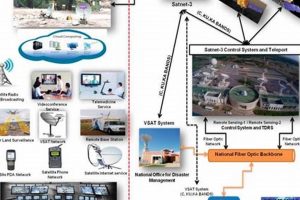
Developing comprehensive plans and actions designed to mitigate risks, protect lives, and minimize damage before, during, and after unforeseen disruptive eventsfrom natural calamities like earthquakes and hurricanes to human-induced crisesforms the foundation of effective protective measures. For example, establishing evacuation routes, stockpiling essential supplies, and implementing early warning systems are crucial components.
These proactive strategies are vital for enhancing community resilience, ensuring the continuity of essential services, and facilitating a swift and efficient recovery process. Historical analyses of past events demonstrate the significant impact that well-defined plans can have on reducing casualties and economic losses. Lessons learned from such events continuously inform and refine best practices, contributing to improved strategies for future events.
This understanding of protective measures serves as a foundation for exploring key aspects, such as risk assessment, planning methodologies, communication strategies, and resource management. The subsequent sections will delve deeper into these critical areas.
Practical Steps for Enhanced Safety and Resilience
Proactive measures can significantly mitigate the impact of unforeseen events. The following recommendations offer guidance for individuals and communities to enhance their safety and resilience.
Tip 1: Develop a Comprehensive Plan: A well-defined plan should outline specific actions to be taken before, during, and after an event. This includes establishing communication protocols, identifying evacuation routes, and designating meeting points.
Tip 2: Assemble an Emergency Kit: Essential supplies such as water, non-perishable food, first-aid materials, flashlights, and a battery-powered radio should be readily available. Regularly check and replenish these supplies.
Tip 3: Stay Informed: Monitor weather reports and official alerts from local authorities. Understand the specific risks prevalent in the area and familiarize oneself with community warning systems.
Tip 4: Secure Important Documents: Keep crucial documents, including identification, insurance policies, and medical records, in a waterproof and portable container. Consider creating digital copies stored securely online.
Tip 5: Practice Emergency Procedures: Regularly rehearse evacuation plans and safety drills. This reinforces preparedness and ensures a more effective response during an actual event.
Tip 6: Strengthen Community Networks: Engage with neighbors and community organizations to establish support systems. Collaborative efforts can enhance overall resilience and facilitate mutual assistance during emergencies.
Tip 7: Learn Basic First Aid and CPR: Acquiring these skills empowers individuals to provide immediate assistance to those in need, potentially saving lives in critical situations.
By implementing these measures, individuals and communities can significantly reduce their vulnerability to unforeseen events and foster a culture of preparedness. These proactive steps contribute to enhanced safety, minimized disruption, and a more rapid recovery process.
These practical tips provide a framework for building resilience. The concluding section will emphasize the ongoing nature of preparedness and the importance of continuous improvement.
1. Risk Assessment
Risk assessment forms the cornerstone of effective emergency and disaster preparedness. It involves a systematic process of identifying potential hazards, analyzing their likelihood and potential impact, and evaluating existing vulnerabilities. This understanding of risk provides a crucial foundation for developing targeted mitigation strategies, prioritizing resource allocation, and designing effective response plans. Cause and effect relationships are central to this process. For instance, a coastal region’s proximity to fault lines increases the risk of tsunamis following an earthquake. Recognizing this connection allows for the development of specific evacuation procedures and infrastructure design to minimize potential damage. Without a thorough risk assessment, preparedness efforts may be misdirected or inadequate, leaving communities vulnerable.
The importance of risk assessment as a component of preparedness is underscored by real-life examples. In areas prone to wildfires, assessing fuel loads, proximity to residential areas, and historical fire patterns informs preventative measures like controlled burns and community education programs. Similarly, understanding the potential impact of a pandemic on healthcare systems allows for the development of surge capacity plans and resource stockpiling strategies. This proactive approach, driven by risk assessment, strengthens community resilience and minimizes the disruptive effects of such events. In practical terms, this understanding translates to informed decision-making regarding building codes, land-use planning, and the development of early warning systems.
In summary, robust risk assessment provides the critical foundation upon which effective preparedness strategies are built. It enables informed resource allocation, prioritized mitigation efforts, and the development of tailored response plans that address specific vulnerabilities. While the process can be complex and resource-intensive, the potential consequences of neglecting this crucial step underscore its fundamental role in safeguarding communities and fostering resilience in the face of unforeseen events. Successfully integrating risk assessment into broader preparedness frameworks remains a continuous challenge, requiring ongoing evaluation and adaptation to evolving threats and vulnerabilities.
2. Planning
Systematic planning is inseparable from effective emergency and disaster preparedness. Planning translates risk assessments into actionable strategies, outlining specific steps to be taken before, during, and after disruptive events. This process considers potential scenarios, defines roles and responsibilities, establishes communication protocols, and determines resource allocation strategies. Cause and effect relationships are integral to planning. For example, anticipating potential infrastructure damage following an earthquake necessitates plans for alternative communication methods and emergency shelter provisions. Without comprehensive planning, responses become reactive and fragmented, amplifying the impact of disasters.
The importance of planning is underscored by numerous real-world examples. Pre-established evacuation routes and designated shelter locations demonstrably reduce casualties during hurricanes. Similarly, detailed pandemic preparedness plans, including resource stockpiling and healthcare surge capacity protocols, mitigate the strain on medical systems. These examples demonstrate the practical significance of translating theoretical risk assessments into concrete action plans. The absence of such plans often results in delayed responses, inadequate resource allocation, and increased vulnerability to cascading failures across critical infrastructure systems.
In summary, meticulous planning provides the essential bridge between risk assessment and effective action. It transforms potential scenarios into manageable steps, enabling coordinated responses, optimized resource utilization, and minimized disruption. While the planning process necessitates considerable effort and foresight, the potential consequences of inadequate planning underscore its vital role in community resilience. Maintaining up-to-date plans, incorporating lessons learned from past events, and adapting to evolving threat landscapes remain ongoing challenges. The efficacy of any preparedness framework hinges on robust, actionable plans that translate awareness into effective, life-saving measures.
3. Communication
Effective communication forms the backbone of successful emergency and disaster preparedness and response. Timely and accurate information dissemination is crucial for coordinating actions, facilitating informed decision-making, and mitigating the impact of disruptive events. From early warnings to post-event recovery efforts, clear communication channels and protocols are essential for ensuring public safety and fostering community resilience. The following facets highlight the multifaceted role of communication in preparedness.
- Public Alert and Warning Systems
Public alert systems, encompassing sirens, mobile alerts, and broadcast announcements, serve as the first line of defense in disseminating critical information about impending threats. Real-world examples include tsunami warnings triggered by seismic activity or evacuation orders issued in the face of approaching wildfires. The efficacy of these systems depends on clear messaging, multiple dissemination channels, and public awareness campaigns that ensure prompt action is taken when alerts are received. These systems can significantly reduce casualties and property damage by enabling timely evacuations and protective measures.
- Interagency Coordination
Effective disaster response necessitates seamless communication between various agencies, including emergency services, government bodies, and non-governmental organizations. Clearly defined communication protocols, shared situational awareness platforms, and interoperable communication systems facilitate coordinated responses, optimize resource allocation, and minimize duplication of efforts. For instance, during large-scale emergencies, interagency communication enables streamlined resource deployment, such as dispatching medical teams to affected areas and coordinating evacuation logistics. Failures in interagency communication can lead to fragmented responses, delayed assistance, and increased vulnerability.
- Community Engagement and Education
Building community resilience requires ongoing communication and education efforts. Public awareness campaigns, community forums, and educational materials empower individuals to prepare for potential disasters, understand their roles in response efforts, and access critical information during emergencies. Examples include community workshops on earthquake preparedness or public service announcements promoting hurricane safety measures. This proactive approach fosters a culture of preparedness, enhances community-level response capabilities, and promotes individual responsibility.
- Post-Disaster Communication
In the aftermath of a disaster, effective communication becomes even more critical. Providing accurate information about available resources, recovery efforts, and ongoing risks helps reduce uncertainty, manage expectations, and facilitate a more efficient recovery process. Establishing dedicated communication channels for disseminating recovery updates, coordinating aid distribution, and addressing public concerns promotes transparency and builds trust between affected communities and responding agencies. This continuous flow of information mitigates the psychological impact of disasters and empowers individuals to navigate the recovery process more effectively.
In conclusion, communication plays a pervasive and crucial role in all phases of emergency and disaster preparedness. From initial warnings to long-term recovery, effective communication strategies underpin coordinated responses, informed decision-making, and community resilience. By investing in robust communication infrastructure, establishing clear protocols, and fostering a culture of open communication, societies can significantly enhance their capacity to withstand and recover from disruptive events. The evolving nature of communication technologies presents both opportunities and challenges, demanding continuous adaptation and innovation to ensure preparedness strategies remain effective in the face of dynamic threat landscapes.
4. Resource Management
Effective resource management is fundamental to successful emergency and disaster preparedness. It encompasses the strategic planning, acquisition, allocation, and utilization of essential resources necessary for mitigating the impact of disruptive events and supporting recovery efforts. This includes tangible assets like medical supplies, food, and shelter, as well as human resources, financial capital, and information systems. Efficient resource management ensures that critical assets are readily available when and where needed, optimizing response effectiveness and minimizing human suffering.
- Pre-Disaster Resource Staging and Stockpiling
Establishing strategically located stockpiles of essential supplies, such as water, food, medical equipment, and temporary shelter materials, is crucial for ensuring a rapid and effective response. Pre-positioning resources reduces reliance on just-in-time delivery, which can be disrupted during emergencies. For example, maintaining regional caches of medical supplies enables rapid deployment to affected areas following an earthquake or hurricane. The effectiveness of pre-disaster stockpiling hinges on accurate needs assessments, proper inventory management, and regular replenishment to ensure resource viability.
- Resource Allocation and Distribution
Efficient resource allocation requires robust logistics systems and decision-making frameworks that prioritize needs and ensure equitable distribution. Real-time information about impacted areas, available resources, and evolving needs informs allocation decisions. For instance, during a pandemic, effective resource allocation might involve prioritizing ventilator distribution to hospitals experiencing surge capacity limitations. Transparent and accountable allocation processes are crucial for maintaining public trust and ensuring resources reach those most in need.
- Human Resource Mobilization and Management
Preparedness extends beyond material resources; it includes mobilizing and managing human resources effectively. This involves training first responders, medical personnel, and volunteers, establishing clear roles and responsibilities, and implementing communication protocols that facilitate coordinated action. For example, training community members in basic first aid and search-and-rescue techniques enhances local response capabilities. Effective human resource management ensures that skilled personnel are readily available to address the diverse needs that arise during emergencies.
- Financial Resource Management
Sound financial resource management underpins effective preparedness and recovery. This includes securing funding for preparedness initiatives, establishing mechanisms for rapid financial disbursement during emergencies, and implementing transparent accounting procedures. Pre-disaster funding allocations for infrastructure improvements, early warning systems, and community education programs demonstrate proactive financial resource management. Similarly, post-disaster financial assistance programs support rebuilding efforts and long-term recovery. Effective financial resource management ensures that adequate funding is available to support all phases of disaster management.
In conclusion, effective resource management is an integral component of comprehensive emergency and disaster preparedness. By strategically planning for resource needs, implementing efficient allocation mechanisms, and investing in both material and human resources, communities enhance their resilience and minimize the disruptive impacts of unforeseen events. The interconnected nature of these facets underscores the importance of a holistic approach to resource management, recognizing that effective preparedness requires coordinated efforts across multiple sectors and disciplines. Continuously evaluating resource management strategies, adapting to evolving threat landscapes, and incorporating lessons learned from past events are crucial for ensuring long-term preparedness and effective disaster response.
5. Training and Education
Training and education are integral components of effective emergency and disaster preparedness. These proactive measures equip individuals and communities with the knowledge, skills, and confidence to respond effectively to disruptive events, minimizing their impact and fostering resilience. From understanding risk factors to executing response plans, training and education empower individuals to take appropriate action before, during, and after emergencies.
- First Responder Training
Specialized training for first responders, including firefighters, paramedics, and law enforcement personnel, is essential for ensuring a coordinated and effective response to emergencies. This training encompasses technical skills, such as search and rescue, medical triage, and fire suppression, as well as communication protocols, incident command system training, and psychological first aid. Well-trained first responders are better equipped to manage complex emergency situations, minimize casualties, and protect public safety. For example, simulated disaster exercises provide valuable hands-on experience in coordinating multi-agency responses.
- Community Emergency Response Team (CERT) Training
CERT programs empower community members to assist themselves, their families, and their neighbors in the aftermath of a disaster. CERT training covers basic disaster response skills, including fire safety, light search and rescue, disaster medical operations, and team organization. These trained volunteers provide valuable support to professional responders, especially during the initial hours following an event when resources may be stretched thin. CERT volunteers played a vital role in supporting relief efforts following Hurricane Katrina, demonstrating the value of community-based preparedness initiatives.
- Public Awareness and Education Campaigns
Raising public awareness about disaster risks and preparedness measures is crucial for fostering a culture of resilience. Public education campaigns utilize various channels, including public service announcements, community workshops, and online resources, to disseminate information about potential hazards, recommended safety measures, and available resources. These campaigns empower individuals to take proactive steps to prepare their homes and families for emergencies, such as developing evacuation plans, assembling emergency kits, and learning basic first aid. Effective public awareness campaigns contribute to increased community preparedness and reduce the overall impact of disasters.
- Specialized Training for Vulnerable Populations
Certain populations, such as individuals with disabilities, older adults, and non-English speakers, may require specialized training and educational resources to ensure their safety during emergencies. This may include providing accessible emergency information, developing tailored evacuation plans, and offering training programs that address specific needs and vulnerabilities. Addressing the unique needs of vulnerable populations enhances overall community resilience and ensures that preparedness efforts are inclusive and equitable. For instance, providing sign language interpretation during emergency briefings ensures accessibility for deaf community members.
In conclusion, training and education are essential investments in community resilience. By equipping individuals with the knowledge, skills, and resources they need to prepare for and respond to emergencies, these initiatives mitigate the impact of disasters, foster self-sufficiency, and strengthen community bonds. The multifaceted nature of training and education underscores the importance of tailored programs that address the specific needs of diverse groups, ensuring that preparedness efforts are inclusive and effective. Continuously evaluating training programs, incorporating lessons learned from past events, and adapting to evolving threat landscapes are crucial for maintaining a state of readiness and ensuring the long-term safety and well-being of communities.
6. Community Engagement
Strong community engagement is paramount for effective emergency and disaster preparedness. Active participation of community members in planning, training, and response efforts significantly strengthens collective resilience. When individuals are informed, prepared, and connected, they are better equipped to navigate the challenges posed by disruptive events. This interconnectedness fosters a sense of shared responsibility and empowers communities to effectively address both individual and collective vulnerabilities. Cause and effect relationships are evident; robust community engagement leads to increased individual preparedness, improved communication networks, and more effective resource mobilization during emergencies. Conversely, a lack of engagement can result in fragmented responses, delayed assistance, and amplified negative consequences. For example, communities with established neighborhood watch programs often demonstrate quicker response times and improved coordination during emergencies.
The importance of community engagement as a component of preparedness is underscored by real-world scenarios. Neighborhoods with active community emergency response teams (CERT) often experience fewer casualties and a faster recovery process following disasters. Likewise, communities that regularly conduct disaster drills and exercises demonstrate improved coordination and communication among residents and responding agencies. These examples highlight the practical significance of fostering community ownership in preparedness initiatives. Establishing community-based early warning systems empowers residents to take proactive measures, such as securing their homes and evacuating vulnerable individuals before a disaster strikes. Similarly, engaging community leaders in planning processes ensures that culturally appropriate and accessible information reaches all segments of the population.
In summary, robust community engagement forms a cornerstone of effective emergency and disaster preparedness. It transforms individual preparedness into collective resilience, amplifying the effectiveness of response and recovery efforts. While building and maintaining strong community networks requires ongoing effort and investment, the demonstrable benefits underscore its critical role in safeguarding communities against the disruptive impacts of unforeseen events. Cultivating trust, fostering open communication, and empowering local leadership are essential for building strong, resilient communities capable of effectively navigating the challenges posed by disasters. The ongoing challenge lies in adapting engagement strategies to evolving community demographics, technological advancements, and emerging threat landscapes. Successfully integrating community engagement into preparedness frameworks is not a one-time effort but a continuous process that demands adaptability, innovation, and a sustained commitment to building strong community partnerships.
7. Post-Event Recovery
Post-event recovery represents the final, yet crucial, phase of the emergency and disaster management cycle. While preparedness focuses on mitigating potential impacts, recovery addresses the aftermath, aiming to restore normalcy and build back better. Effective recovery is intrinsically linked to preparedness; robust pre-disaster planning streamlines post-event efforts, facilitating a more rapid and resilient return to stability. This interconnectedness highlights the cyclical nature of disaster management, where lessons learned from recovery inform and enhance future preparedness strategies.
- Infrastructure Restoration
Rebuilding damaged infrastructure is a cornerstone of post-event recovery. This encompasses restoring essential services such as power, water, transportation, and communication networks. The speed and efficiency of infrastructure restoration significantly impact community well-being and economic stability. Prioritized restoration plans, developed during the preparedness phase, expedite the recovery process. For instance, pre-negotiated contracts with construction companies can accelerate the rebuilding of critical infrastructure following a disaster. The pace of infrastructure restoration often directly correlates with the overall recovery timeline.
- Economic Recovery
Economic recovery focuses on restoring businesses, livelihoods, and financial stability within affected communities. This involves providing financial assistance to businesses and individuals, promoting job creation, and rebuilding critical economic sectors. Preparedness measures, such as business continuity plans and insurance coverage, mitigate economic losses and facilitate a quicker recovery. For example, businesses with well-defined continuity plans can resume operations more rapidly after a disaster, minimizing economic disruption and preserving jobs. The resilience of local economies often depends on the effectiveness of pre-disaster economic preparedness strategies.
- Psychosocial Support
Disasters often have profound psychological and social impacts on affected communities. Psychosocial support services, including counseling, mental health services, and community support programs, are essential for addressing trauma, promoting emotional well-being, and fostering community healing. Integrating psychosocial support into preparedness plans ensures that these services are readily available in the aftermath of an event. Community-based support groups, established prior to a disaster, can provide immediate emotional support and facilitate long-term recovery. Addressing the psychosocial needs of a community is crucial for fostering long-term resilience.
- Lessons Learned and Preparedness Enhancement
Post-event analysis provides invaluable insights for improving future preparedness efforts. Evaluating response effectiveness, identifying gaps in planning, and incorporating lessons learned into updated plans strengthens community resilience. This iterative process ensures that preparedness strategies remain relevant and effective in the face of evolving threats. For instance, analyzing communication challenges experienced during a past disaster can inform the development of improved communication protocols for future events. The ability to learn from past events is a hallmark of effective disaster management.
In conclusion, post-event recovery is not merely an aftermath but an integral component of the broader preparedness cycle. Effective recovery efforts, informed by pre-disaster planning and executed with community engagement, build resilience and mitigate the long-term impacts of disruptive events. The interconnectedness of recovery and preparedness underscores the importance of a holistic approach to disaster management, where each phase informs and strengthens the others. By prioritizing preparedness, communities not only mitigate immediate impacts but also lay the foundation for a more effective and resilient recovery process. Continuously evaluating recovery strategies, incorporating lessons learned, and adapting to evolving challenges are crucial for building stronger, more resilient communities capable of withstanding and recovering from the inevitable disruptions of the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding effective strategies for mitigating risks and fostering resilience in the face of unforeseen events.
Question 1: How much water should be stored in an emergency kit?
Storing one gallon of water per person per day for a minimum of three days is recommended for drinking and sanitation purposes.
Question 2: What types of food are appropriate for emergency supplies?
Non-perishable, ready-to-eat, or easily prepared food items are ideal. Examples include canned goods, energy bars, and dried fruits. Regularly rotating these supplies ensures freshness.
Question 3: Beyond basic supplies, what other items should be included in an emergency kit?
A comprehensive kit should include a first-aid kit, medications, a flashlight, a battery-powered radio, extra batteries, a multi-tool or knife, sanitation supplies, and copies of important documents.
Question 4: How frequently should emergency plans be reviewed and updated?
Regular review, at least annually, is recommended to ensure plans remain relevant and reflect changes in household composition, contact information, or community risks.
Question 5: What role do local authorities play in emergency preparedness?
Local authorities provide crucial information regarding community-specific risks, evacuation procedures, and available resources. Staying informed about local guidance is essential for effective preparedness.
Question 6: What are the most common misconceptions about preparing for unforeseen events?
One common misconception is that emergencies are unlikely to occur. Another is that personal preparedness is unnecessary if local authorities are responsible for response. Individual and community preparedness are complementary and crucial for effective mitigation.
Proactive measures, informed by reliable information, are the cornerstone of effective risk mitigation and resilience. These FAQs offer foundational knowledge for building individual and community preparedness strategies.
The following section provides further resources for enhancing preparedness and accessing additional information.
Emergency and Disaster Preparedness
Effective emergency and disaster preparedness necessitates a multifaceted approach encompassing risk assessment, planning, communication, resource management, training, community engagement, and post-event recovery. Each element plays a crucial, interconnected role in mitigating the impact of unforeseen events and fostering resilience. From individual actions like assembling emergency kits to community-wide initiatives such as establishing early warning systems, proactive measures significantly reduce vulnerabilities and enhance recovery capabilities. The exploration of these key aspects emphasizes the importance of integrating preparedness into all facets of community life, from infrastructure development to public education.
Building resilient communities requires a sustained commitment to preparedness, continuous improvement of strategies, and a shared understanding that safeguarding against unforeseen events is a collective responsibility. The potential consequences of inadequate preparedness underscore the critical need for ongoing investment in proactive measures that protect lives, minimize disruption, and ensure a more secure future. Cultivating a culture of preparedness empowers individuals, strengthens communities, and fosters a more resilient society capable of effectively navigating the challenges posed by an uncertain world.