and recovery efforts. Software provides tools for collecting and analyzing damage data, generating reports, and visualizing the extent of the impact. This information helps prioritize recovery efforts, allocate resources effectively, and inform decision-making about long-term rebuilding strategies. For example, following a flood, software with integrated aerial imagery can assess the extent of inundation and identify damaged buildings, enabling targeted assistance to affected residents.
These facets of response, facilitated by disaster management software, are interconnected and contribute to a more effective and coordinated response to disasters. By leveraging these tools, organizations can minimize the impact of disasters, save lives, and facilitate a quicker transition to recovery operations. The ability to adapt and respond dynamically based on real-time information is crucial for successful disaster management.
4. Recovery
Recovery, the final stage of the disaster management cycle, focuses on restoring communities and infrastructure after a disaster. Disaster management software plays a vital role in supporting long-term recovery efforts by providing tools for damage assessment, resource allocation, rebuilding planning, and community engagement. Effective recovery strategies are essential for restoring normalcy, rebuilding resilient communities, and mitigating the long-term impacts of disasters.
- Damage Assessment and Needs Analysis
Accurate damage assessments and needs analyses are crucial for informing recovery efforts. Software facilitates this process by providing tools for collecting damage data, analyzing needs, and prioritizing recovery projects. This information enables efficient resource allocation and ensures that aid reaches those who need it most. For example, following a hurricane, software can be used to assess damage to housing, infrastructure, and businesses, informing decisions about rebuilding priorities and resource allocation.
- Resource Allocation and Management
Efficient resource allocation and management are essential for effective recovery. Software enables organizations to track available resources, manage logistics, and distribute aid effectively. This streamlined process ensures that resources are used efficiently and reach affected communities promptly. For instance, software can track the distribution of food, water, and medical supplies to disaster-stricken areas, ensuring equitable distribution and minimizing waste.
- Rebuilding and Reconstruction Planning
Developing comprehensive rebuilding and reconstruction plans is critical for long-term recovery. Software supports this process by providing tools for project management, budgeting, and tracking progress. This ensures that rebuilding efforts are coordinated, efficient, and aligned with community needs. For example, software can be used to manage the reconstruction of damaged schools, hospitals, and other critical infrastructure, ensuring that projects are completed on time and within budget. This can also include integrating building codes and land-use planning regulations to mitigate future risk.
- Community Engagement and Support
Engaging with affected communities and providing ongoing support is vital for successful recovery. Software facilitates communication with residents, collects feedback, and provides platforms for community participation in recovery planning. This inclusive approach ensures that recovery efforts are responsive to community needs and priorities. For instance, software can provide online portals for residents to access information about recovery programs, apply for assistance, and provide feedback on recovery efforts. This can also include facilitating communication with insurance providers and government agencies to streamline the recovery process.
These facets of recovery, facilitated by disaster management software, are crucial for building back better and fostering more resilient communities. By leveraging these tools, organizations can streamline recovery efforts, minimize long-term impacts, and empower communities to rebuild stronger and more prepared for future events. The recovery phase represents not just restoring what was lost, but also learning from past events to mitigate future risks and build greater resilience.
5. Communication
Effective communication forms the backbone of successful disaster management, enabling coordinated responses and informed decision-making. Disaster management software serves as a critical communication hub, connecting various stakeholders and facilitating information flow throughout all phases of disaster management. Examining the facets of communication within these software solutions highlights their crucial role in mitigating risks, facilitating effective responses, and supporting recovery efforts.
- Real-time Information Dissemination
Software facilitates immediate communication during emergencies. Real-time alerts, updates, and critical information reach relevant parties concurrently, enabling swift, coordinated action. For example, automated alerts regarding a chemical spill can instantly notify nearby residents, emergency responders, and relevant authorities, facilitating timely evacuations and containment efforts.
- Multi-Agency Collaboration
Disaster response frequently involves multiple agencies. Software provides centralized communication platforms, fostering inter-agency collaboration and information sharing. For instance, during a wildfire, firefighters, law enforcement, and emergency medical services can communicate seamlessly through the platform, coordinating efforts and sharing real-time updates on fire perimeters, evacuation routes, and resource needs. This coordinated approach improves overall response efficiency and minimizes duplication of efforts.
- Public Communication and Engagement
Informing the public during a disaster is crucial. Software solutions offer tools for disseminating information to the public through various channels, such as mobile apps, social media integration, and SMS alerts. Providing timely and accurate updates about evacuation orders, shelter locations, and safety procedures helps reduce public anxiety and facilitates effective community response. For instance, during a hurricane, regular updates on storm trajectory, evacuation routes, and shelter availability can be disseminated through the software, ensuring public safety and minimizing confusion.
- Post-Disaster Communication and Reporting
After a disaster, effective communication remains crucial for coordinating recovery efforts. Software platforms provide tools for documenting damage, tracking recovery progress, and facilitating communication between relief organizations, government agencies, and affected communities. This streamlined communication supports efficient resource allocation, facilitates needs assessments, and ensures that recovery efforts are aligned with community priorities. For example, after an earthquake, software can be used to track the progress of rebuilding efforts, document damage assessments, and communicate with affected residents about available aid and support services.
These interconnected communication facets, facilitated by disaster management software, are essential for navigating all stages of a disaster. By providing a centralized platform for information sharing, collaboration, and public engagement, these solutions empower organizations and communities to effectively prepare for, respond to, and recover from disasters, minimizing their impact and fostering greater resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Addressing common inquiries regarding applications for managing disasters provides clarity on their functionality and benefits.
Question 1: What types of disasters can these applications address?
These applications support management of various disaster types, including natural disasters (earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, wildfires), technological disasters (industrial accidents, hazardous material spills), and human-caused disasters (pandemics, terrorist attacks). Their adaptability allows customization for specific organizational needs and diverse hazard profiles.
Question 2: How do these applications enhance communication during a crisis?
These platforms provide centralized communication hubs, enabling real-time information sharing among stakeholders, including emergency responders, government agencies, and the public. Features such as secure messaging, automated alerts, and geospatial data integration streamline communication and enhance situational awareness.
Question 3: What role do these applications play in long-term recovery?
Beyond immediate response, these tools support long-term recovery by facilitating damage assessments, resource allocation, and rebuilding efforts. They provide platforms for tracking progress, managing resources, and coordinating activities among various stakeholders involved in the recovery process.
Question 4: How do these applications integrate with existing systems?
Modern applications offer interoperability features, enabling integration with existing data sources and systems, such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS), weather data feeds, and early warning systems. This integration enhances data sharing, improves situational awareness, and avoids data silos.
Question 5: What security measures are implemented in these applications to protect sensitive data?
Data security is paramount. These applications typically employ robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, to protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with relevant data privacy regulations. Specific security features vary based on the application and vendor.
Question 6: How can organizations choose the right application for their needs?
Selecting the appropriate application requires careful consideration of organizational needs, specific hazards, budget constraints, and integration requirements. Consulting with disaster management professionals and conducting thorough product evaluations can assist in making informed decisions. A comprehensive needs assessment is crucial for successful implementation.
Understanding the capabilities and benefits of these applications is crucial for effective disaster preparedness and response. These tools empower organizations and communities to mitigate risks, enhance resilience, and effectively manage the challenges posed by various disaster scenarios.
Further exploration of specific features and functionalities can provide deeper insight into how these applications can be tailored to meet diverse organizational requirements.
Conclusion
Disaster management software provides critical tools for mitigating risks, enhancing preparedness, streamlining response efforts, and facilitating effective recovery. From real-time information sharing and resource allocation to damage assessment and community engagement, these applications empower organizations and communities to navigate the complexities of disaster management. Understanding the core functionalities and benefits spanning the cycle from mitigation to recovery underscores the importance of these technological solutions in building resilience and minimizing the impact of disruptive events.
Investing in robust technological solutions for disaster management is not merely a matter of preparedness; it is a strategic imperative for safeguarding communities, protecting critical infrastructure, and ensuring business continuity. As the frequency and intensity of disasters continue to rise globally, the effective utilization of these tools becomes increasingly vital for building a more resilient and secure future. The proactive adoption and integration of disaster management software represent a crucial step towards minimizing the human and economic costs of disasters and fostering a more resilient world.