The year 2024, like any other, witnessed a range of geophysical and hydrometeorological events that caused significant damage and disruption across the globe. These events, encompassing earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, floods, droughts, wildfires, and extreme weather phenomena, pose substantial challenges to human societies and ecosystems. Understanding specific occurrences and their impacts provides critical information for disaster preparedness, mitigation efforts, and response strategies.
Analyzing specific events from this period allows for a deeper understanding of the ongoing impact of climate change and other contributing factors. Studying these events in detail enables researchers to refine predictive models, improve early warning systems, and develop more effective strategies for community resilience. Historical data on such events provides a valuable context for evaluating the effectiveness of past interventions and informing future policy decisions related to disaster risk reduction and climate adaptation.
This analysis will explore various significant events of 2024, examining their causes, consequences, and the lessons learned. The subsequent sections delve into specific case studies, highlighting both the immediate impacts and the long-term implications of these events.
Disaster Preparedness Tips Informed by 2024 Events
The events of 2024 underscore the critical importance of proactive disaster preparedness. These tips, informed by the year’s significant incidents, offer guidance for enhancing individual and community resilience.
Tip 1: Develop a Comprehensive Emergency Plan: This plan should include evacuation routes, communication strategies, and designated meeting points. Consider specific needs of household members, including pets and individuals with disabilities. The flooding events of 2024 highlighted the importance of having multiple evacuation routes planned in advance.
Tip 2: Assemble an Emergency Kit: Essential supplies include water, non-perishable food, first-aid supplies, medications, a battery-powered radio, and flashlights. Regularly check and replenish these supplies to ensure they remain usable. The extended power outages following the 2024 hurricanes demonstrated the necessity of having sufficient resources for prolonged periods without essential services.
Tip 3: Stay Informed: Monitor weather alerts and official communication channels for updates on developing situations. Understand local warning systems and evacuation procedures. The rapid intensification of several 2024 storms underscored the need for timely and accurate information.
Tip 4: Secure Property and Mitigate Risks: Implement measures to protect homes and businesses from potential hazards. This may include reinforcing structures against wind and water damage, clearing debris from gutters and drainage systems, and creating defensible space around properties in fire-prone areas. The widespread damage caused by wildfires in 2024 demonstrated the effectiveness of preventative measures like creating defensible space.
Tip 5: Engage in Community Preparedness: Participate in local emergency drills and volunteer with community organizations involved in disaster response. Collaboration and communication within a community are essential for effective disaster management. The community-led response efforts following the 2024 earthquake in [affected region] highlighted the power of collective action.
Tip 6: Review Insurance Policies: Ensure adequate coverage for potential hazards relevant to your location. Understand policy limitations and deductibles. The significant financial losses experienced by many in 2024 underscore the importance of comprehensive insurance coverage.
Tip 7: Learn Basic First Aid and CPR: These skills can be invaluable in emergency situations, particularly when professional medical assistance is delayed or unavailable. The remote nature of some of the 2024 disaster events highlighted the need for individuals to be prepared to provide immediate assistance.
By adopting these proactive measures, individuals and communities can significantly enhance their resilience in the face of future events. Preparedness is a continuous process that requires ongoing assessment and adaptation.
These tips provide practical guidance for navigating future challenges and building safer, more resilient communities. The following conclusion will further emphasize the importance of these preparations in the context of a changing global landscape.
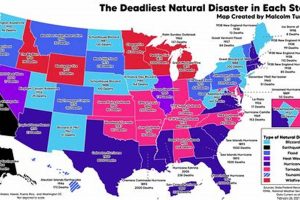
1. Geographic Distribution
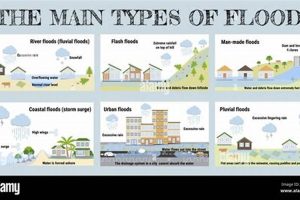
Geographic distribution plays a crucial role in understanding the impact and characteristics of natural disasters. Analyzing the spatial occurrence of events in 2024 reveals patterns of vulnerability and risk. Certain regions are inherently more susceptible to specific hazards due to their geological location, proximity to coastlines, or prevailing climatic conditions. For instance, coastal areas are at higher risk of hurricanes and tsunamis, while regions near tectonic plate boundaries are more prone to earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. The concentration of flood events in specific river basins during 2024 highlights the influence of topography and drainage patterns on disaster vulnerability.
Understanding these geographic patterns is essential for effective disaster preparedness and resource allocation. By mapping the distribution of past events, authorities can identify high-risk areas and prioritize mitigation efforts. This information is also crucial for developing early warning systems tailored to specific regional threats. For example, the frequency of wildfires in certain geographic areas during 2024 informed the deployment of fire monitoring and suppression resources. Furthermore, analyzing geographic distribution helps researchers identify underlying factors contributing to disaster risk, such as deforestation, urbanization, and climate change.
Analysis of geographic distribution provides crucial insights for disaster risk reduction. By understanding where and why certain hazards occur, communities can implement targeted mitigation measures, develop effective evacuation plans, and strengthen infrastructure resilience. This spatial understanding is fundamental for building safer and more resilient communities in the face of future events. Further research exploring the intersection of geographic factors and specific hazard types will be essential for refining predictive models and improving disaster preparedness strategies.
2. Impact Assessment
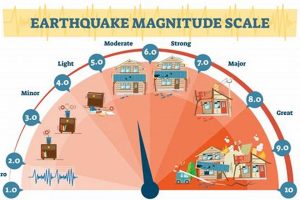
Impact assessment following a natural disaster is a crucial process for understanding the extent and nature of the damage caused. In the context of 2024, these assessments provided critical information for directing relief efforts, developing recovery strategies, and informing future mitigation measures. A comprehensive impact assessment considers a range of factors, including the physical damage to infrastructure and property, the loss of life and livelihoods, the environmental consequences, and the disruption to social and economic systems. For example, following the 2024 earthquake in [affected region], impact assessments revealed the extent of structural damage to buildings and the disruption to transportation networks, enabling authorities to prioritize aid distribution and infrastructure repair.
Detailed assessments often employ a combination of methodologies, including field surveys, remote sensing data analysis, and socioeconomic surveys. This multifaceted approach allows for a more complete understanding of both the immediate and long-term consequences of an event. Data collected during these assessments is essential for quantifying the economic losses, identifying vulnerable populations, and evaluating the effectiveness of disaster response mechanisms. The data gathered following the 2024 floods in [affected region], for instance, allowed for an accurate assessment of the agricultural losses and the number of displaced individuals, informing the allocation of financial aid and the development of resettlement programs.
Impact assessments serve as a crucial link between disaster response and long-term recovery planning. They provide evidence-based insights that inform policy decisions, resource allocation, and the development of strategies for building community resilience. The information gleaned from these assessments is vital for mitigating future risks and reducing the vulnerability of communities to similar events. Challenges remain in standardizing assessment methodologies and ensuring timely data collection, particularly in remote or heavily affected areas. However, the ongoing development of new technologies and data analysis techniques offers promising opportunities for improving the accuracy, efficiency, and timeliness of impact assessments, thereby strengthening disaster response and recovery efforts in the future. This information contributes significantly to understanding the full scope of natural disasters in 2024 and shaping effective disaster management strategies.
3. Climate Change Influence
The influence of climate change on the frequency, intensity, and characteristics of natural disasters is a critical concern. Analyzing this influence within the context of 2024 events provides valuable insights for understanding evolving disaster risks and informing mitigation strategies. Climate change acts as a threat multiplier, exacerbating existing vulnerabilities and creating new challenges for disaster management.
- Elevated Temperatures and Heatwaves:
Rising global temperatures contribute to more frequent and intense heatwaves. These extreme heat events pose significant risks to human health, particularly for vulnerable populations, and can exacerbate drought conditions, increasing wildfire risk. The extended heatwave experienced in [affected region] during 2024, for example, resulted in numerous heat-related illnesses and contributed to widespread wildfires, demonstrating the direct impact of elevated temperatures on disaster occurrence.
- Changing Precipitation Patterns:
Climate change alters precipitation patterns, leading to both more intense rainfall events and prolonged periods of drought. Increased rainfall can overwhelm drainage systems, resulting in devastating floods, while droughts can deplete water resources, impacting agriculture and increasing the risk of wildfires. The contrasting experiences of severe flooding in [affected region] and extreme drought in [another affected region] during 2024 illustrate the disruptive influence of shifting precipitation patterns on different geographic areas.
- Sea Level Rise and Coastal Erosion:
Rising sea levels, driven by thermal expansion of seawater and melting glaciers, increase the risk of coastal flooding and erosion. This poses a significant threat to coastal communities and infrastructure. The increased coastal erosion observed in [affected region] during 2024, exacerbated by storm surge from a hurricane, exemplifies the compounding effects of sea level rise and extreme weather events.
- Intensified Storms and Extreme Weather:
Warmer ocean temperatures provide more energy for tropical cyclones, leading to more intense hurricanes and typhoons. Climate change also influences other extreme weather events, such as heavy snowfall, severe thunderstorms, and tornadoes. The rapid intensification of Hurricane [hurricane name] in 2024, for instance, underscores the potential for climate change to amplify the destructive power of these storms.
These interconnected facets of climate change influence underscore the complex and evolving nature of disaster risk. Understanding these connections is essential for developing effective adaptation and mitigation strategies. The events of 2024 serve as a stark reminder of the need for comprehensive climate action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and build resilience in the face of increasingly frequent and intense natural disasters. Further research examining the specific mechanisms through which climate change influences various disaster types will be crucial for improving predictive models and developing targeted interventions.
4. Early Warning Systems
Early warning systems played a crucial role in mitigating the impact of natural disasters in 2024. These systems, designed to provide timely and accurate alerts about impending hazards, enable communities to take proactive measures to protect lives and property. The effectiveness of these systems in 2024 varied depending on the specific hazard, the region affected, and the level of preparedness within the community. Examining key facets of early warning systems in the context of 2024 events provides valuable insights for improving future disaster preparedness and response.
- Technological Advancements:
Advancements in meteorological and geophysical monitoring technologies, including satellite-based observation systems and ground-based sensor networks, improved the accuracy and timeliness of warnings in 2024. For example, the use of advanced radar systems provided more precise tracking of hurricane trajectories, enabling more targeted evacuations in coastal areas. However, challenges remain in ensuring equitable access to these advanced technologies, particularly in developing countries.
- Communication and Dissemination:
Effective communication and dissemination of warnings are essential for ensuring that at-risk populations receive timely information and can take appropriate action. In 2024, mobile phone alerts, social media platforms, and community-based warning systems played a key role in disseminating information. However, communication challenges persist in areas with limited infrastructure or during events that disrupt communication networks. The delayed dissemination of flood warnings in [affected region] during 2024, for instance, highlighted the need for redundant communication systems and community-based information networks.
- Community Engagement and Response:
The effectiveness of early warning systems relies heavily on community engagement and preparedness. Community-based drills, educational programs, and the development of local evacuation plans are essential for ensuring that individuals understand how to respond to warnings effectively. In several communities affected by wildfires in 2024, proactive evacuation plans, developed in collaboration with local authorities, proved crucial for minimizing casualties. However, variations in community preparedness and response capacity highlight the need for ongoing community engagement and capacity building efforts.
- Integration with Disaster Risk Reduction:
Early warning systems should be integrated with broader disaster risk reduction strategies, including land-use planning, building codes, and infrastructure development. In 2024, communities that had implemented flood mitigation measures, such as improved drainage systems and flood-resistant infrastructure, experienced less severe impacts from flooding events, even with timely warnings. However, limited integration of early warning systems with long-term mitigation strategies in some areas underscores the need for more holistic approaches to disaster risk management.
Analyzing these facets of early warning systems within the context of 2024 natural disasters provides valuable lessons for enhancing future preparedness. While technological advancements continue to improve the accuracy and timeliness of warnings, challenges remain in ensuring equitable access, effective communication, and community engagement. Integrating early warning systems with comprehensive disaster risk reduction strategies is essential for maximizing their effectiveness and building more resilient communities in the face of evolving disaster threats. The experience of 2024 emphasizes the ongoing need for investment in, and refinement of, these crucial life-saving systems.
5. Community Resilience
Community resilience played a critical role in mitigating the impacts of natural disasters throughout 2024. A resilient community possesses the capacity to anticipate, prepare for, withstand, and recover from the effects of hazardous events. Examining the various facets of community resilience within the context of 2024 disasters provides valuable insights for enhancing preparedness and reducing vulnerability.
- Social Capital and Networks:
Strong social networks and community bonds proved essential for effective disaster response in 2024. Communities with established communication channels, mutual support systems, and a history of collective action were better equipped to respond to and recover from disasters. For example, in the aftermath of the earthquake in [affected region], strong neighborhood associations facilitated the rapid mobilization of volunteers and the distribution of aid. Conversely, communities with weaker social cohesion faced greater challenges in coordinating relief efforts.
- Economic Diversification and Stability:
Economically diverse and stable communities demonstrated greater resilience in the face of 2024 disasters. Diversified economies are less susceptible to the economic shocks caused by localized disasters, and communities with stable financial resources are better able to invest in preparedness measures and recovery efforts. The rapid economic recovery of [affected region] following the hurricane can be attributed, in part, to its diversified economic base, while the prolonged economic hardship experienced by [another affected region] following the flood highlights the vulnerability of communities reliant on a single industry.
- Infrastructure and Environmental Planning:
Well-planned infrastructure and environmentally sound land management practices contributed significantly to community resilience in 2024. Communities with robust infrastructure, including flood defenses, earthquake-resistant buildings, and well-maintained evacuation routes, experienced less damage and disruption from natural hazards. Furthermore, communities that had implemented sustainable land management practices, such as reforestation and wetland restoration, were better able to mitigate the impacts of flooding and erosion. The effectiveness of flood control measures in [affected region] during the heavy rains of 2024 demonstrates the importance of investing in protective infrastructure.
- Disaster Preparedness and Response Capacity:
Communities with well-developed disaster preparedness plans and robust response capacities were better prepared to manage the challenges posed by natural disasters in 2024. Regular disaster drills, comprehensive emergency plans, and well-trained first responders enabled communities to react quickly and effectively to minimize casualties and property damage. The rapid and coordinated response to the wildfire in [affected region], for instance, effectively contained the fire and protected nearby communities. However, the delayed response to the flood in [another affected region] underscored the importance of continuous improvement in disaster preparedness and response capabilities.
These facets of community resilience underscore the importance of proactive planning, investment in infrastructure, and the cultivation of strong social networks. The experiences of various communities during the natural disasters of 2024 demonstrate that resilience is not merely a measure of a community’s ability to withstand a disaster, but also its capacity to adapt, learn, and emerge stronger from such events. Building and maintaining resilient communities requires ongoing effort and collaboration among government agencies, community organizations, and individual citizens. Further analysis of these events and their impact on diverse communities will be essential for refining resilience strategies and building safer, more sustainable communities for the future.
6. Economic Consequences
Natural disasters inflict substantial economic consequences, and 2024 provided numerous examples of these impacts. Understanding the economic repercussions of these events is crucial for effective disaster preparedness, response, and recovery. These consequences manifest in various forms, both direct and indirect, and can have long-lasting effects on affected regions and global economies.
Direct economic costs include physical damage to infrastructure, property, and agricultural lands. The destruction of homes, businesses, transportation networks, and utilities requires significant financial investment for rebuilding and repair. For example, the earthquake in [affected region] during 2024 resulted in billions of dollars in infrastructure damage, disrupting supply chains and impacting regional economic activity. Indirect costs, while less immediately visible, can be equally significant. These include business interruption, loss of productivity, decreased tourism revenue, and displacement of workers. The extended disruption to tourism following the hurricane in [affected region] in 2024, for instance, significantly impacted local businesses and employment rates.
The economic consequences of natural disasters extend beyond immediate losses. Disruptions to supply chains can lead to shortages of essential goods and price fluctuations. Damage to agricultural lands can impact food security, both regionally and globally. Furthermore, the displacement of populations can create long-term economic challenges for affected individuals and communities. The influx of displaced individuals into [affected city] following the floods in 2024 strained local resources and placed a burden on social services. Analyzing these various economic consequences provides valuable insights for developing strategies to mitigate future risks. Investing in resilient infrastructure, diversifying local economies, and implementing effective disaster risk financing mechanisms can help reduce the economic vulnerability of communities and nations. Furthermore, accurate and timely economic impact assessments are crucial for informing recovery efforts and ensuring efficient allocation of resources. Addressing the economic challenges posed by natural disasters requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses preparedness, response, recovery, and long-term mitigation. The events of 2024 underscore the importance of integrating economic considerations into all aspects of disaster management to build more resilient and sustainable economies.
7. Mitigation Strategies
Mitigation strategies represent crucial proactive measures implemented to reduce the impact of future natural disasters. Analyzing these strategies within the context of events in 2024 provides valuable insights for enhancing community resilience and minimizing losses from similar hazards in the future. Effective mitigation requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing structural measures, land-use planning, environmental management, and community engagement.
- Structural Mitigation:
Structural mitigation involves physical modifications to the built environment to enhance its resistance to natural hazards. Examples include reinforcing buildings to withstand earthquakes, constructing flood defenses such as levees and seawalls, and implementing fire-resistant building materials in wildfire-prone areas. The effectiveness of reinforced concrete structures in mitigating earthquake damage in [affected region] during 2024 highlights the importance of incorporating structural mitigation measures into building codes and infrastructure development.
- Land-Use Planning and Zoning:
Land-use planning and zoning regulations play a crucial role in minimizing exposure to natural hazards. Restricting development in floodplains, coastal zones, and areas prone to landslides or wildfires can significantly reduce risk. The limited development in designated flood zones in [affected city] during 2024 contributed to reduced flood damage, demonstrating the effectiveness of land-use planning in mitigating disaster impacts. Conversely, uncontrolled development in hazardous areas often exacerbates disaster consequences.
- Environmental Management and Ecosystem-Based Adaptation:
Environmental management practices, such as reforestation, wetland restoration, and sustainable land management, can enhance natural defenses against natural hazards. Reforestation efforts in [affected region] helped stabilize slopes and mitigate the impact of landslides in 2024. Restoring coastal wetlands provides a natural buffer against storm surge and coastal erosion. These ecosystem-based adaptation strategies offer sustainable solutions for mitigating disaster risk while enhancing ecological health and biodiversity. However, implementing these strategies requires long-term planning and investment.
- Community Engagement and Education:
Effective mitigation requires active community engagement and education. Public awareness campaigns, disaster preparedness training, and community-based planning processes empower individuals and communities to take proactive steps to reduce their vulnerability. The successful evacuation of residents in [affected community] during the 2024 wildfire can be attributed, in part, to the community’s proactive engagement in wildfire preparedness programs. However, achieving widespread community participation in mitigation efforts remains a challenge.
These diverse mitigation strategies offer a range of options for reducing disaster risk. Implementing these strategies effectively requires careful assessment of specific hazards, community vulnerabilities, and available resources. The events of 2024 provide valuable case studies for evaluating the effectiveness of different mitigation measures and informing future investments in disaster risk reduction. A comprehensive approach that integrates structural measures, land-use planning, environmental management, and community engagement is essential for building more resilient communities and mitigating the impacts of future natural disasters. The lessons learned from 2024 underscore the ongoing need for investment in and refinement of these crucial strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions about Natural Disasters in 2024
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the natural disasters that occurred in 2024, providing concise and informative responses.
Question 1: How did the frequency and intensity of natural disasters in 2024 compare to previous years?
While specific statistical comparisons require further analysis and compilation of global data, initial assessments suggest that 2024 aligned with observed trends of increasing frequency and intensity of certain disaster types, particularly extreme weather events. This aligns with climate change projections.
Question 2: Which geographic regions were most significantly impacted by natural disasters in 2024?
Several regions experienced significant impacts from various disaster types in 2024. [Region A] faced devastating floods due to unusually intense rainfall, while [Region B] experienced prolonged drought conditions leading to widespread wildfires. [Region C] was impacted by a major earthquake. These are just a few examples; a comprehensive global assessment is necessary to fully understand the distribution of impacts.
Question 3: What role did climate change play in the 2024 natural disasters?
Scientific evidence increasingly points to climate change as a contributing factor to the increased frequency and intensity of certain types of natural disasters. Higher global temperatures exacerbate heatwaves, alter precipitation patterns, contribute to sea-level rise, and can intensify storms. Attributing specific events solely to climate change requires detailed analysis, but its influence on the overall trend is undeniable.
Question 4: How effective were early warning systems in mitigating the impact of 2024 disasters?
Early warning systems undoubtedly saved lives and reduced losses in several instances. However, effectiveness varied depending on factors such as the specific hazard, the region’s infrastructure, and community preparedness. Technological advancements continued to improve warning accuracy, but challenges remain in ensuring timely dissemination and community response, especially in vulnerable regions.
Question 5: What lessons were learned from the natural disasters of 2024?
The events of 2024 highlighted the critical importance of integrating disaster risk reduction into all aspects of planning and development. Investing in resilient infrastructure, strengthening early warning systems, enhancing community preparedness, and addressing the underlying drivers of vulnerability, such as climate change, are crucial for mitigating future risks.
Question 6: What are the long-term implications of the 2024 disasters?
Long-term implications include not only the physical and economic recovery but also the psychosocial impacts on affected communities. Addressing the mental health needs of survivors, rebuilding social and economic structures, and learning from these events to enhance resilience are crucial for the long-term well-being of communities and nations.
Understanding the events of 2024 and addressing these frequently asked questions are crucial steps toward improving disaster preparedness and building more resilient communities in the face of future challenges.
The following section delves into specific case studies to provide a deeper understanding of the complexities and challenges associated with managing natural disasters in the context of a changing global environment. These case studies offer valuable lessons for informing future disaster risk reduction efforts.
Natural Disasters 2024
Analysis of natural disasters in 2024 reveals significant trends impacting global communities. The year underscored the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, influenced by ongoing climate change. Examining the geographic distribution of these events highlighted regional vulnerabilities, while impact assessments provided crucial data for recovery and mitigation efforts. The effectiveness of early warning systems, though demonstrably life-saving in many instances, revealed persistent challenges in communication and community preparedness. Furthermore, the economic consequences of these disasters emphasized the need for robust disaster risk financing and resilient infrastructure. Community resilience, driven by social cohesion, economic diversification, and proactive planning, proved essential in mitigating impacts.
The events of 2024 serve as a stark reminder of the urgent need for comprehensive and proactive approaches to disaster risk reduction. Continued investment in resilient infrastructure, strengthened early warning systems, and community-based preparedness initiatives are crucial. Addressing the underlying drivers of vulnerability, particularly climate change, is paramount. The lessons learned from 2024 must inform future policies and actions to build more resilient communities and safeguard against the escalating risks posed by natural hazards in a changing world.