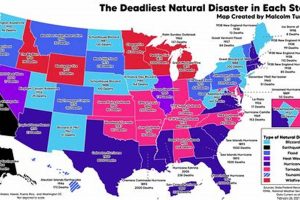
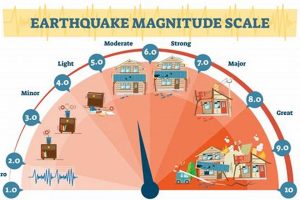
Developing proactive strategies to mitigate the impact of unforeseen environmental events, such as earthquakes, floods, or wildfires, involves establishing plans for evacuation, resource storage, and communication. For instance, assembling a kit containing essential supplies like water, non-perishable food, first-aid materials, and flashlights constitutes a practical measure.
Prior planning significantly reduces risks to life and property by ensuring individuals and communities possess the knowledge and tools to respond effectively during emergencies. Historically, regions with robust preemptive measures have demonstrated greater resilience and faster recovery in the aftermath of such events. A well-defined strategy can minimize chaos, enhance coordination among response teams, and facilitate the efficient allocation of resources.
This exploration delves into key components of effective strategies, including risk assessment, planning, communication protocols, and resource management, providing a framework for enhancing community and individual resilience.
Tips for Effective Disaster Preparedness
Implementing proactive measures enhances resilience and minimizes the impact of unforeseen environmental events. The following recommendations provide a framework for developing comprehensive strategies:
Tip 1: Conduct a Thorough Risk Assessment: Identify potential hazards specific to one’s geographical location. This includes evaluating vulnerability to earthquakes, floods, wildfires, hurricanes, and other relevant threats. Consulting local authorities or geological surveys can provide valuable insights.
Tip 2: Develop a Comprehensive Plan: Formulate a detailed plan outlining evacuation routes, communication protocols, and designated meeting points. This plan should encompass provisions for individuals with special needs, pets, and essential documents.
Tip 3: Assemble an Emergency Kit: Prepare a readily accessible kit containing essential supplies, including water, non-perishable food, first-aid materials, flashlights, batteries, a radio, and a multi-tool. Regularly inspect and replenish these supplies.
Tip 4: Establish Communication Protocols: Designate an out-of-area contact person and ensure all family members have their contact information. Establish clear communication procedures within the household and with external contacts.
Tip 5: Secure Important Documents: Safeguard crucial documents such as birth certificates, passports, insurance policies, and medical records in a waterproof and fireproof container. Creating digital copies and storing them securely online is also recommended.
Tip 6: Practice Regularly: Conduct periodic drills to familiarize household members with evacuation routes and emergency procedures. This reinforces preparedness and enhances responsiveness during actual events.
Tip 7: Stay Informed: Monitor weather reports and official alerts from local authorities. Sign up for emergency notification systems to receive timely updates and instructions.
Adopting these measures significantly improves the ability to navigate unforeseen events, safeguarding lives and minimizing potential losses.
By integrating these strategies into daily life, individuals and communities cultivate a culture of preparedness, fostering resilience and minimizing the impact of future environmental challenges.
1. Risk Assessment
Risk assessment forms the cornerstone of effective strategies for mitigating the impact of natural disasters. A comprehensive understanding of potential hazards and vulnerabilities allows for informed decision-making and the development of targeted preparedness measures. Without a thorough risk assessment, efforts may be misdirected and prove inadequate during an actual event.
- Hazard Identification
This initial step involves identifying all credible threats within a specific geographic area. These hazards can range from earthquakes and floods to wildfires and extreme weather events. For example, coastal regions face a higher risk of tsunamis and hurricanes, while mountainous areas may be more susceptible to landslides and avalanches. Accurately identifying potential hazards provides the foundation for subsequent planning and mitigation efforts.
- Vulnerability Analysis
Vulnerability analysis examines the susceptibility of individuals, communities, and infrastructure to identified hazards. This includes considering factors such as building codes, population density, socioeconomic conditions, and access to emergency services. For instance, older buildings may be more vulnerable to seismic activity, while communities with limited access to transportation may face greater challenges evacuating during a flood. Understanding specific vulnerabilities allows for the development of targeted interventions.
- Impact Assessment
This facet assesses the potential consequences of a natural disaster, including potential loss of life, economic damage, and disruption to essential services. For example, a major earthquake in a densely populated urban area could result in significant casualties and widespread infrastructure damage. Quantifying potential impacts emphasizes the importance of preparedness and informs resource allocation decisions.
- Mitigation Strategies
Based on the identified hazards, vulnerabilities, and potential impacts, mitigation strategies are developed to reduce risk. These strategies can include structural measures like reinforcing buildings or implementing flood control systems, as well as non-structural measures such as land-use planning, public awareness campaigns, and early warning systems. Effective mitigation strategies minimize the potential consequences of natural disasters and enhance community resilience.
By systematically evaluating hazards, vulnerabilities, and potential impacts, communities can develop and implement comprehensive strategies that minimize risk and enhance overall preparedness. A robust risk assessment process provides a framework for informed decision-making, enabling communities to allocate resources effectively and prioritize mitigation efforts. This proactive approach is crucial for safeguarding lives, minimizing economic losses, and fostering resilient communities in the face of natural disasters.
2. Planning
Planning constitutes a critical component of effective natural disaster preparation, directly influencing outcomes during and after such events. A well-defined plan provides a structured framework for action, minimizing panic and facilitating coordinated responses. The absence of preemptive planning can exacerbate the impact of disasters, leading to increased casualties, greater property damage, and prolonged recovery periods. For instance, communities with established evacuation plans and designated shelters often experience significantly fewer casualties during hurricanes compared to those lacking such strategies. Planning enables the efficient allocation of resources, the timely dissemination of information, and the coordinated mobilization of emergency personnel.
Effective planning encompasses various crucial elements, including the identification of potential hazards, the development of evacuation routes, the establishment of communication protocols, and the allocation of essential resources. A comprehensive plan should also address the specific needs of vulnerable populations, such as individuals with disabilities, the elderly, and those with limited access to transportation. Real-life examples abound, illustrating the practical significance of meticulous planning. Following the 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami in Japan, communities with well-rehearsed evacuation plans and robust seawalls experienced considerably less damage compared to areas lacking such preparedness measures. This underscores the importance of integrating scientific data, local knowledge, and community input into disaster preparedness planning processes.
In summary, proactive planning serves as a cornerstone of effective natural disaster preparation, mitigating potential impacts and facilitating recovery. While the unpredictable nature of these events poses inherent challenges, meticulous planning empowers communities to anticipate potential scenarios, coordinate responses effectively, and minimize losses. The practical significance of this understanding translates directly into enhanced community resilience and improved outcomes in the face of natural disasters. Integrating planning into broader societal frameworks, such as urban development and infrastructure design, further strengthens overall disaster preparedness.
3. Communication
Effective communication constitutes a cornerstone of successful natural disaster preparation and response. Timely and accurate information dissemination plays a crucial role in mitigating risks, facilitating coordinated action, and fostering public safety. Without robust communication systems, communities become vulnerable to misinformation, delayed responses, and increased casualties during emergencies. Establishing clear communication protocols before, during, and after a disaster proves essential for optimizing resource allocation, coordinating evacuation efforts, and providing timely assistance to affected populations.
- Early Warning Systems
Early warning systems represent a critical component of disaster preparedness, enabling communities to anticipate and prepare for impending threats. These systems utilize various technologies, including weather radar, seismic monitoring, and satellite imagery, to detect and predict natural hazards. Timely dissemination of warnings through various channels, such as mobile alerts, public address systems, and broadcast media, empowers individuals and communities to take proactive measures, such as evacuating vulnerable areas or securing property. For instance, the effectiveness of tsunami warning systems in coastal regions has demonstrably reduced casualties by providing advance notice, enabling timely evacuations. The efficacy of such systems hinges on reliable communication infrastructure and public awareness campaigns.
- Emergency Alerts and Public Information
During a natural disaster, access to accurate and up-to-date information becomes paramount. Emergency alerts provide real-time updates on the evolving situation, including evacuation orders, safety instructions, and the location of emergency shelters. Disseminating this information through multiple channels, such as mobile alerts, social media platforms, and radio broadcasts, ensures broad reach and accessibility. For example, during Hurricane Katrina, the delayed and inconsistent dissemination of information contributed to confusion and hampered evacuation efforts. Lessons learned from such events underscore the importance of establishing clear communication protocols and utilizing diverse channels to reach affected populations.
- Coordination Among Response Agencies
Effective communication among various response agencies, including emergency services, law enforcement, and healthcare providers, is crucial for coordinated disaster response. Establishing clear lines of communication, utilizing standardized protocols, and employing interoperable communication technologies facilitate seamless information sharing and resource allocation. For instance, during the 2010 Haiti earthquake, communication breakdowns among international aid organizations hampered relief efforts and delayed the delivery of essential supplies. Experiences from such events highlight the need for pre-established communication frameworks and interagency training exercises.
- Post-Disaster Communication
In the aftermath of a natural disaster, communication plays a vital role in coordinating recovery efforts, providing support to affected communities, and disseminating information regarding available resources. Establishing channels for individuals to report their status, request assistance, and access essential services facilitates efficient resource allocation and supports community rebuilding. Following the 2011 Japanese tsunami, online platforms and community bulletin boards served as vital communication hubs, enabling individuals to connect with family members, access support services, and contribute to recovery efforts. The effectiveness of post-disaster communication directly impacts the speed and efficiency of recovery processes.
These facets of communication underscore its integral role in all stages of natural disaster preparedness and response. Investing in robust communication infrastructure, establishing clear protocols, and fostering public awareness contribute significantly to community resilience and minimize the impact of natural disasters. By prioritizing communication as a core element of disaster preparedness strategies, communities enhance their capacity to respond effectively, mitigate risks, and foster a culture of preparedness.
4. Resource Management
Resource management constitutes a critical component of effective natural disaster preparation, directly influencing a community’s capacity to respond to and recover from such events. Efficient allocation and utilization of essential resources, including water, food, medical supplies, and personnel, can significantly impact outcomes during emergencies. A lack of adequate resource management can lead to shortages, delays in aid delivery, and increased vulnerability among affected populations. For example, following Hurricane Katrina in 2005, logistical challenges hampered the distribution of essential supplies, highlighting the critical need for robust resource management systems. Conversely, communities with pre-established resource stockpiles and distribution plans demonstrate greater resilience in the face of disasters. Understanding the interconnectedness of resource management and disaster preparedness allows for the development of comprehensive strategies that optimize resource allocation and enhance community resilience.
Effective resource management encompasses several key aspects, including pre-disaster resource stockpiling, the development of distribution networks, and the establishment of inventory management systems. Accurately assessing the potential needs of a community based on historical data and projected impact scenarios informs resource allocation decisions. Diversification of resource suppliers and storage locations minimizes the risk of disruptions due to infrastructure damage. Real-time tracking of resource availability and utilization enables dynamic adjustments during an evolving disaster situation. Furthermore, incorporating principles of sustainability into resource management practices ensures long-term resilience. Following the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake, communities with decentralized resource stockpiles experienced greater success in providing aid compared to those reliant on centralized distribution hubs, demonstrating the practical significance of adaptable resource management strategies. The integration of technology, such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and inventory management software, further enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of resource allocation during emergencies.
In summary, effective resource management forms an integral part of comprehensive natural disaster preparedness strategies. Proactive planning, strategic allocation, and efficient utilization of essential resources minimize the impact of disasters, facilitate recovery efforts, and enhance community resilience. Recognizing the interconnectedness of resource management with other aspects of disaster preparedness, such as communication and community engagement, strengthens overall preparedness frameworks. Addressing potential challenges, such as resource scarcity and logistical constraints, through innovative solutions and collaborative partnerships further enhances community capacity to navigate future disasters and build more resilient societies. Integrating resource management considerations into broader policy frameworks, such as land-use planning and infrastructure development, reinforces disaster preparedness efforts and promotes sustainable community development.
5. Community Engagement
Community engagement constitutes a critical aspect of effective natural disaster preparation, fostering resilience and enhancing collective capacity to respond to and recover from such events. Active participation of community members in planning, preparedness activities, and post-disaster recovery significantly strengthens overall disaster resilience. Without robust community engagement, individual efforts may prove fragmented and less effective in mitigating the impact of disasters. For example, communities with established neighborhood support networks and volunteer training programs demonstrate greater resilience during emergencies compared to those lacking such collaborative structures. Understanding the crucial role of community engagement in disaster preparedness enables the development of comprehensive strategies that empower individuals, strengthen social networks, and enhance collective response capabilities.
- Collaborative Planning and Preparedness
Engaging community members in the development of disaster preparedness plans ensures that strategies reflect local needs, vulnerabilities, and resources. This collaborative approach fosters a sense of ownership and empowers individuals to take proactive measures. For instance, community-based workshops and participatory mapping exercises can identify vulnerable populations, determine evacuation routes, and establish communication protocols. Such collaborative efforts enhance the effectiveness of disaster preparedness plans and facilitate coordinated responses during emergencies.
- Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about potential hazards, preparedness measures, and available resources empowers individuals to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions. Community education programs, public service announcements, and disaster preparedness drills equip community members with the knowledge and skills necessary to respond effectively during emergencies. For example, conducting regular earthquake drills in schools and community centers enhances preparedness and reduces panic during actual seismic events. Effective public awareness campaigns foster a culture of preparedness and encourage proactive community participation.
- Volunteer Training and Capacity Building
Training community members in first aid, search and rescue, and other essential skills strengthens local response capacity and reduces reliance on external assistance. Establishing volunteer networks and providing training opportunities empowers individuals to contribute actively to disaster response and recovery efforts. Following the 2010 Haiti earthquake, local volunteers played a crucial role in providing immediate assistance to affected communities before the arrival of international aid organizations. Investing in community-based volunteer training programs enhances overall disaster resilience and strengthens collective response capabilities.
- Post-Disaster Recovery and Reconstruction
Engaging community members in post-disaster recovery and reconstruction efforts fosters a sense of ownership and promotes long-term resilience. Involving local residents in needs assessments, damage assessments, and rebuilding initiatives ensures that recovery efforts align with community priorities and address specific needs. Following Hurricane Sandy in 2012, community-based organizations played a vital role in distributing aid, providing support services, and facilitating the rebuilding of affected neighborhoods. Community participation in post-disaster recovery accelerates the process, strengthens social cohesion, and promotes sustainable community development.
These facets of community engagement highlight its significance in building disaster-resilient communities. By fostering collaborative planning, promoting public awareness, investing in volunteer training, and engaging community members in post-disaster recovery, societies enhance their capacity to prepare for, respond to, and recover from natural disasters. Recognizing the interconnectedness of community engagement with other aspects of disaster preparedness, such as resource management and communication, strengthens overall preparedness frameworks. Furthermore, promoting inclusivity and addressing the specific needs of vulnerable populations within community engagement initiatives ensures equitable access to resources and support services during emergencies. Building strong, engaged communities constitutes a fundamental pillar of effective natural disaster preparedness, fostering resilience and minimizing the impact of such events.
6. Post-Disaster Recovery
Post-disaster recovery represents not merely an aftermath phase but an integral component of comprehensive natural disaster preparation. Effective recovery strategies, integrated into preparedness planning, significantly influence long-term community resilience and the capacity to withstand future events. Pre-disaster planning for recovery, encompassing aspects such as resource allocation, infrastructure restoration, and psychosocial support mechanisms, accelerates the return to normalcy and mitigates the long-term consequences of disasters. The absence of pre-emptive recovery planning often results in prolonged displacement, economic hardship, and increased community vulnerability. For instance, communities with pre-established recovery plans and designated reconstruction zones often experience faster rebuilding processes and reduced economic losses compared to those lacking such foresight. Understanding the interconnectedness of post-disaster recovery and pre-disaster preparation enables the development of holistic strategies that address both immediate response needs and long-term recovery objectives.
The connection between post-disaster recovery and natural disaster preparation manifests in several crucial aspects. Firstly, pre-disaster identification of critical infrastructure and essential services informs prioritization during recovery efforts, ensuring rapid restoration of vital functionalities. Secondly, pre-arranged agreements with external agencies and organizations streamline resource mobilization and expedite aid delivery in the aftermath of a disaster. Thirdly, incorporating community input into recovery planning fosters local ownership and empowers residents to actively participate in rebuilding efforts, accelerating the return to normalcy. Examples such as the aftermath of the 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami in Japan demonstrate the practical significance of integrating recovery considerations into pre-disaster planning. Coastal communities with pre-established tsunami evacuation routes and designated assembly points experienced significantly lower casualty rates and faster recovery times compared to areas lacking such preparedness measures. These real-world examples underscore the critical role of recovery planning in minimizing the long-term impacts of disasters.
In conclusion, post-disaster recovery constitutes not a separate phase but a crucial element of comprehensive natural disaster preparation. Integrating recovery considerations into pre-disaster planning enhances community resilience, accelerates the return to normalcy, and mitigates long-term consequences. Challenges such as resource limitations, logistical constraints, and psychological trauma necessitate innovative solutions and collaborative partnerships. Recognizing the cyclical nature of disaster preparedness, response, and recovery fosters a proactive approach to building more resilient communities capable of withstanding future events and minimizing their impact. Incorporating lessons learned from past disasters into recovery planning frameworks strengthens preparedness strategies and promotes sustainable community development, fostering a culture of preparedness and enhancing societal capacity to navigate the complexities of natural hazards.
Frequently Asked Questions
Addressing common inquiries regarding proactive measures for mitigating the impact of natural disasters provides clarity and fosters a culture of preparedness. The following questions and answers offer practical guidance for individuals and communities seeking to enhance their resilience.
Question 1: How does one begin developing a personalized strategy?
Initiating the process involves assessing potential hazards specific to one’s geographical location. Consulting local authorities or geological surveys facilitates hazard identification. Subsequently, developing a comprehensive plan encompassing evacuation routes, communication protocols, and resource allocation constitutes a crucial step.
Question 2: What essential supplies should be included in an emergency kit?
An emergency kit should contain water, non-perishable food, first-aid materials, flashlights, batteries, a radio, a multi-tool, and essential documents. Regularly inspecting and replenishing these supplies ensures preparedness.
Question 3: What role does communication play in effective strategies?
Communication plays a vital role in disseminating timely information, coordinating responses, and facilitating access to resources during emergencies. Establishing clear communication protocols within households and with external contacts is essential.
Question 4: How can individuals contribute to community-level preparedness efforts?
Participating in community-based planning initiatives, volunteering for training programs, and supporting local emergency response organizations strengthens collective resilience. Engaging with neighbors and community leaders fosters a culture of preparedness.
Question 5: What measures can be taken to safeguard important documents during a disaster?
Storing crucial documents in a waterproof and fireproof container safeguards them against damage. Creating digital copies and storing them securely online provides an additional layer of protection.
Question 6: How can one stay informed about potential hazards and official alerts?
Monitoring weather reports, subscribing to emergency notification systems, and staying updated through official channels, such as local government websites and social media platforms, ensures access to timely and accurate information.
Proactive measures significantly enhance resilience and minimize the impact of natural disasters. Continuous learning and adaptation remain essential for navigating the evolving landscape of disaster preparedness.
Exploring additional resources and engaging with local emergency management agencies provides further insights and strengthens individual and community preparedness.
Natural Disaster Preparation
Proactive strategies for mitigating the impact of natural disasters necessitate a multifaceted approach encompassing risk assessment, planning, communication, resource management, community engagement, and post-disaster recovery. Understanding potential hazards, developing comprehensive plans, establishing robust communication protocols, and efficiently managing resources constitute crucial elements of effective preparation. Furthermore, fostering community engagement strengthens collective response capabilities and accelerates recovery processes. Integrating these elements into a cohesive framework enhances overall resilience and minimizes the impact of unforeseen environmental events.
Investing in robust preparation measures represents a societal imperative, safeguarding lives, minimizing economic losses, and fostering sustainable community development. The unpredictable nature of natural disasters necessitates continuous adaptation, innovation, and collaboration to navigate future challenges effectively. Prioritizing preparedness equips communities to respond effectively, mitigate risks, and build a more resilient future in the face of evolving environmental threats.