Ghana’s principal agency for disaster preparedness, mitigation, response, and recovery is a governmental body responsible for coordinating efforts to protect lives and property from natural and human-induced hazards. This agency develops and implements national disaster management policies, conducts risk assessments, provides training and public education, and mobilizes resources during emergencies, collaborating with various stakeholders, including international organizations and local communities.
Effective disaster management is crucial for safeguarding Ghana’s development gains and reducing the socio-economic impact of disasters. By investing in proactive measures and building national resilience, the agency contributes to sustainable development and the well-being of the populace. The organizations history reflects the nation’s growing understanding of disaster risks and its commitment to strengthening capacities for effective disaster response. From initial frameworks to the establishment of a comprehensive institutional structure, the evolution of disaster management in Ghana underscores its ongoing importance.
This understanding of the institutions role provides a foundation for exploring its specific functions, recent activities, and future challenges. Further examination will delve into specific programs, community engagement strategies, and the crucial role of collaboration in enhancing national disaster preparedness and resilience.
Disaster Preparedness Tips
Preparedness is crucial for minimizing the impact of disasters. These tips offer practical advice for enhancing personal and community safety.
Tip 1: Develop a Household Emergency Plan: A well-defined plan, including evacuation routes, communication protocols, and designated meeting points, ensures coordinated action during emergencies. Families should practice the plan regularly.
Tip 2: Assemble an Emergency Kit: Essential supplies such as water, non-perishable food, first-aid supplies, a flashlight, and a radio should be readily accessible. Kits should be customized to address specific needs, including medications and infant care items.
Tip 3: Secure Homes and Properties: Reinforcing roofs, trimming overhanging branches, and securing loose objects can mitigate damage from strong winds and flooding. Regular property maintenance enhances resilience.
Tip 4: Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and heed official warnings from relevant authorities. Understanding potential hazards allows for timely precautionary measures.
Tip 5: Learn Basic First Aid and CPR: These skills can prove invaluable in providing immediate assistance to injured individuals before professional help arrives. Local organizations often offer training courses.
Tip 6: Participate in Community Drills: Engaging in community-level emergency exercises helps familiarize individuals with evacuation procedures and promotes collaborative responses.
Tip 7: Educate Others: Sharing disaster preparedness information with family, friends, and neighbors strengthens community resilience as a whole. Disseminating knowledge empowers collective action.
Proactive measures significantly increase the likelihood of a positive outcome during a disaster. By adopting these practices, individuals contribute to their safety and the well-being of their communities.
Taking these steps provides a solid foundation for navigating emergencies effectively. Further information and resources can be accessed through official channels to bolster disaster preparedness efforts.
1. Mitigation
Mitigation constitutes a cornerstone of Ghana’s national disaster management strategy. It represents the proactive efforts undertaken to reduce or eliminate the risks and impacts of disasters before they occur. This proactive approach not only minimizes potential losses of life and property but also contributes to long-term sustainable development by addressing underlying vulnerabilities. The organization recognizes that investing in mitigation measures is significantly more cost-effective than responding to disasters after they strike. For example, implementing robust building codes in earthquake-prone areas, constructing flood defenses in vulnerable communities, and establishing early warning systems for floods and droughts are all examples of mitigation measures that can significantly reduce the impact of future events. These initiatives often involve partnerships with local communities, international organizations, and research institutions to leverage expertise and resources.
The effectiveness of mitigation relies heavily on accurate risk assessments, data analysis, and community engagement. Understanding the specific hazards a region faces, combined with knowledge of local vulnerabilities, allows for the development of targeted and impactful mitigation strategies. For example, promoting sustainable land management practices can mitigate the risks of landslides, while public awareness campaigns can educate communities about fire safety and prevention. By empowering communities with knowledge and resources, the organization fosters a culture of preparedness and resilience, contributing to a safer and more sustainable future. Regular reviews and updates of mitigation strategies are essential to ensure they remain relevant and effective in the face of changing environmental conditions and societal needs.
In conclusion, mitigation plays a pivotal role within Ghana’s overarching disaster management framework. By prioritizing proactive measures to reduce risk and vulnerability, the nation strengthens its resilience against future disasters. This strategic focus not only protects lives and livelihoods but also fosters sustainable development and economic growth by minimizing disruptions and facilitating quicker recovery in the event of unforeseen calamities. The ongoing commitment to refining and implementing effective mitigation strategies reflects the organization’s dedication to safeguarding Ghana’s future.
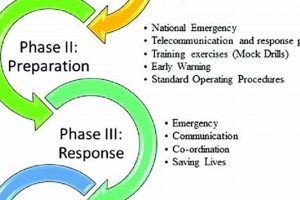
2. Preparedness
Preparedness forms a critical pillar within the mandate of Ghana’s national disaster management organization. It represents the proactive planning and resource allocation undertaken to anticipate and effectively respond to disasters. This proactive stance recognizes that preemptive measures significantly reduce the human and economic costs associated with disaster events. Preparedness encompasses a range of activities, including the development of comprehensive disaster preparedness plans, the establishment of early warning systems, the stockpiling of essential supplies, and the training of personnel and communities in disaster response procedures. For example, conducting regular simulation exercises allows communities to practice evacuation procedures and refine response protocols, ensuring a more coordinated and effective response in the event of a real disaster. Investments in robust communication infrastructure ensure timely dissemination of warnings and facilitate information sharing during emergencies. The effectiveness of preparedness hinges on continuous assessment, adaptation, and community engagement.
A well-prepared nation is better equipped to manage the immediate impacts of a disaster and to transition more smoothly into recovery. Preparedness reduces the strain on resources during a crisis, allowing for a more targeted and efficient allocation of aid. For instance, pre-positioned emergency supplies can provide immediate relief to affected populations, while trained first responders can quickly deploy to provide medical assistance and search and rescue operations. Moreover, preparedness fosters a culture of resilience within communities, empowering individuals with the knowledge and skills to protect themselves and their families during emergencies. This proactive approach not only mitigates immediate impacts but also lays the groundwork for a faster and more sustainable recovery process. By minimizing disruption to essential services and infrastructure, preparedness contributes to long-term economic stability and social well-being.
In conclusion, preparedness stands as a crucial component of effective disaster management in Ghana. By prioritizing proactive planning, resource allocation, and community engagement, the nation enhances its ability to respond effectively to disasters, minimize their impact, and facilitate a swift and sustainable recovery. Challenges may include resource constraints, evolving disaster risks, and ensuring equitable access to preparedness measures across all communities. Addressing these challenges requires ongoing investment, innovation, and collaboration among all stakeholders to build a more resilient nation. The organization’s dedication to strengthening preparedness underscores its commitment to safeguarding lives, livelihoods, and the nation’s future.
3. Response
Response, within the context of Ghana’s national disaster management framework, signifies the immediate actions taken to protect lives, minimize damage, and address the urgent needs of affected populations during and immediately after a disaster. This encompasses a wide range of activities, from search and rescue operations and the provision of emergency medical assistance to the establishment of temporary shelters and the distribution of essential supplies like food, water, and blankets. Effective response hinges on pre-existing preparedness measures, including established communication protocols, trained personnel, and pre-positioned resources. For instance, following the 2015 Accra floods, the organization coordinated rescue efforts, provided relief to displaced communities, and facilitated damage assessments to inform recovery efforts. The speed and efficiency of the response are critical in mitigating the immediate impacts of a disaster and setting the stage for long-term recovery.
The organization’s response mechanisms operate at multiple levels, from national coordination to localized community action. This multi-tiered approach allows for a targeted and context-specific response, recognizing that disaster impacts vary across different regions and communities. Collaboration with international partners, non-governmental organizations, and local communities strengthens the overall response capacity. For example, international partnerships can provide access to specialized expertise and resources, while local community involvement ensures that relief efforts are tailored to specific needs and cultural sensitivities. The organization’s response strategy also emphasizes continuous improvement, incorporating lessons learned from past events to enhance future performance. Regular reviews of response protocols, training programs, and communication systems ensure that the organization remains prepared to address evolving disaster risks and challenges.
In conclusion, response represents a critical phase of disaster management in Ghana. A well-coordinated and timely response can significantly reduce casualties, alleviate suffering, and lay the foundation for a more effective recovery process. Challenges may include limited resources, logistical complexities, and the need for adaptable response strategies in the face of unpredictable disaster events. Addressing these challenges necessitates ongoing investment in training, infrastructure, and technology, as well as strengthening partnerships and community engagement. The organization’s commitment to enhancing its response capabilities underscores its dedication to protecting lives and building a more resilient nation.
4. Recovery
Recovery, a crucial phase overseen by Ghana’s national disaster management organization, encompasses the long-term process of rebuilding communities and restoring normalcy after a disaster. This phase extends beyond immediate relief efforts, focusing on restoring infrastructure, revitalizing the economy, and providing psychosocial support to affected populations. Recovery efforts are multifaceted, involving the reconstruction of homes and public buildings, the rehabilitation of agricultural lands, the restoration of essential services like healthcare and education, and the provision of economic assistance to businesses and individuals. For instance, after the 2007 floods in the Northern Region, the organization played a key role in coordinating the reconstruction of damaged infrastructure, providing support for agricultural recovery, and implementing programs to enhance community resilience against future floods. Successful recovery requires a holistic approach, addressing both the physical and psychosocial needs of affected communities. This involves not just rebuilding physical structures but also addressing the emotional and psychological impacts of the disaster, promoting community cohesion, and fostering a sense of hope for the future.
The organization’s approach to recovery emphasizes community participation and ownership. Recognizing that sustainable recovery requires the active involvement of affected communities, the organization works closely with local leaders, community organizations, and individuals to ensure that recovery efforts are aligned with local needs and priorities. This participatory approach not only fosters a sense of ownership and empowerment but also ensures that recovery efforts are culturally sensitive and sustainable in the long term. For example, community-based recovery programs might involve training local residents in construction skills, providing micro-finance opportunities to support small businesses, and establishing community-managed early warning systems. By investing in local capacity building, the organization strengthens community resilience and reduces vulnerability to future disasters. Effective recovery also requires close coordination with various stakeholders, including government agencies, non-governmental organizations, international partners, and the private sector. This collaborative approach ensures that resources are effectively mobilized and deployed, avoiding duplication of efforts and maximizing impact.
In conclusion, recovery constitutes a complex and long-term undertaking that is essential for restoring normalcy and building back better after a disaster. Challenges may include securing adequate funding, coordinating diverse stakeholders, addressing the long-term psychosocial impacts of disasters, and ensuring equitable access to recovery resources. The organization’s commitment to community-driven recovery, coupled with its focus on building back better, reflects its dedication to not just restoring what was lost but also creating more resilient communities that are better prepared for future challenges. Ongoing evaluation and adaptation of recovery strategies are essential to ensuring that lessons learned from past disasters are incorporated into future recovery efforts, further strengthening Ghana’s capacity to manage and recover from disaster events effectively.
5. Coordination
Effective disaster management hinges on seamless coordination. For Ghana’s national disaster management body, coordination is not merely a supporting function, but rather the central mechanism that integrates all aspects of disaster risk reduction and response. It ensures that diverse stakeholders, each with specific roles and expertise, work together harmoniously towards a common goal: minimizing the human and economic costs of disasters. This intricate process involves establishing clear communication channels, defining roles and responsibilities, and facilitating information sharing among various actors.
- Inter-Agency Collaboration:
Coordination facilitates collaboration among various government agencies, ensuring a unified and efficient response. For example, during flood events, the meteorological agency provides critical weather data, while the Ministry of Health coordinates medical response, and the Ministry of Works and Housing addresses infrastructure damage. This synergy prevents duplication of effort and maximizes the impact of interventions.
- Community Engagement:
Coordination extends to engaging local communities, recognizing their crucial role in effective disaster preparedness and response. Local knowledge, combined with community-based early warning systems, enhances the timeliness and effectiveness of response efforts. Community participation ensures that relief and recovery initiatives are tailored to specific needs and cultural contexts.
- International Partnerships:
Coordination facilitates collaboration with international organizations, providing access to technical expertise, financial resources, and best practices. Partnerships with organizations like the United Nations and international NGOs enhance capacity building, support the development of early warning systems, and facilitate knowledge sharing, strengthening national disaster management capabilities.
- Information Management:
Effective coordination relies on robust information management systems. Real-time data sharing, accurate damage assessments, and timely dissemination of information to relevant stakeholders ensure informed decision-making and facilitate a coordinated response. This includes using technology and established communication protocols to streamline information flow during emergencies.
These facets of coordination are integral to the success of Ghana’s disaster management framework. By fostering collaboration, leveraging diverse expertise, and ensuring efficient resource allocation, coordination enhances the nation’s capacity to prepare for, respond to, and recover from disasters. Strengthening coordination mechanisms, particularly through enhanced communication systems, capacity building initiatives, and community engagement strategies, remains a continuous priority for building a more resilient nation. This ongoing focus underscores the importance of a coordinated approach in mitigating the impact of disasters and safeguarding the well-being of communities across Ghana.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding disaster preparedness and the role of Ghana’s disaster management agency. Understanding these key aspects empowers individuals and communities to contribute to national resilience.
Question 1: How can individuals contribute to national disaster preparedness?
Individual contributions are crucial. Developing household emergency plans, assembling emergency kits, and participating in community drills significantly enhance preparedness. Staying informed about potential hazards and educating others about disaster safety further strengthen community resilience.
Question 2: What is the role of the agency in disaster recovery?
The agency coordinates long-term recovery efforts, focusing on restoring infrastructure, revitalizing the economy, and providing psychosocial support. This involves collaboration with various stakeholders to ensure effective resource allocation and community participation in rebuilding efforts.
Question 3: How does the agency address the specific needs of vulnerable populations during disasters?
Recognizing the heightened vulnerability of certain groups, targeted interventions address specific needs. This may involve providing accessible evacuation support for persons with disabilities, prioritizing shelter allocation for displaced families, and offering specialized medical care for the elderly and infants.
Question 4: How does the agency collaborate with international organizations?
International partnerships provide access to technical expertise, financial resources, and best practices. These collaborations enhance capacity building, support early warning system development, and facilitate knowledge sharing to strengthen national disaster management capabilities.
Question 5: What measures are in place to mitigate the impact of climate change on disaster risks?
Recognizing the increasing impact of climate change, strategies focus on climate change adaptation and mitigation. This includes promoting sustainable land management practices, developing climate-resilient infrastructure, and integrating climate change considerations into disaster risk assessments and preparedness plans.
Question 6: How can the public access early warnings and disaster-related information?
The agency utilizes multiple channels to disseminate early warnings and critical information. This includes SMS alerts, radio broadcasts, social media platforms, and community-based warning systems to ensure timely and accessible communication during emergencies.
Proactive engagement with disaster preparedness and response mechanisms contributes significantly to national resilience. Accessing further resources and information through official channels strengthens individual and community preparedness efforts.
Further exploration of specific programs and initiatives offers deeper insight into the agencys comprehensive approach to disaster management. The following section delves into recent projects and future strategies.
Conclusion
Ghana’s disaster management framework, embodied by its dedicated organization, represents a multifaceted approach to safeguarding the nation from the impact of disasters. From proactive mitigation strategies to comprehensive preparedness measures, swift response mechanisms, and resilient recovery programs, the framework addresses the entire disaster management cycle. Emphasis on community engagement, inter-agency collaboration, and international partnerships underscores the importance of a coordinated and inclusive approach. Investing in disaster risk reduction is not merely a reactive measure but a crucial investment in sustainable development, safeguarding lives, livelihoods, and the nation’s future.
The ongoing commitment to strengthening disaster management capacities reflects a proactive vision for a more resilient Ghana. Continuous improvement of strategies, informed by lessons learned and evolving disaster risks, remains crucial. Collective action, involving individuals, communities, government agencies, and international partners, is essential to building a nation equipped to effectively manage the challenges posed by disasters and secure a safer future for all.