The city of Portland, Oregon, faces potential threats from various geophysical and meteorological events. These range from infrequent but high-impact occurrences like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions to more common hazards such as flooding, wildfires, and severe storms. Landslides, often triggered by heavy rainfall or seismic activity, also pose a risk to the region. Understanding these diverse threats is crucial for effective preparedness and mitigation strategies.
Preparedness for these diverse hazards is vital for the safety and resilience of Portland’s residents and infrastructure. Historically, the region has experienced significant floods, winter storms, and wildfires, underscoring the need for robust emergency plans and community education. Mitigation efforts, including building codes designed to withstand seismic activity and land use planning that minimizes risk in floodplains and wildfire-prone areas, contribute to long-term community safety and reduce potential economic losses.
This article will delve into the specific hazards facing Portland, exploring the science behind them, the potential impact on the community, and the steps individuals and the city can take to prepare and mitigate risks. Topics covered will include earthquake preparedness, flood zone mapping, wildfire prevention strategies, and emergency response resources available to residents.
Preparedness Tips for Portland, Oregon
Residents can take proactive steps to mitigate risks and enhance personal safety in the face of potential hazards.
Tip 1: Develop an Emergency Plan: Create a household emergency plan that includes communication strategies, evacuation routes, and designated meeting points. This plan should account for the specific needs of all household members, including pets.
Tip 2: Build an Emergency Kit: Assemble a kit containing essential supplies such as water, non-perishable food, first-aid materials, flashlights, a battery-powered radio, and extra batteries. This kit should be readily accessible and sufficient to sustain household members for several days.
Tip 3: Sign Up for Emergency Alerts: Register for local emergency alert systems to receive timely notifications about impending threats and evacuation orders. Familiarize oneself with various communication channels used by local authorities.
Tip 4: Know Your Evacuation Routes: Identify primary and secondary evacuation routes from your home and workplace. Practice these routes to ensure familiarity and efficiency in the event of an evacuation order.
Tip 5: Secure Your Property: Take steps to secure your property against potential damage from wind, flooding, or earthquakes. This may include reinforcing roofing, anchoring large furniture, and trimming trees near power lines.
Tip 6: Understand Insurance Coverage: Review insurance policies to ensure adequate coverage for potential hazards. Consider flood insurance, even if residing outside designated floodplains, as flooding can occur in various circumstances.
Tip 7: Participate in Community Preparedness Events: Attend community workshops and drills focused on disaster preparedness. These events provide valuable information and practical skills that can enhance personal safety and community resilience.
By taking these preparatory actions, individuals contribute to their own safety and the overall resilience of the community in the event of a disaster. These measures are essential for minimizing potential harm and fostering a culture of preparedness.
The following section will delve deeper into specific disaster scenarios, providing detailed information about the unique characteristics of each threat and tailored preparedness strategies.
1. Earthquakes
Portland, Oregon, faces a significant earthquake risk due to its proximity to the Cascadia Subduction Zone. This zone, where the Juan de Fuca plate subducts beneath the North American plate, has the potential to generate large-magnitude earthquakes. Geological records indicate the zone has produced megathrust earthquakes in the past, with the most recent occurring in 1700. The potential impact of a major earthquake on Portland includes widespread structural damage to buildings and infrastructure, disruptions to transportation and communication networks, and the triggering of secondary hazards such as landslides and tsunamis. Understanding the seismic hazard posed by the Cascadia Subduction Zone is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies and enhancing community resilience.
The specific effects of an earthquake in Portland would depend on the magnitude, depth, and location of the event. Factors such as soil conditions and building construction also influence vulnerability to damage. While building codes have improved over time to incorporate seismic design principles, older structures may be more susceptible to damage. Furthermore, the liquefaction potential of certain soil types poses a significant risk to infrastructure stability during an earthquake. Preparedness measures such as securing heavy objects, developing evacuation plans, and reinforcing building structures are critical for mitigating potential losses.
Mitigating earthquake risks requires a multi-faceted approach. Strengthening building codes and retrofitting existing structures to enhance seismic resistance is essential. Public awareness campaigns and educational programs can equip residents with the knowledge and skills needed to respond effectively during an earthquake. Developing robust emergency response plans and conducting regular drills are crucial for ensuring a coordinated and efficient response in the aftermath of a major seismic event. Continued research and monitoring of the Cascadia Subduction Zone contribute to a better understanding of the seismic hazard and inform effective mitigation strategies.
2. Flooding
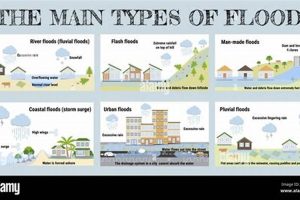
Flooding poses a significant threat to Portland, Oregon, stemming from various sources. The Willamette and Columbia Rivers, which converge near the city, are prone to seasonal flooding, particularly during periods of heavy rainfall and snowmelt. Urbanization contributes to increased runoff, exacerbating flood risks in low-lying areas. Coastal flooding, driven by storm surges and high tides, also presents a concern, particularly during severe weather events. Furthermore, localized flooding can occur due to inadequate drainage systems and the blockage of waterways by debris.
Historical flood events, such as the Vanport Flood of 1948, highlight the devastating impact flooding can have on the city. The Vanport Flood, caused by a combination of heavy snowmelt and rainfall, resulted in significant loss of life and property, underscoring the importance of flood preparedness and mitigation measures. More recent flood events, while less catastrophic, have continued to cause disruptions and economic losses, emphasizing the ongoing need for effective flood management strategies. These strategies include levee maintenance, improved drainage systems, and land-use planning that restricts development in flood-prone areas. Understanding historical flood patterns and incorporating climate change projections into flood risk assessments are crucial for developing effective long-term mitigation plans.
Addressing flood risks in Portland requires a comprehensive approach involving infrastructural improvements, community education, and emergency preparedness. Investing in robust flood defenses, such as levees and floodwalls, can protect vulnerable areas. Public awareness campaigns can educate residents about flood risks and promote individual preparedness measures, such as developing evacuation plans and assembling emergency kits. Implementing early warning systems and improving flood forecasting capabilities can provide timely alerts to residents, enabling them to take appropriate action. Continued research and monitoring of hydrological conditions and climate change impacts are essential for informing adaptive flood management strategies and enhancing community resilience.
3. Wildfires
While not traditionally considered a primary threat to Portland, Oregon itself, wildfires represent an increasing concern due to the confluence of urban development and wildland areas in the surrounding region. The increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires, driven by climate change and prolonged periods of drought, pose a significant risk to air quality, public health, and the surrounding natural environment. Understanding wildfire behavior and developing effective mitigation strategies are critical for protecting the city and its inhabitants from the impacts of these events.
- Proximity to Wildland-Urban Interface (WUI)
Portland’s location near the WUI, where urban development meets forested areas, increases the city’s vulnerability to wildfire impacts. While wildfires may not originate within city limits, smoke and ash can be carried by wind, impacting air quality and posing health risks to residents, particularly those with respiratory conditions. Embers carried by wind can also ignite fires in urban areas, creating a direct threat to property and infrastructure. Managing vegetation in the WUI and implementing fire-resistant building materials in new construction are critical mitigation strategies.
- Impact on Air Quality
Wildfire smoke contains particulate matter and hazardous gases that can significantly degrade air quality, posing respiratory and cardiovascular health risks. During wildfire events, Portland has experienced days with unhealthy air quality levels, prompting public health advisories and impacting daily activities. Improving air quality monitoring and developing public health response plans are essential for mitigating the health impacts of wildfire smoke.
- Strain on Emergency Response Resources
Large wildfires in the region can strain emergency response resources, potentially diverting personnel and equipment from other emergencies within the city. Coordinating regional response efforts and ensuring adequate resources are available are crucial for effectively managing wildfire events and minimizing impacts on the city’s overall emergency response capabilities.
- Economic Impacts
Wildfire smoke and associated health impacts can lead to decreased productivity, business closures, and disruptions to tourism, impacting the local economy. Investing in wildfire prevention and mitigation efforts can minimize these economic losses and contribute to long-term economic stability.
Addressing the wildfire threat to Portland requires a regional approach that incorporates forest management practices, community preparedness measures, and public health interventions. Promoting responsible land management in the WUI, enhancing early warning systems, and developing community evacuation plans are crucial components of a comprehensive wildfire mitigation strategy. Furthermore, investing in public health infrastructure, such as clean air shelters and public awareness campaigns, can minimize the health impacts of wildfire smoke. By proactively addressing these challenges, Portland can enhance its resilience to the growing threat of wildfires and protect the health and well-being of its residents.
4. Landslides
Landslides represent a significant natural hazard in Portland, Oregon, due to the region’s topography, geology, and climate. The city’s hilly terrain, combined with areas of unstable soil and bedrock, creates conditions conducive to landslides. Heavy rainfall, a characteristic of the Pacific Northwest climate, can saturate the soil, increasing its weight and reducing its strength, thus triggering slope failures. Seismic activity, such as earthquakes along the Cascadia Subduction Zone, can also destabilize slopes and induce landslides. The consequences of landslides can range from property damage and infrastructure disruption to loss of life.
Several factors contribute to landslide susceptibility in the Portland area. The presence of marine sedimentary rocks and volcanic deposits, which are prone to weathering and erosion, increases the instability of slopes. Deforestation and urbanization can further exacerbate landslide risks by altering natural drainage patterns and increasing surface runoff. Specific areas within Portland, particularly those located on steep slopes or near rivers and streams, are identified as having higher landslide susceptibility. Mapping these high-risk areas and implementing land-use regulations that restrict development in these zones are crucial mitigation strategies. Examples of historical landslides in the region, such as the 1996 landslide in the West Hills, underscore the destructive potential of these events and the importance of proactive mitigation measures.
Mitigating landslide risks in Portland requires a multi-faceted approach that incorporates geological assessments, engineering solutions, and community education. Conducting thorough geotechnical investigations to identify unstable slopes and assess landslide hazards is a crucial first step. Implementing engineering solutions, such as retaining walls, slope stabilization techniques, and improved drainage systems, can enhance slope stability and reduce landslide risks. Educating residents about landslide warning signs and preparedness measures can empower individuals to take appropriate actions to protect themselves and their property. Monitoring weather conditions and implementing early warning systems can provide timely alerts to residents in high-risk areas, enabling them to evacuate if necessary. Integrating landslide hazard assessments into urban planning and development decisions is essential for minimizing future risks and promoting sustainable development in the Portland area.
5. Volcanic Eruptions
While not an immediate threat, volcanic eruptions pose a long-term risk to Portland, Oregon, primarily due to the presence of Mount Hood, an active stratovolcano located approximately 50 miles east of the city. Although Mount Hood’s last major eruptive period ended in the late 18th century, the volcano remains active and has the potential for future eruptions. Understanding the potential hazards associated with a volcanic eruption is crucial for developing effective preparedness and mitigation strategies.
- Ashfall
A significant eruption of Mount Hood could deposit substantial ashfall across the Portland metropolitan area. Ashfall can disrupt transportation systems, grounding aircraft and making roads hazardous. It can also contaminate water supplies, damage infrastructure, and pose respiratory health risks. The thickness of ash accumulation, coupled with its abrasive and corrosive properties, can severely impact power grids and communication networks. Preparedness measures such as having N95 masks readily available and understanding procedures for cleaning ashfall are crucial.
- Lahars
Lahars, or volcanic mudflows, are a significant hazard associated with Mount Hood. These rapidly flowing mixtures of water, rock, and volcanic debris can be triggered by eruptions, melting snow and ice, or heavy rainfall on unstable volcanic slopes. Lahars can travel considerable distances downstream, potentially impacting communities along river valleys. Mapping lahar inundation zones and developing evacuation plans for at-risk areas are critical mitigation strategies.
- Pyroclastic Flows
While less likely to directly impact Portland due to the distance from Mount Hood, pyroclastic flows are a devastating volcanic hazard. These fast-moving currents of hot gas and volcanic material can incinerate everything in their path. Monitoring volcanic activity and understanding the potential reach of pyroclastic flows is crucial for ensuring public safety in areas closer to the volcano.
- Long-Term Impacts
Beyond the immediate impacts of an eruption, volcanic activity can have long-term consequences for the environment and the economy. Ashfall can disrupt agricultural activities and damage ecosystems. Volcanic gases released during eruptions can contribute to air pollution and climate change. Developing long-term recovery plans and incorporating volcanic hazard assessments into land-use planning are essential for mitigating these long-term impacts.
Considering the potential impacts of a Mount Hood eruption is a vital component of comprehensive disaster preparedness for the Portland metropolitan area. Integrating volcanic hazard assessments into emergency response plans, promoting public awareness about volcanic risks, and coordinating regional preparedness efforts are essential for enhancing community resilience in the face of this potential threat. While the probability of a major eruption in the near future remains low, proactive planning and preparedness measures are crucial for mitigating potential losses and ensuring the long-term safety and well-being of the region’s inhabitants.
6. Severe Storms
Severe storms represent a significant component of the natural hazard landscape in Portland, Oregon. While the region may not experience the same frequency of extreme weather events as other parts of the United States, severe storms can still generate substantial impacts, including high winds, heavy rainfall, flooding, landslides, and power outages. Understanding the specific characteristics and potential consequences of severe storms in the Portland area is crucial for effective preparedness and mitigation.
- High Winds
Strong winds associated with severe storms can down trees, damage power lines, and disrupt transportation. Windstorms can occur throughout the year but are more frequent during the fall and winter months. The topography of the region, with hills and valleys channeling wind flow, can exacerbate wind speeds in certain areas. Past windstorms have resulted in widespread power outages, property damage, and transportation disruptions, highlighting the importance of securing loose objects and preparing for potential power losses during severe weather events.
- Heavy Rainfall
Intense rainfall associated with severe storms can lead to flash flooding, particularly in urban areas with impervious surfaces. Localized flooding can inundate streets and basements, disrupt transportation networks, and overwhelm drainage systems. The combination of heavy rainfall and steep slopes in certain parts of Portland increases the risk of landslides. Effective stormwater management practices and public awareness of flood risks are crucial for minimizing the impacts of heavy rainfall events.
- Thunderstorms and Lightning
While less frequent than in other regions, thunderstorms can occur in Portland, bringing with them the risk of lightning strikes. Lightning can ignite fires, damage electrical equipment, and pose a direct threat to human safety. Implementing lightning protection measures and seeking shelter during thunderstorms are essential safety precautions. Furthermore, the combination of lightning and dry vegetation during the summer months increases the risk of wildfires.
- Ice Storms
Freezing rain events can create hazardous conditions, coating surfaces with ice and leading to power outages, transportation disruptions, and an increased risk of falls. The weight of accumulated ice can break tree branches and down power lines, leading to widespread power outages that can last for several days. Preparing for potential power outages and exercising caution when traveling during icy conditions are essential safety measures.
The diverse nature of severe storms and their potential cascading impacts underscore the importance of comprehensive preparedness strategies in Portland. Developing community-wide emergency plans, investing in resilient infrastructure, and promoting public awareness about severe weather risks are critical for mitigating potential losses and enhancing community resilience in the face of these events. By understanding the specific threats posed by severe storms and taking proactive steps to prepare, Portland can minimize disruptions and protect the safety and well-being of its residents.
Frequently Asked Questions about Natural Hazards in Portland, Oregon
This section addresses common inquiries regarding potential natural hazards affecting Portland, Oregon. Understanding these risks is crucial for informed preparedness and community resilience.
Question 1: What is the biggest natural disaster threat to Portland?
While several hazards pose risks, a Cascadia Subduction Zone earthquake presents the most significant potential for widespread devastation due to its potential magnitude and the ensuing secondary hazards like tsunamis and landslides. However, other hazards like flooding, wildfires, and severe storms require equal consideration in preparedness planning.
Question 2: How often do major natural disasters occur in Portland?
The frequency of major events varies depending on the specific hazard. While significant Cascadia earthquakes occur on a timescale of centuries, floods and severe storms are more frequent occurrences. Landslides and wildfires, influenced by factors like rainfall and drought, can also pose regular threats.
Question 3: Is flood insurance necessary in Portland, even if not living near a river?
Flood insurance is advisable even for properties outside designated floodplains. Localized flooding can occur due to heavy rainfall, inadequate drainage systems, or other factors. Assessing individual property risk and consulting with insurance professionals is recommended.
Question 4: What early warning systems are in place for natural disasters in Portland?
Various alert systems exist, including Public Alerts, Wireless Emergency Alerts (WEA), and local notification systems. Registering for these alerts and understanding their functionality is crucial for timely warnings.
Question 5: What steps can individuals take to prepare for a natural disaster in Portland?
Essential preparedness measures include developing a household emergency plan, building an emergency kit, understanding evacuation routes, and staying informed about potential hazards through reliable sources like official government websites and local news outlets.
Question 6: What resources are available to Portland residents for disaster preparedness assistance?
The City of Portland’s Bureau of Emergency Management, the American Red Cross, and neighborhood emergency teams offer resources and support for disaster preparedness. Accessing these resources can provide valuable information and assistance in developing personalized preparedness plans.
Preparedness is an ongoing process. Staying informed, engaging with local resources, and proactively planning for various scenarios are essential for individual and community resilience in the face of potential natural hazards.
Continue reading for detailed information on specific disaster preparedness strategies and resources.
Natural Disasters
This exploration of potential natural hazards affecting Portland, Oregon, underscores the region’s vulnerability to a range of threats, from earthquakes and volcanic eruptions to floods, wildfires, landslides, and severe storms. Understanding the specific characteristics of each hazard and their potential cascading impacts is fundamental to effective risk mitigation and community resilience. The historical record of past events serves as a stark reminder of the disruptive power of these natural forces and the ongoing need for vigilance and preparedness. This article has highlighted the importance of proactive measures, from individual preparedness plans and emergency kits to community-wide infrastructure improvements and early warning systems.
The multifaceted nature of natural hazards facing Portland necessitates a comprehensive and collaborative approach to preparedness. Continued investment in scientific research, enhanced monitoring capabilities, and ongoing public education are essential for minimizing potential losses and fostering a culture of resilience. Proactive engagement with available resources, including local government agencies and community organizations, empowers individuals and communities to navigate the complexities of disaster preparedness and build a safer, more resilient future for Portland, Oregon. The imperative to prepare is not merely a civic responsibility; it is a collective investment in the long-term well-being and sustainability of the region.