The Alamo City, while boasting a vibrant culture and rich history, faces potential threats from various severe weather events. These range from extreme temperatures and droughts to flooding, hailstorms, and tornadoes. Less frequent, but still possible, are wildfires and seismic activity. Understanding the specific risks associated with each hazard is crucial for residents and visitors.
Preparedness for these events is essential for community safety and resilience. Historical records demonstrate the impact of past events, such as the devastating 1921 flood and periods of intense drought, underscoring the need for proactive measures. Mitigating potential damage and ensuring rapid response and recovery are vital for minimizing disruption and protecting lives and property. This requires ongoing public awareness campaigns, robust infrastructure development, and effective emergency management strategies.
This information will explore specific hazards in greater detail, outlining their characteristics, potential impact, and appropriate safety measures. Furthermore, it will delve into the city’s preparedness initiatives, available resources, and community involvement in disaster mitigation and response.
Disaster Preparedness Tips for San Antonio
Proactive measures can significantly reduce risks associated with severe weather events. The following recommendations offer practical guidance for residents and visitors to enhance personal safety and community resilience.
Tip 1: Develop a Family Emergency Plan: Establish a communication plan, including designated meeting points and out-of-town contacts. Practice the plan regularly.
Tip 2: Assemble an Emergency Kit: Include essential supplies such as water, non-perishable food, first-aid supplies, medications, flashlights, batteries, and a NOAA weather radio.
Tip 3: Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and alerts through local news, NOAA weather radio, and official city communication channels.
Tip 4: Understand Evacuation Routes: Familiarize oneself with designated evacuation routes and procedures specific to the area.
Tip 5: Protect Property: Secure loose items outdoors, trim trees near structures, and consider flood insurance if residing in a flood-prone area.
Tip 6: Conserve Water During Droughts: Implement water conservation practices such as limiting outdoor watering and repairing leaks promptly.
Tip 7: Learn Basic First Aid and CPR: Possessing these skills can prove invaluable during emergencies.
Adopting these preventative measures significantly increases preparedness for various hazards, promoting individual and community safety.
By understanding the specific risks and implementing these strategies, individuals can contribute to a more resilient community, better equipped to navigate and recover from the impacts of severe weather.
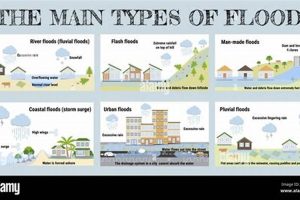
1. Flooding
Flooding represents a significant natural disaster threat to San Antonio. The city’s location within the Balcones Escarpment, coupled with rapid urbanization and impervious surfaces, creates conditions conducive to flash flooding. Heavy rainfall events, particularly during the hurricane season, can overwhelm drainage systems and lead to rapid water level rises in creeks and rivers. Low-lying areas and those near waterways are particularly vulnerable. The consequences can include property damage, infrastructure disruption, displacement of residents, and even loss of life. The 1921 San Antonio flood serves as a stark reminder of the devastating potential of such events, resulting in significant loss of life and widespread property destruction. More recently, significant flooding events in 2013 and 2018 caused substantial damage and highlighted the ongoing vulnerability.
Understanding the specific flood risks within San Antonio is crucial for effective mitigation and response. Factors such as soil type, topography, and proximity to drainage systems influence flood susceptibility. Detailed flood maps, available through resources like the National Flood Insurance Program, delineate areas at varying risk levels. These resources assist residents and city planners in making informed decisions regarding development, infrastructure improvements, and emergency preparedness. Implementing strategies such as improved drainage infrastructure, flood control dams, and early warning systems can significantly reduce flood risk and enhance community resilience.
Addressing flood risk in San Antonio requires a multi-faceted approach incorporating infrastructure improvements, public awareness campaigns, and effective emergency response protocols. Recognizing the dynamic nature of flood risk due to changing weather patterns and urban development, ongoing assessment and adaptation of mitigation strategies are essential. Collaboration between governmental agencies, community organizations, and residents is vital for creating a more flood-resilient city and safeguarding lives and property.
2. Drought
Drought poses a significant and recurring threat to San Antonio, impacting water resources, increasing wildfire risk, and stressing the regional ecosystem. While less immediately dramatic than floods or severe storms, extended periods of drought can have profound and lasting consequences. Understanding drought’s complex interplay with other natural hazards and human activities is crucial for effective mitigation and adaptation.
- Water Stress
Reduced rainfall and high temperatures deplete water reservoirs and aquifers, stressing the region’s water supply. This impacts agriculture, industry, and residential water use, necessitating water conservation measures and potentially leading to economic hardship. The Edwards Aquifer, a primary water source for San Antonio, is particularly vulnerable to drought conditions. Its recharge rate is directly affected by rainfall, and prolonged drought can lead to significant declines in water levels, triggering restrictions and impacting various sectors of the economy.
- Wildfire Risk
Dry vegetation and parched landscapes create ideal conditions for wildfires, which can spread rapidly and pose significant threats to life and property. Drought exacerbates this risk, making vegetation more flammable and increasing the intensity and duration of wildfires. The urban-wildland interface areas surrounding San Antonio are particularly susceptible. These areas, where human development meets natural landscapes, experience increased fire risk due to the proximity of flammable vegetation to homes and infrastructure.
- Ecosystem Impacts
Extended periods of drought stress native vegetation, impacting local ecosystems and wildlife. Reduced water availability affects plant growth and survival, disrupting food chains and impacting biodiversity. The sensitive ecosystems within and around San Antonio, including the Hill Country and riparian areas, are particularly vulnerable. Drought can lead to habitat loss, reduced wildlife populations, and increased susceptibility to invasive species, impacting the overall ecological health of the region.
- Economic Consequences
Drought can have cascading economic impacts. Agricultural losses due to reduced crop yields affect farmers and food prices. Water restrictions impact businesses reliant on water, and increased energy demands for water pumping strain power grids. Tourism can also suffer as natural attractions are impacted by drought conditions. These economic consequences underscore the importance of drought preparedness and proactive mitigation strategies.
The multifaceted impacts of drought highlight its significance as a natural hazard in San Antonio. Integrating drought planning into broader disaster preparedness strategies is essential for building community resilience and mitigating the long-term consequences of this recurring challenge. This includes implementing sustainable water management practices, promoting water conservation, enhancing wildfire preparedness, and protecting vulnerable ecosystems.
3. Severe Storms
Severe storms represent a significant threat within the spectrum of natural disasters affecting San Antonio. These meteorological events, characterized by high winds, heavy rainfall, hail, and the potential for tornadoes, pose substantial risks to life, property, and infrastructure. Understanding the specific characteristics and potential impacts of severe storms in this region is crucial for effective preparedness and mitigation.
- Hailstorms
Hail, often accompanying severe thunderstorms, can cause extensive damage to property, vehicles, and crops. The size and intensity of hailstorms can vary significantly, with large hailstones capable of causing substantial structural damage and posing a threat to personal safety. San Antonio’s location within a hail-prone region necessitates robust building codes and insurance coverage to mitigate potential losses. Frequent hailstorms can strain local resources and disrupt daily life.
- Tornadoes
While less frequent than hailstorms, tornadoes pose a considerable threat due to their destructive potential. These violently rotating columns of air can cause catastrophic damage along their paths, impacting homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure. While San Antonio is not located within the traditional “Tornado Alley,” the city has experienced tornadoes in the past, underscoring the need for preparedness. Early warning systems and community education are essential for minimizing casualties and property damage.
- High Winds
Severe thunderstorms often generate strong winds capable of downing trees, power lines, and damaging structures. These winds can disrupt transportation, cause widespread power outages, and create hazardous conditions. Preparing for high wind events includes securing loose objects outdoors, reinforcing weak structures, and having a plan for extended power outages. Understanding the potential for wind damage is crucial for minimizing disruptions and ensuring community safety.
- Lightning
Lightning strikes, a common occurrence during severe storms, pose a significant threat of fire and electrocution. Protecting individuals and property from lightning requires taking precautions such as seeking shelter indoors during thunderstorms, avoiding contact with metal objects, and installing lightning protection systems. Public awareness campaigns emphasizing lightning safety are vital for preventing injuries and fatalities.
The various facets of severe storms contribute significantly to the overall natural disaster risk profile of San Antonio. Implementing comprehensive preparedness strategies, including early warning systems, robust building codes, and community education programs, is crucial for minimizing the impact of these events and fostering community resilience. By understanding the specific threats posed by severe storms, individuals and communities can take proactive steps to protect lives, property, and maintain essential services during these hazardous weather events.
4. Extreme Heat
Extreme heat is a significant natural hazard in San Antonio, posing substantial risks to public health and stressing critical infrastructure. While often overlooked compared to more visually dramatic events like floods or tornadoes, extended periods of extreme heat can have severe consequences, particularly for vulnerable populations. Understanding the specific challenges posed by extreme heat in San Antonio requires examining its multifaceted impacts and the city’s preparedness strategies.
- Public Health Impacts
High temperatures, especially when combined with high humidity, can lead to heat exhaustion, heat stroke, and other heat-related illnesses. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly, children, individuals with chronic illnesses, and those experiencing homelessness, are particularly susceptible. Extreme heat events can strain healthcare systems and increase mortality rates. Public awareness campaigns emphasizing heat safety measures and providing access to cooling centers are crucial for protecting public health during these periods.
- Infrastructure Strain
Extreme heat places significant stress on critical infrastructure, particularly the power grid. Increased demand for air conditioning can lead to power outages, further exacerbating the health risks associated with extreme heat. The aging infrastructure in some areas of San Antonio can be particularly vulnerable to these stresses. Investing in grid resilience and implementing energy efficiency measures are crucial for mitigating the impacts of extreme heat on essential services.
- Economic Impacts
Extreme heat can disrupt economic activity, impacting outdoor industries such as construction, agriculture, and tourism. Reduced worker productivity and increased absenteeism can lead to economic losses. Heat-related damage to infrastructure, including roads and bridges, can also disrupt transportation and commerce. Implementing adaptive strategies, such as adjusting work schedules and providing heat-resilient infrastructure, is essential for minimizing economic disruptions.
- Environmental Impacts
Extreme heat exacerbates drought conditions by increasing evaporation rates and stressing vegetation. This can lead to increased wildfire risk and further strain water resources. The urban heat island effect, where urban areas experience higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas, intensifies these impacts. Implementing strategies to mitigate the urban heat island effect, such as increasing green spaces and using reflective roofing materials, can help reduce the environmental consequences of extreme heat.
The multifaceted nature of extreme heat’s impacts underscores its significance as a natural hazard in San Antonio. Integrating heat preparedness into broader disaster management plans is crucial for safeguarding public health, maintaining essential services, and minimizing economic disruptions. Proactive measures, including community outreach, infrastructure improvements, and urban planning strategies, are essential for building a more heat-resilient city and protecting vulnerable populations from the increasing threat of extreme heat events.
5. Wildfires
While not as immediately prominent as flooding or severe storms, wildfires represent a significant and growing threat within the natural disaster landscape of San Antonio. The convergence of factors such as drought, increasing temperatures, and the expansion of the wildland-urban interface creates conditions conducive to wildfire ignition and rapid spread. Understanding the specific risks associated with wildfires and their potential impact on the city is crucial for effective preparedness and mitigation.
- Fuel Availability and Drought
Extended periods of drought desiccate vegetation, creating abundant fuel for wildfires. The prevalence of flammable grasses and brush in the region, coupled with drought conditions, significantly increases the risk of ignition and rapid fire spread. The intensity and duration of droughts directly influence fuel loads and contribute to the severity of wildfire seasons. Effective land management practices, including prescribed burns and vegetation thinning, can help reduce fuel availability and mitigate wildfire risk.
- Urban-Wildland Interface Expansion
The expansion of residential areas into previously undeveloped wildlands creates the wildland-urban interface, increasing the potential for interactions between human activities and wildfire. This proximity of homes and infrastructure to flammable vegetation elevates the risk of property damage and loss of life during wildfire events. Implementing fire-resistant building materials and landscaping practices within these interface areas is essential for minimizing risk.
- Climate Change Influences
Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns associated with climate change are projected to exacerbate wildfire risk in the San Antonio region. Increased temperatures contribute to drier conditions and higher fuel loads, while altered precipitation patterns can prolong drought periods. Understanding these long-term trends and incorporating them into wildfire management strategies is crucial for adapting to evolving risks.
- Impact on Air Quality and Public Health
Wildfires generate significant smoke and particulate matter, impacting air quality and posing respiratory health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations. Smoke plumes can travel long distances, affecting air quality in urban areas and exacerbating existing respiratory conditions. Monitoring air quality during wildfire events and providing public health advisories are essential for protecting community health.
The increasing threat of wildfires necessitates a comprehensive approach to mitigation and preparedness in San Antonio. Integrating wildfire risk assessments into urban planning, implementing effective land management practices, and promoting public awareness of wildfire safety are crucial steps in protecting lives, property, and the surrounding environment. By recognizing the complex interplay of factors contributing to wildfire risk, the community can proactively address this growing challenge and enhance overall resilience in the face of natural disasters.
Frequently Asked Questions about Natural Disasters in San Antonio
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the range of natural hazards affecting San Antonio, providing concise and informative responses based on available data and expert recommendations.
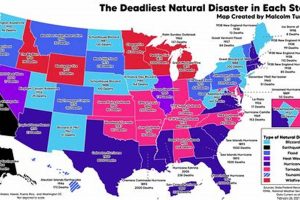
Question 1: What is the most common natural disaster in San Antonio?
Flash flooding is historically the most frequent natural disaster impacting San Antonio, exacerbated by the city’s topography and rapid urbanization. However, drought and extreme heat also pose significant recurring threats.
Question 2: How does the Edwards Aquifer impact San Antonio’s vulnerability to drought?
The Edwards Aquifer, a primary water source for the region, is highly susceptible to drought conditions. Reduced recharge rates during extended dry periods can lead to water shortages and restrictions, impacting various sectors of the economy and daily life.
Question 3: Is San Antonio at risk for tornadoes?
While not located within “Tornado Alley,” San Antonio has experienced tornadoes and remains at risk. Preparedness, including early warning systems and community education, is crucial for mitigating potential damage and loss of life.
Question 4: What are the primary risks associated with extreme heat in San Antonio?
Extreme heat poses significant public health risks, particularly to vulnerable populations. Heat-related illnesses, increased energy demands, and infrastructure strain are key concerns during extended heat waves. Access to cooling centers and public awareness campaigns are essential for mitigating these risks.
Question 5: How does wildfire risk in San Antonio relate to drought conditions?
Drought significantly increases wildfire risk by creating dry vegetation that serves as fuel. The combination of drought, high temperatures, and wind can lead to rapid wildfire spread, threatening lives, property, and air quality.
Question 6: Where can residents find reliable information about natural disaster preparedness in San Antonio?
The City of San Antonio’s Office of Emergency Management website, along with resources from the National Weather Service and the American Red Cross, provide valuable information on preparedness measures specific to the region’s various hazards.
Understanding the specific risks associated with each hazard and adopting proactive measures are crucial for individual and community safety. Preparedness enhances resilience and minimizes the impact of natural disasters.
For further detailed information and resources, continue to the next section which outlines specific preparedness steps for each major hazard.
Natural Disasters in San Antonio
This exploration has highlighted the diverse range of natural hazards impacting San Antonio, from the frequent threat of flooding and the recurring challenge of drought to the potential for severe storms, extreme heat, and wildfires. Understanding the specific characteristics of each hazard, coupled with recognizing the city’s unique vulnerabilities due to topography, rapid urbanization, and reliance on the Edwards Aquifer, is fundamental to effective disaster preparedness and mitigation.
Proactive measures, including robust infrastructure development, comprehensive emergency management plans, community education initiatives, and individual preparedness actions, are essential for building a resilient community. Addressing these challenges requires ongoing assessment of evolving risks, adaptation to changing climate conditions, and collaborative efforts among governmental agencies, community organizations, and residents. Ultimately, a proactive and informed approach to natural disaster preparedness is crucial for safeguarding lives, protecting property, and ensuring the long-term sustainability and well-being of San Antonio.