Information concerning recent catastrophic events caused by natural forces, such as earthquakes, floods, wildfires, and volcanic eruptions, plays a vital role in understanding the dynamic relationship between humanity and the environment. For instance, analyzing the aftermath of a specific hurricane can provide insights into building codes, evacuation procedures, and the efficacy of disaster relief efforts.
Staying informed about these occurrences offers numerous benefits, including heightened public awareness, improved disaster preparedness, and informed policy decisions. Historical data reveals trends and patterns in these events, allowing for better prediction models and mitigation strategies. Understanding the past helps shape future responses and enhances community resilience in the face of environmental challenges.
Exploring specific examples of recent natural events, their impact on affected communities, and the ongoing recovery efforts provides a deeper understanding of the complex interplay of environmental factors and human response. This knowledge is crucial for fostering informed decision-making at individual, community, and global levels.
Tips for Staying Informed and Prepared
Maintaining awareness of recent environmental catastrophes and understanding their potential impacts is crucial for individual and community safety. The following tips offer practical guidance for preparedness and informed action.
Tip 1: Reliable Information Sources: Consult official sources like governmental meteorological agencies, geological surveys, and international disaster relief organizations for accurate information. Avoid spreading misinformation from unverified sources.
Tip 2: Early Warning Systems: Familiarize oneself with local early warning systems for various types of disasters. Sign up for relevant alerts and understand evacuation procedures.
Tip 3: Emergency Preparedness Kits: Assemble a comprehensive kit containing essential supplies such as water, non-perishable food, first-aid supplies, and necessary medications.
Tip 4: Communication Plan: Establish a family communication plan to ensure contact during emergencies. Identify meeting points and designate an out-of-area contact.
Tip 5: Insurance Coverage: Review insurance policies to ensure adequate coverage for potential disaster-related damages. Document valuable possessions and property.
Tip 6: Community Involvement: Participate in community disaster preparedness initiatives and volunteer with local organizations. Collective action strengthens community resilience.
By implementing these measures, individuals and communities can significantly enhance their preparedness for natural disasters, mitigate potential impacts, and contribute to a more resilient and informed society.
Understanding the dynamic nature of environmental hazards and adopting proactive strategies are essential for navigating the challenges posed by these events and promoting a safer future.
1. Recent Occurrences
Comprehending the impact of natural disasters necessitates analyzing recent events. These occurrences provide crucial data for understanding emerging trends, evaluating preparedness strategies, and informing future mitigation efforts. Examining specific facets of recent events offers valuable insights into the complex interplay of environmental forces and human response.
- Geographic Distribution
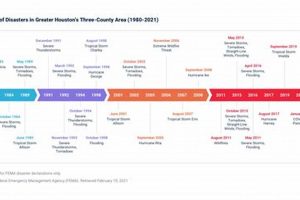
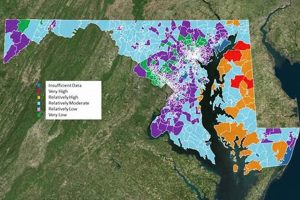
Analyzing the geographic distribution of recent events reveals patterns and potential vulnerabilities. For instance, a concentration of seismic activity along a specific fault line highlights areas requiring enhanced earthquake preparedness. Understanding geographic trends informs resource allocation and infrastructure development decisions.
- Magnitude and Intensity
The magnitude and intensity of recent events offer crucial data for assessing the destructive potential of natural hazards. Comparing the intensity of recent hurricanes, for example, provides insights into the effectiveness of building codes and evacuation procedures. This information is essential for refining safety protocols and strengthening community resilience.
- Environmental Impact
Assessing the environmental impact of recent events is crucial for understanding long-term consequences. Analyzing the effects of wildfires on air quality and deforestation, for example, informs environmental protection policies and restoration efforts. Understanding these impacts contributes to sustainable environmental management.
- Socioeconomic Consequences
Examining the socioeconomic consequences of recent events reveals the multifaceted impact on affected communities. Analyzing the displacement of populations following floods, for example, highlights the need for effective disaster relief and long-term recovery strategies. Understanding these consequences informs policy decisions and resource allocation for community support.
By analyzing these facets of recent occurrences, a more comprehensive understanding of the complexities of natural disasters emerges. This knowledge is crucial for developing effective strategies for disaster preparedness, mitigation, and response, ultimately contributing to safer and more resilient communities.
2. Geographic Location
Geographic location plays a crucial role in understanding the distribution, impact, and frequency of natural disasters. Analyzing spatial patterns of these events reveals underlying geological, meteorological, and environmental factors that contribute to their occurrence. This understanding is essential for effective risk assessment, disaster preparedness, and mitigation strategies.
- Proximity to Tectonic Plates
Areas situated near tectonic plate boundaries experience higher seismic activity, increasing the likelihood of earthquakes and tsunamis. The Ring of Fire, for example, encircles the Pacific Ocean and is known for its high concentration of volcanic and seismic activity. Understanding plate tectonics informs building codes and infrastructure development in these vulnerable regions.
- Coastal Regions and Low-Lying Areas
Coastal communities and low-lying areas face increased vulnerability to hurricanes, storm surges, and flooding. The elevation and topography of coastal areas influence the extent of inundation and damage caused by these events. Analyzing coastal geography informs evacuation plans and coastal defense strategies.
- Arid and Semi-Arid Regions
Regions characterized by arid and semi-arid climates are susceptible to droughts and wildfires. Vegetation type, prevailing wind patterns, and precipitation levels influence the frequency and intensity of these events. Understanding these factors informs land management practices and fire prevention strategies.
- Mountainous Terrain
Mountainous regions are prone to landslides, avalanches, and flash floods. Slope stability, snowpack accumulation, and rainfall intensity influence the occurrence and severity of these events. Analyzing terrain characteristics informs infrastructure development and disaster preparedness in mountainous areas.
Analyzing geographic location in conjunction with historical data and environmental factors provides valuable insights for predicting future events, mitigating potential impacts, and developing effective response strategies. This comprehensive approach enhances community resilience and promotes informed decision-making in the face of natural disasters.
3. Impact Assessment
Impact assessment plays a crucial role in understanding the consequences of natural disasters. Analyzing the effects of these events on both human populations and the environment provides valuable data for informing disaster response, recovery efforts, and future mitigation strategies. This assessment involves evaluating the extent of damage, identifying affected populations, and quantifying economic losses. Understanding the multifaceted impacts of these events is essential for developing effective strategies to minimize future risks and enhance community resilience. For instance, assessing the damage caused by a recent hurricane, including infrastructure destruction, displacement of residents, and economic disruption, informs resource allocation for relief efforts and guides the development of more resilient building codes.
Impact assessments often involve interdisciplinary approaches, incorporating data from various sources, such as satellite imagery, field surveys, and socioeconomic analyses. This comprehensive approach enables a more nuanced understanding of the cascading effects of natural disasters. For example, analyzing the long-term effects of a drought on agricultural production, water resources, and human health provides valuable insights for developing sustainable resource management strategies and drought mitigation plans. The practical significance of this understanding lies in its ability to inform policy decisions, guide resource allocation, and enhance community preparedness, ultimately contributing to more resilient societies.
In conclusion, impact assessment provides a crucial framework for understanding the complex interplay between natural disasters and human societies. By systematically analyzing the effects of these events, valuable insights can be gained to inform effective disaster response, promote sustainable recovery, and enhance community resilience in the face of future hazards. Addressing the challenges associated with accurate and timely impact assessment, such as data availability and logistical constraints, remains crucial for improving disaster management and minimizing the human and economic costs of these events.
4. Response Efforts
Effective response efforts are crucial in mitigating the impact of natural disasters. Analyzing these efforts in the context of current events provides valuable insights for improving disaster management strategies, enhancing community resilience, and minimizing human suffering. Understanding the complexities and challenges associated with disaster response is essential for developing more effective and coordinated approaches. Examining key facets of response efforts illuminates their critical role in addressing the immediate and long-term consequences of natural disasters.
- Immediate Relief
Providing immediate relief to affected populations is paramount in the aftermath of a natural disaster. This includes providing essential resources such as food, water, shelter, and medical assistance. For example, following an earthquake, search and rescue teams are deployed to locate and extract survivors trapped under rubble, while medical personnel establish triage centers to provide emergency care. The effectiveness of immediate relief efforts often depends on pre-existing disaster preparedness plans and the coordination between various agencies.
- Infrastructure Restoration
Restoring critical infrastructure, such as transportation networks, communication systems, and power grids, is essential for facilitating recovery efforts. Following a hurricane, for instance, restoring road access enables the delivery of aid and the evacuation of affected communities. The speed and efficiency of infrastructure restoration significantly impact the long-term recovery process and the ability of communities to rebuild.
- Community Support and Displacement Management
Natural disasters often lead to displacement of populations, requiring effective management of temporary shelters and provision of psychosocial support. Following a flood, for example, establishing temporary housing and providing counseling services helps address the immediate needs of displaced communities. Addressing the long-term needs of displaced populations, including access to housing, employment, and education, is crucial for successful community recovery.
- Long-Term Recovery and Reconstruction
Long-term recovery and reconstruction involve rebuilding damaged infrastructure, restoring economic activity, and implementing measures to enhance community resilience. Following a wildfire, for instance, rebuilding homes, restoring businesses, and implementing fire prevention measures contribute to long-term recovery. The effectiveness of these efforts depends on factors such as access to funding, community participation, and the integration of disaster risk reduction strategies.
Analyzing these facets of response efforts within the context of current events about natural disasters provides a comprehensive understanding of the challenges and opportunities associated with disaster management. By examining the successes and shortcomings of past responses, valuable lessons can be learned to improve future strategies, enhance community resilience, and minimize the human and economic costs of natural disasters. Moreover, understanding the evolving nature of disaster risks, influenced by factors such as climate change and urbanization, necessitates continuous adaptation and innovation in response efforts to effectively address the challenges posed by future events.
5. Scientific Analysis
Scientific analysis provides crucial insights into the underlying causes, mechanisms, and consequences of natural disasters. Examining current events through a scientific lens enhances understanding of these complex phenomena, informing disaster preparedness, mitigation strategies, and response efforts. Analyzing seismic data following an earthquake, for example, helps determine the earthquake’s epicenter, magnitude, and depth, which are crucial for assessing the extent of damage and guiding rescue operations. Similarly, analyzing meteorological data during a hurricane helps predict its trajectory, intensity, and potential impact, enabling timely evacuations and resource allocation.
The importance of scientific analysis as a component of understanding current events about natural disasters is underscored by its ability to establish cause-and-effect relationships. For instance, analyzing geological data can reveal the underlying causes of landslides, such as unstable slopes or excessive rainfall, informing land-use planning and mitigation measures. Furthermore, scientific analysis contributes to the development of predictive models, enabling more accurate forecasting of future events. Analyzing historical weather patterns and climate data, for example, can improve the accuracy of hurricane forecasts, allowing communities to prepare more effectively. The practical significance of this understanding lies in its capacity to inform policy decisions, guide resource allocation, and ultimately save lives and property.
In conclusion, scientific analysis provides a crucial framework for understanding the complexities of natural disasters. By applying scientific methods to analyze current events, valuable insights can be gained into the causes, impacts, and potential future occurrences of these events. Addressing the challenges associated with data collection, analysis, and dissemination of scientific information remains crucial for improving disaster preparedness, mitigation, and response. Continued investment in scientific research and technological advancements will further enhance the ability to predict, prepare for, and mitigate the impacts of natural disasters, contributing to more resilient communities and a safer future.
6. Community Resilience
Community resilience plays a vital role in mitigating the impacts of natural disasters. Examining current events reveals a direct correlation between resilient communities and their capacity to withstand, adapt to, and recover from these events. The ability of a community to effectively prepare for, respond to, and recover from a disaster significantly influences the extent of damage, displacement, and long-term consequences. For instance, communities with established early warning systems, evacuation plans, and robust social networks often experience fewer casualties and recover more quickly following a disaster compared to communities lacking such preparedness measures.
The importance of community resilience as a component of understanding current events about natural disasters is underscored by its capacity to minimize human suffering and economic losses. Communities with strong social cohesion, effective communication networks, and access to resources are better equipped to cope with the challenges posed by disasters. For example, following a hurricane, a community with a well-organized volunteer network can quickly mobilize resources, provide support to affected individuals, and facilitate the recovery process. Furthermore, resilient communities are more likely to adopt mitigation measures, such as building codes and land-use planning, that reduce their vulnerability to future disasters. The practical significance of this understanding lies in its potential to inform policy decisions, guide resource allocation, and promote community-based disaster preparedness initiatives. Investing in community resilience building activities, such as disaster drills, public awareness campaigns, and the development of local emergency plans, can significantly enhance a community’s ability to withstand and recover from future events.
In conclusion, community resilience is an essential factor in mitigating the impacts of natural disasters. Analyzing current events reveals the crucial role that resilient communities play in minimizing human suffering, economic losses, and long-term disruption. Addressing the challenges associated with building and sustaining community resilience, such as limited resources, social inequalities, and environmental vulnerabilities, remains crucial for enhancing disaster preparedness and promoting sustainable recovery. By prioritizing community-based approaches to disaster management, fostering collaboration among stakeholders, and integrating resilience-building strategies into development planning, societies can significantly enhance their capacity to withstand and recover from the increasing frequency and intensity of natural disasters.
7. Future Mitigation
Analysis of current events surrounding natural disasters informs future mitigation strategies. Understanding the causes, impacts, and responses to recent events provides valuable insights for developing more effective measures to reduce vulnerability and enhance resilience. Examining these events through a mitigation lens highlights the crucial role of proactive planning, infrastructure development, and community engagement in minimizing the impact of future disasters. This proactive approach is essential for creating safer and more sustainable communities in the face of increasing environmental challenges.
- Infrastructure Development
Investing in resilient infrastructure is crucial for mitigating the impact of future disasters. Current events demonstrate the vulnerability of critical infrastructure, such as transportation networks, communication systems, and power grids, to natural hazards. For example, the devastation caused by recent hurricanes underscores the need for stronger building codes, elevated roadways, and reinforced power lines. Incorporating disaster-resistant design principles into infrastructure development enhances community resilience and minimizes disruption in the aftermath of future events. For instance, constructing buildings with reinforced concrete and deep foundations can significantly reduce damage from earthquakes, while designing bridges to withstand high wind speeds mitigates the impact of hurricanes. This proactive approach to infrastructure development minimizes economic losses, protects lives, and ensures the functionality of essential services following a disaster.
- Land-Use Planning and Zoning
Effective land-use planning and zoning regulations play a crucial role in minimizing vulnerability to natural hazards. Analyzing current events, such as floods and landslides, reveals the importance of avoiding development in high-risk areas. For example, restricting construction in floodplains or on unstable slopes reduces the likelihood of property damage and loss of life. Implementing smart growth principles, such as promoting higher-density development in safer areas and preserving natural buffers, enhances community resilience and minimizes exposure to natural hazards. Furthermore, incorporating green infrastructure solutions, such as permeable pavements and green roofs, can mitigate the impact of flooding and reduce urban heat island effects. This proactive approach to land-use planning safeguards communities from future disasters and promotes sustainable development practices.
- Early Warning Systems and Evacuation Planning
Robust early warning systems and effective evacuation plans are essential for minimizing casualties and facilitating timely responses to natural disasters. Current events highlight the importance of disseminating timely and accurate information to at-risk populations. For example, the effectiveness of tsunami warning systems in saving lives during recent tsunamis underscores the value of investing in advanced monitoring technologies and public awareness campaigns. Furthermore, developing comprehensive evacuation plans, including designated evacuation routes, shelters, and transportation resources, ensures the safe and efficient movement of people away from danger zones. Regularly testing and updating these plans, incorporating lessons learned from recent events, enhances community preparedness and minimizes the impact of future disasters.
- Community Education and Engagement
Empowering communities through education and engagement is crucial for fostering a culture of preparedness and resilience. Current events demonstrate the vital role of community participation in disaster response and recovery. For example, communities with active volunteer networks, established communication channels, and disaster preparedness training programs often experience faster recovery times and fewer casualties. Promoting public awareness about disaster risks, providing training on emergency procedures, and establishing community emergency response teams strengthens community resilience and empowers individuals to take proactive measures to protect themselves and their families. This collaborative approach to disaster preparedness fosters a sense of shared responsibility and enhances community-level capacity to cope with future events.
By integrating these facets of future mitigation into disaster management strategies, communities can significantly reduce their vulnerability to natural hazards. Analyzing current events provides valuable lessons for refining mitigation approaches, improving infrastructure design, and enhancing community preparedness. This proactive approach is essential for building resilient communities, minimizing the impact of future disasters, and creating a safer and more sustainable future in the face of evolving environmental challenges. Moreover, continued investment in research, technological advancements, and international collaboration is crucial for developing innovative mitigation strategies and enhancing global capacity to address the increasing complexities of natural disasters.
Frequently Asked Questions about Current Natural Disaster Events
This section addresses common inquiries regarding recent natural disasters, providing concise and informative responses based on scientific understanding and established data.
Question 1: How does climate change influence the frequency and intensity of natural disasters?
Scientific evidence suggests a strong link between climate change and the increasing frequency and intensity of certain natural disasters. Rising global temperatures contribute to more intense heatwaves, droughts, and wildfires. Warmer ocean temperatures fuel stronger hurricanes and typhoons. Changes in precipitation patterns can lead to more frequent and severe floods in some regions and prolonged droughts in others. While not every natural disaster can be directly attributed to climate change, the observed trends indicate a significant influence on the overall pattern and severity of these events.
Question 2: What are the most effective strategies for mitigating the impact of natural disasters?
Effective mitigation strategies encompass a range of approaches, from infrastructure improvements to community-based preparedness programs. Investing in resilient infrastructure, such as reinforced buildings and flood defenses, can significantly reduce the physical damage caused by disasters. Land-use planning and zoning regulations can restrict development in high-risk areas, minimizing exposure to hazards. Early warning systems, coupled with effective evacuation plans, are crucial for saving lives. Community education and engagement empower individuals to take proactive measures to protect themselves and their families.
Question 3: How can individuals contribute to disaster preparedness and response?
Individual preparedness plays a vital role in minimizing personal risk and supporting community resilience. Developing a family emergency plan, including communication protocols and evacuation routes, ensures coordinated action during a disaster. Assembling an emergency supply kit with essential items such as food, water, and first-aid supplies provides immediate resources in the aftermath of an event. Participating in community-based disaster preparedness programs, such as volunteer training and drills, strengthens collective response capabilities. Staying informed about potential hazards and heeding official warnings are crucial for individual safety.
Question 4: What are the long-term consequences of natural disasters on affected communities?
Natural disasters can have profound long-term consequences on affected communities, extending beyond immediate physical damage. Economic disruption, displacement of populations, and psychological trauma can persist for years following an event. Loss of livelihoods, damage to infrastructure, and disruption of essential services impede recovery efforts. Displacement can lead to social and economic instability, requiring long-term support for affected families. Psychological trauma, including post-traumatic stress disorder, can have lasting effects on individuals and communities. Addressing these long-term consequences requires comprehensive recovery plans, including economic assistance, psychosocial support, and community rebuilding initiatives.
Question 5: How can technology improve disaster prediction and response?
Technological advancements play an increasingly important role in enhancing disaster prediction, monitoring, and response. Advanced sensors, satellite imagery, and sophisticated modeling tools provide more accurate and timely information about impending hazards. Real-time monitoring of seismic activity, weather patterns, and environmental conditions enables early warning systems to issue timely alerts. Mobile technologies facilitate communication and information sharing during emergencies, connecting affected communities with relief organizations and providing access to critical information. Data analytics and machine learning algorithms can process vast amounts of information to identify patterns, predict future events, and optimize resource allocation for response efforts.
Question 6: What are the challenges associated with accurately predicting natural disasters?
Accurately predicting natural disasters remains a significant challenge due to the complex and often unpredictable nature of these events. While scientific understanding of geophysical and meteorological processes has advanced considerably, predicting the precise timing, location, and magnitude of events remains difficult. Factors such as the chaotic nature of weather systems, the complex interactions between tectonic plates, and the influence of human activities on the environment contribute to the inherent uncertainty in disaster prediction. Despite these challenges, ongoing research and technological advancements continue to improve forecasting capabilities, providing valuable time for preparedness and response efforts.
Understanding the complexities of natural disasters requires continuous learning and adaptation. Staying informed about current events, scientific advancements, and best practices for preparedness and mitigation empowers individuals, communities, and nations to effectively address the challenges posed by these events.
Further exploration of specific disaster types and regional vulnerabilities provides a deeper understanding of the diverse challenges and opportunities associated with building a more resilient and sustainable future.
Conclusion
Exploration of current events surrounding natural disasters reveals the complex interplay of environmental forces, human vulnerability, and societal response. Analysis of recent occurrences, geographic influences, impact assessments, and response strategies provides crucial insights for enhancing preparedness and mitigation efforts. Scientific advancements in understanding these phenomena contribute to improved prediction models and risk assessments. Furthermore, examination of community resilience highlights the critical role of social cohesion, preparedness planning, and effective communication in minimizing the impact of disasters.
The increasing frequency and intensity of natural disasters underscore the urgent need for proactive measures to mitigate risks and enhance resilience. Continued investment in scientific research, infrastructure development, community engagement, and international collaboration is essential for navigating the challenges posed by these events. Understanding the dynamic nature of natural hazards and embracing proactive strategies are paramount for building a safer and more sustainable future for all.