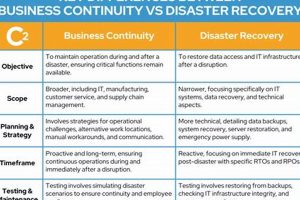
Restoring functionality after a significant disruption is distinct from the ability to withstand and adapt to such events. The former focuses on reactive measures taken after an incident to reinstate operations, often... Read more »

Data loss, system downtime, and operational disruption are significant challenges organizations face following unforeseen events such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, or hardware failures. These events can lead to lost revenue, reputational damage,... Read more »
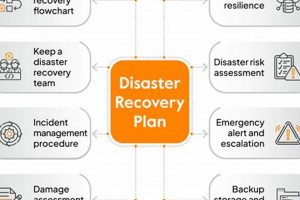
Business continuity hinges on the ability to restore critical operations and data following unforeseen events. Consider a scenario where a company’s primary data center becomes inoperable due to a natural disaster. Without... Read more »
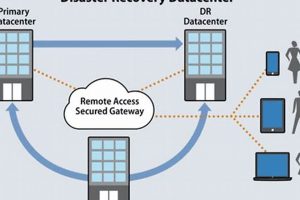
A separate and fully equipped location allows an organization to resume operations following a significant disruption, such as a natural disaster, cyberattack, or equipment failure. This alternative processing facility can house duplicate... Read more »

A robust plan for business continuity involves the ability to restore crucial IT infrastructure and systems following a disruptive event. This process often involves establishing redundant systems and backups, along with detailed... Read more »

Data protection and restoration in the face of disruptive eventsranging from hardware malfunctions and cyberattacks to natural disastersis a critical aspect of business continuity. A comprehensive strategy ensures that essential information remains... Read more »

Organizations categorize their recovery strategies into various levels, each offering a different balance between recovery time objective (RTO) the maximum acceptable downtime and recovery point objective (RPO) the maximum acceptable data loss.... Read more »

Protecting information assets involves two key processes: routinely copying data to a separate storage location and implementing a plan to restore systems and data after an unforeseen event. For instance, a business... Read more »

A situation involving significant data loss requiring professional retrieval services exemplifies a critical failure in data management. This can range from a single hard drive crash resulting in the loss of personal... Read more »
The recovery point objective defines the maximum acceptable data loss in the event of a disruptive incident. For example, an objective of one hour means a business can tolerate losing, at most,... Read more »


