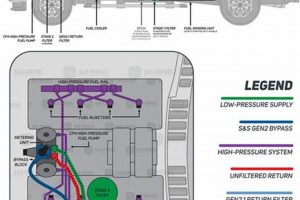
The high-pressure fuel pump found in certain 6.7-liter diesel engines is known to be susceptible to catastrophic failure due to fuel contamination. A collection of components designed to mitigate this risk typically includes a fuel filtration system significantly more robust than the factory-installed version, often incorporating a lift pump to ensure adequate fuel supply and pressure. Such kits may also contain fuel additives intended to lubricate the pump and prevent metal-on-metal contact within its delicate internal mechanisms.
Preventing catastrophic pump failure is critical for vehicle owners. Repairs can be extremely costly, often exceeding $10,000, and can lead to significant downtime. Proactive measures offer substantial long-term cost savings and preserve vehicle reliability. Increased awareness of this potential failure point has led to the development of these preventative maintenance solutions, providing owners with options to protect their investment.
This article will further explore the components included in these preventative kits, the different filtration technologies available, and best practices for installation and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the fuel system.
Preventative Maintenance Tips for 6.7L Diesel Engines
Proactive maintenance is crucial for mitigating the risk of high-pressure fuel pump failure in 6.7-liter diesel engines. The following tips outline essential steps to protect these vital components.
Tip 1: Upgrade Fuel Filtration. Install a high-quality aftermarket fuel filtration system designed to remove significantly smaller particulate matter than the factory standard. This added filtration helps prevent abrasive contaminants from reaching the high-pressure pump.
Tip 2: Incorporate a Lift Pump. Installing a lift pump helps ensure consistent fuel supply and adequate pressure to the high-pressure pump, reducing strain and cavitation potential.
Tip 3: Use Lubricity Additives. Supplementing fuel with lubricity additives helps compensate for the reduced lubricity of modern diesel fuels, further protecting the high-pressure pump’s internal components.
Tip 4: Drain Water Separators Regularly. Regularly draining the water separator, a critical component of upgraded filtration systems, removes accumulated water and contaminants from the fuel system, preventing potential damage.
Tip 5: Adhere to Recommended Fueling Practices. Fueling at reputable stations with high turnover rates helps minimize the risk of contaminated fuel entering the vehicle.
Tip 6: Observe Fuel Pressure. Regularly monitor fuel pressure to identify potential issues early on. Sudden pressure drops or fluctuations can indicate problems requiring immediate attention.
Tip 7: Maintain Proper Fuel System Hygiene. Keeping the entire fuel system clean, from the fuel tank to the injectors, helps minimize the introduction of contaminants.
Implementing these preventative measures significantly reduces the risk of catastrophic pump failure, protecting a substantial investment and ensuring reliable vehicle operation.
By taking proactive steps, owners can enjoy the long-term benefits of a healthy and robust fuel system, avoiding costly repairs and downtime associated with high-pressure pump failures.
1. Enhanced Filtration
Enhanced filtration plays a critical role in safeguarding the CP4 high-pressure fuel pump found in 6.7 Powerstroke engines. This pump is highly susceptible to damage from contaminants present in fuel. Consequently, upgrading the filtration system is a cornerstone of any effective prevention strategy.
- Micron Rating and Particle Removal:
Standard fuel filters often lack the necessary fine filtration to remove microscopic particles that can damage the CP4 pump. Enhanced filtration systems employ filters with significantly lower micron ratings, typically in the 2-5 micron range, effectively capturing these damaging particles. This prevents abrasive wear and premature pump failure. For instance, a 2-micron filter will trap particles as small as 2 micrometers, substantially reducing the risk of damage compared to the factory-installed 10-micron or higher filter.
- Water Separation:
Water contamination in fuel can also contribute to CP4 pump failure. Enhanced filtration systems often include water separators designed to coalesce and remove water from the fuel. This protects the pump from corrosion and other water-related damage. Efficient water separation ensures that the pump receives only clean, dry fuel, further extending its lifespan.
- Filter Media and Construction:
The filter media and overall construction of the filter element significantly impact its effectiveness. Enhanced filtration systems often utilize synthetic media with a larger surface area for greater contaminant holding capacity. Robust filter housings prevent bypass and ensure consistent filtration performance, even under high pressure. Materials chosen resist degradation from fuel and additives, maintaining long-term filtration integrity.
- Pre-Pump and Post-Pump Filtration Strategies:
Multiple filtration stages, including pre-pump and post-pump filtration, provide comprehensive protection. A pre-pump filter removes larger contaminants, protecting both the lift pump (if installed) and the CP4 pump. A post-pump filter provides a final barrier against any remaining particles. This multi-stage approach ensures the CP4 pump receives the cleanest fuel possible.
By incorporating these advanced filtration strategies, a comprehensive prevention kit effectively protects the CP4 pump from the damaging effects of fuel contaminants, contributing significantly to the engine’s long-term reliability and performance. The investment in enhanced filtration offers a significant return by preventing costly pump failures and associated downtime.
2. Lift Pump Support
Lift pump support is integral to a comprehensive CP4 disaster prevention strategy for 6.7 Powerstroke engines. The CP4 high-pressure fuel pump, while capable of impressive pressure generation, can be susceptible to damage if subjected to certain operating conditions. A lift pump addresses these vulnerabilities by providing a consistent and regulated fuel supply.
- Preventing Cavitation:
Cavitation, the formation of vapor bubbles within the fuel due to low pressure, can erode internal pump components. A lift pump maintains positive fuel pressure at the CP4 pump inlet, minimizing the risk of cavitation. This consistent pressure prevents the damaging implosion of these vapor bubbles against the pump’s delicate internal parts.
- Reducing CP4 Pump Strain:
The CP4 pump operates under extreme pressure. Drawing fuel from the tank adds to its workload. A lift pump pre-pressurizes the fuel, reducing the strain on the CP4 pump and extending its operational life. This allows the CP4 pump to focus solely on generating high pressure for injection, rather than also having to pull fuel from the tank.
- Improved Cold Weather Performance:
In cold temperatures, fuel can become more viscous, increasing the load on the CP4 pump. A lift pump helps overcome this increased viscosity by ensuring a consistent fuel supply, improving cold-start performance and minimizing wear during cold weather operation.
- Facilitating Enhanced Filtration:
Many enhanced filtration systems, crucial for CP4 protection, benefit from the consistent fuel pressure provided by a lift pump. This consistent flow rate allows the filters to operate within their optimal range, maximizing their effectiveness in removing harmful contaminants.
By mitigating cavitation, reducing strain on the CP4 pump, improving cold weather performance, and facilitating enhanced filtration, lift pump support forms a cornerstone of CP4 disaster prevention. This proactive measure significantly improves the reliability and longevity of the 6.7 Powerstroke fuel system, preventing costly repairs and ensuring consistent engine performance.
3. Lubricity Additives
Lubricity additives play a vital role in protecting the CP4 high-pressure fuel pump within a 6.7 Powerstroke engine. These pumps operate under extremely high pressures and rely on the fuel itself for lubrication. Modern diesel fuels, particularly ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD), often lack sufficient lubricity to adequately protect these intricate pump mechanisms. This deficiency can lead to accelerated wear, metal-on-metal contact, and ultimately, catastrophic pump failure. Lubricity additives supplement the fuel’s lubricating properties, reducing friction and wear within the CP4 pump. This added lubrication forms a protective film between critical components, mitigating the risk of scoring, galling, and seizures, significantly extending the pump’s lifespan.
Consider a scenario where two identical 6.7 Powerstroke engines operate under similar conditions. One utilizes fuel treated with a lubricity additive, while the other operates on ULSD alone. Over time, the engine without the additive experiences significantly greater wear within the CP4 pump due to the fuel’s reduced lubricating properties. This increased wear can manifest as decreased fuel pressure, rough running, and ultimately, complete pump failure. The engine utilizing the lubricity additive, however, maintains adequate lubrication, reducing wear and extending the CP4 pump’s operational life considerably. This example illustrates the direct impact of lubricity additives on CP4 pump longevity and the importance of including them in a comprehensive prevention strategy.
The practical significance of understanding the role of lubricity additives is substantial. By incorporating these additives into a 6.7 Powerstroke maintenance regimen, owners can proactively protect their CP4 pumps from premature failure, avoiding costly repairs and extended downtime. While enhanced filtration and lift pump support are crucial components of a comprehensive prevention kit, lubricity additives address the fundamental issue of inadequate fuel lubrication, providing a vital layer of protection for this critical and often vulnerable component. Therefore, selecting and using an appropriate lubricity additive is essential for preserving the long-term health and reliability of the 6.7 Powerstroke fuel system.
4. Water Separation
Water contamination in fuel poses a significant threat to the CP4 high-pressure fuel pump in 6.7 Powerstroke engines. This pump, operating under immense pressure, is highly susceptible to corrosion and damage caused by free water in the fuel system. Water, unlike diesel fuel, is essentially non-compressible. When introduced into the high-pressure environment of the CP4 pump, it can lead to metal fatigue, erosion, and ultimately, catastrophic failure. Effective water separation is, therefore, a critical aspect of a comprehensive prevention kit.
Water can enter the fuel system through various means, including condensation within the fuel tank, contaminated fuel at the pump, and even through microscopic breaches in fuel lines. While seemingly insignificant, even small amounts of water can accumulate over time and cause substantial damage. Consider a scenario where a vehicle regularly refuels at a station with poorly maintained storage tanks. Over time, small amounts of water ingested with each fill-up accumulate within the vehicle’s fuel system. Without adequate water separation, this accumulated water gradually corrodes internal components of the CP4 pump, eventually leading to premature failure. Conversely, a vehicle equipped with an effective water separator removes this water from the fuel before it reaches the pump, preventing corrosion and extending the pump’s lifespan. This illustrates the practical importance of water separation in protecting the CP4 pump.
Effective water separation relies on multiple strategies. Fuel filters often incorporate coalescing media that encourages small water droplets to merge into larger drops, which then fall into a collection bowl within the filter housing. Regular draining of this water separator is essential for optimal performance. Additionally, some prevention kits include dedicated water separator units positioned strategically within the fuel system to maximize water removal efficiency. The strategic implementation of these separation methods prevents water-induced damage, ensuring the long-term reliability and performance of the CP4 pump. Understanding the critical role of water separation empowers owners to take proactive steps to protect their investment and avoid costly repairs associated with water-related pump failures.
5. Monitoring Fuel Pressure
Monitoring fuel pressure is a critical diagnostic tool for preventing catastrophic failure of the CP4 high-pressure fuel pump in 6.7 Powerstroke engines. Fuel pressure readings offer valuable insights into the health and performance of the entire fuel system, enabling proactive identification of potential issues before they escalate into costly repairs. A drop in fuel pressure can indicate various problems, including a failing lift pump, clogged filters, or even the initial stages of CP4 pump degradation. By regularly monitoring fuel pressure, potential problems can be addressed early, preventing further damage and extending the life of the CP4 pump.
Consider a scenario where a vehicle’s lift pump begins to fail. This failure might initially manifest as a slight, intermittent drop in fuel pressure, often unnoticed during regular driving. However, continuous monitoring, especially under load, reveals this subtle pressure fluctuation. Addressing the failing lift pump at this early stage prevents the CP4 pump from being subjected to the damaging effects of inadequate fuel supply, thus averting a much more expensive repair. Conversely, ignoring these early warning signs could lead to complete lift pump failure, placing significant strain on the CP4 pump and potentially leading to its catastrophic failure. This example highlights the direct correlation between monitoring fuel pressure and preventing costly CP4 pump repairs.
Integrating fuel pressure monitoring into a preventative maintenance plan offers significant practical benefits. Analog gauges, digital displays, and even onboard diagnostic systems provide readily accessible data. Establishing a baseline fuel pressure reading under normal operating conditions allows for easy identification of deviations from the norm. Regularly recording these readings, particularly during towing or heavy loads, provides a valuable historical record for tracking fuel system performance. This proactive approach empowers owners to address potential issues early, minimizing downtime and maximizing the life of the CP4 pump. Understanding the critical role of fuel pressure monitoring provides a crucial advantage in protecting the 6.7 Powerstroke engine from costly fuel system failures.
6. Fuel System Hygiene
Maintaining meticulous fuel system hygiene is paramount in preventing CP4 high-pressure fuel pump failures in 6.7 Powerstroke engines. Contaminants, even microscopic particles, can wreak havoc within the precisely engineered tolerances of this critical component. Fuel system hygiene encompasses a range of practices designed to minimize the presence and impact of these contaminants, complementing other preventative measures like enhanced filtration and lift pump support. Neglecting fuel system hygiene renders other preventative measures less effective, increasing the risk of costly pump failure.
Consider a scenario where a vehicle receives regular fuel filter changes and utilizes a high-quality lift pump, yet the fuel tank remains contaminated with rust, debris, or microbial growth. These contaminants, despite the presence of other preventative measures, can still enter the fuel lines and reach the CP4 pump, causing accelerated wear and potential failure. Conversely, a vehicle with a meticulously maintained fuel system, including a clean tank and contaminant-free fuel lines, benefits from enhanced protection against CP4 pump failure. Regularly inspecting and cleaning the fuel tank, replacing fuel lines as needed, and using quality fuel additives to prevent microbial growth are all essential aspects of maintaining optimal fuel system hygiene. This proactive approach minimizes the introduction of contaminants into the high-pressure fuel pump, further enhancing the effectiveness of other preventative measures like filtration and lift pumps.
The practical significance of fuel system hygiene lies in its ability to minimize the risk of CP4 pump failure by reducing the presence of harmful contaminants. This proactive maintenance strategy, while often overlooked, plays a crucial role in ensuring the long-term reliability and performance of the 6.7 Powerstroke engine. Integrating fuel system hygiene practices into regular maintenance schedules significantly reduces the likelihood of costly repairs and extended downtime associated with CP4 pump failures. Understanding the critical role of fuel system hygiene, in conjunction with other preventative measures, provides a comprehensive approach to protecting this vital component and ensuring the overall health of the fuel system.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding preventative measures for CP4 high-pressure fuel pump failures in 6.7 Powerstroke engines. Understanding these key aspects is crucial for informed decision-making and proactive maintenance.
Question 1: Why is the CP4 pump considered problematic in 6.7 Powerstroke engines?
The CP4 pump operates at extremely high pressures and is sensitive to fuel contamination and lubricity issues prevalent in modern diesel fuels. This combination of factors makes it susceptible to premature failure.
Question 2: What are the typical symptoms of a failing CP4 pump?
Symptoms may include low fuel pressure, rough engine running, difficulty starting, excessive noise from the fuel system, and the presence of metal shavings in the fuel filter.
Question 3: How much does a CP4 pump replacement typically cost?
Replacement costs can vary significantly, but typically range from $8,000 to $12,000 or more, including parts and labor. This cost often includes replacing other fuel system components damaged by metal debris from the failed pump.
Question 4: Is a disaster prevention kit a guaranteed solution to prevent CP4 failure?
While a prevention kit significantly reduces the risk of failure, it’s not an absolute guarantee. Consistent maintenance, adherence to recommended fuel practices, and regular monitoring remain essential.
Question 5: What is the recommended maintenance schedule for a vehicle with a prevention kit installed?
Maintenance schedules should adhere to the kit manufacturer’s recommendations and may involve more frequent filter changes and additive replenishment compared to factory recommendations.
Question 6: Can a prevention kit be installed on a vehicle that has already experienced CP4 pump issues?
If the pump has already failed, a kit will not repair the damage. However, after pump replacement, installing a kit can protect the new pump from similar failure.
Investing in preventative measures significantly reduces the risk and associated costs of CP4 pump failure, promoting long-term engine reliability. Proactive maintenance is key to protecting this critical component.
For further information regarding specific product recommendations and installation guidance, consult a qualified diesel mechanic or refer to reputable industry resources.
CP4 Disaster Prevention Kit 6.7 Powerstroke
This exploration of preventative measures for 6.7 Powerstroke engines highlights the critical role of the CP4 disaster prevention kit. Enhanced filtration, lift pump support, lubricity additives, water separation, fuel pressure monitoring, and meticulous fuel system hygiene all contribute significantly to mitigating the risk of catastrophic high-pressure fuel pump failure. These preventative strategies work synergistically to protect the CP4 pump from the damaging effects of fuel contamination, inadequate lubrication, and excessive strain, ensuring long-term engine reliability and performance.
The substantial cost associated with CP4 pump failure underscores the importance of proactive investment in preventative measures. While no preventative measure offers an absolute guarantee against failure, implementing a comprehensive strategy significantly reduces the risk and associated financial burden. Protecting this vital component through diligent maintenance and preventative measures ensures uninterrupted operation and safeguards against potentially crippling repair costs. The long-term health and reliability of the 6.7 Powerstroke engine depend on a proactive approach to fuel system maintenance, making the CP4 disaster prevention kit a prudent investment for any owner.