
Protecting digital assets and ensuring business continuity are paramount in today’s interconnected world. For organizations located in Birmingham, a comprehensive strategy encompassing data protection and restoration procedures following unforeseen events is essential.... Read more »

This 2018 legislation amended the Stafford Act to streamline and improve the federal government’s disaster preparedness and response efforts. It introduced reforms affecting hazard mitigation, pre-disaster planning, and the delivery of federal... Read more »
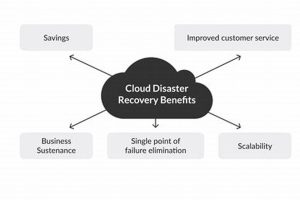
Minimizing downtime and data loss following unforeseen events like natural disasters, cyberattacks, or equipment failures is crucial for any organization. A robust plan to restore critical IT infrastructure and operations allows businesses... Read more »

The process of investigating, analyzing, and learning from a catastrophic failure like the Space Shuttle Challenger incident is crucial for preventing similar events in the future. This involves meticulous examination of technical... Read more »

Securing business continuity and minimizing operational disruption after unforeseen events like natural disasters, cyberattacks, or hardware failures necessitates skilled professionals. These specialists develop and implement strategies involving data backup and restoration, infrastructure... Read more »

Maintaining business continuity during unforeseen events like natural disasters, cyberattacks, or system failures requires a robust disaster recovery plan. In the context of cloud computing environments like Amazon Web Services (AWS), this... Read more »
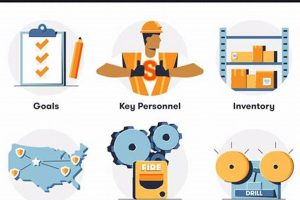
The process of restoring critical business operations after an unforeseen disruptive eventwhether a natural disaster, cyberattack, or equipment failureis crucial for organizational survival. For example, a robust plan might involve backing up... Read more »
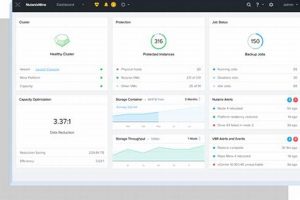
Protecting business operations from unforeseen events like natural disasters, cyberattacks, or hardware failures requires a robust continuity plan. A platform approach to business continuity leverages software-defined infrastructure to create resilient and easily... Read more »

Positions within this field in Florida center on minimizing the impact of disruptive events on organizations. These professionals work to restore critical business functions and data following natural disasters like hurricanes, as... Read more »
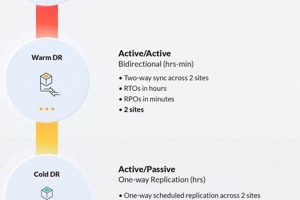
A fully operational replica of a primary data center, ready to assume operations immediately in case of a disaster, allows for minimal downtime and business disruption. This secondary location mirrors the production... Read more »


