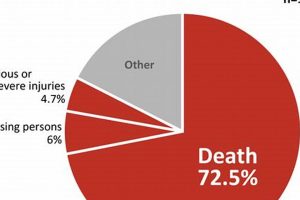
The tragic fire that swept through a Rhode Island nightclub in 2003 during a Great White concert resulted in 100 fatalities and over 200 injuries. Pyrotechnics ignited flammable acoustic foam, rapidly engulfing the venue in flames and toxic smoke. This catastrophic event remains one of the deadliest single-building fires in U.S. history, and the fourth-deadliest nightclub fire in world history. The incident became a case study in fire safety code enforcement and the dangers of pyrotechnics in overcrowded venues.
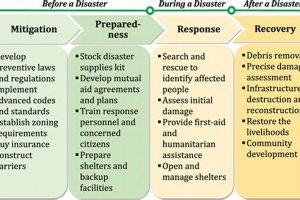
This event prompted widespread changes in fire safety regulations across the United States, including stricter enforcement of existing codes related to occupancy limits, sprinkler systems, and the use of flammable materials in public spaces. The disaster highlighted the critical importance of adequate escape routes and emergency preparedness in entertainment venues. Its legacy continues to shape fire safety practices and building codes nationwide, aiming to prevent similar tragedies.
The following sections will delve deeper into specific aspects of this tragedy, including eyewitness accounts, the legal aftermath, and the long-term impact on fire safety regulations. Further examination will explore the factors contributing to the rapid spread of the fire, the challenges faced by first responders, and the ongoing efforts to improve public safety in similar venues.
Fire Safety Tips for Public Venues
The 2003 Rhode Island nightclub fire provides invaluable lessons in fire safety and prevention. These tips aim to enhance safety awareness and preparedness in similar environments.
Tip 1: Be Aware of Exits: Upon entering any public venue, immediately locate all available exits, including primary and secondary escape routes. Visualize potential escape paths in case of emergency.
Tip 2: Check for Sprinklers and Fire Extinguishers: Note the presence and location of fire suppression systems such as sprinklers and fire extinguishers. Familiarize oneself with their operation if possible.
Tip 3: Report Overcrowding: If a venue appears dangerously overcrowded, report it to management or security personnel. Overcrowding obstructs escape routes and increases risk during emergencies.
Tip 4: Be Cautious of Flammable Materials: Be mindful of potentially flammable decorations or materials within the venue. Report any concerns to venue staff.
Tip 5: React Quickly to Smoke or Fire: If smoke or fire is detected, immediately evacuate the premises using the nearest available exit. Alert others in the vicinity while remaining calm and orderly.
Tip 6: Designate a Meeting Point: When attending events with a group, establish a designated meeting point outside the venue in case of separation during an emergency.
Tip 7: Support Venue Safety Improvements: Advocate for stricter fire safety codes and regulations in public venues. Support businesses that prioritize safety measures and staff training.
Prioritizing fire safety awareness and preparedness can significantly reduce risks in public spaces. Implementing these precautions contributes to a safer environment for everyone.
By understanding the factors that contributed to the Rhode Island nightclub tragedy, individuals and communities can take proactive steps towards preventing future disasters.
1. Pyrotechnics
Pyrotechnics played a pivotal role in the 2003 nightclub fire, directly igniting the chain of events that led to the tragic loss of life. Understanding the specific types of pyrotechnics used, their intended purpose, and the regulatory environment surrounding their use is crucial for comprehending the disaster.
- Type of Pyrotechnics Used
The band Great White used gerb-style pyrotechnics, which produce a shower of sparks. These devices, while visually appealing, pose a significant fire hazard when used in close proximity to flammable materials. In the nightclub, the sparks ignited polyurethane foam used for soundproofing, rapidly spreading flames throughout the venue.
- Intended Purpose and Regulations
The pyrotechnics were intended to enhance the band’s stage performance. However, their use inside the nightclub violated state fire codes, which prohibited indoor pyrotechnic displays without proper permits and safety precautions. The absence of appropriate oversight and adherence to regulations contributed directly to the disaster.
- Interaction with Flammable Materials
The polyurethane foam lining the club’s walls and ceiling was highly flammable. The intense heat generated by the pyrotechnics readily ignited the foam, creating a rapidly spreading fire that produced thick, toxic smoke. This combination of pyrotechnics and flammable materials proved disastrous.
- Consequences of Misuse
The misuse of pyrotechnics in the nightclub had devastating consequences. The rapid spread of the fire, fueled by the flammable foam, overwhelmed the venue’s limited exits and fire suppression capabilities. The resulting inferno and toxic smoke led to extensive loss of life and injuries.
The interplay of these factors the type of pyrotechnics used, their improper deployment in violation of regulations, and their interaction with highly flammable materials directly caused the rapid escalation of the fire and contributed significantly to the tragic outcome. This incident underscores the critical need for strict adherence to fire safety regulations, particularly concerning the use of pyrotechnics in public venues.
2. Flammable Materials
Flammable materials within the nightclub significantly contributed to the rapid spread and intensity of the 2003 fire. Cheap polyurethane foam, used as soundproofing on the walls and ceiling, became the primary fuel source, transforming the venue into a virtual inferno within minutes. This foam, while effective for sound absorption, lacked adequate fire retardant properties. Its widespread use in the club, coupled with the absence of effective fire barriers, created a highly dangerous environment susceptible to rapid fire spread. This particular type of foam, though common at the time, is now largely recognized as a serious fire hazard in public spaces.
The ignition source, pyrotechnics used by the performing band, ignited the foam almost instantly. The ensuing flames spread rapidly across the ceiling and walls, engulfing the entire club in a matter of minutes. The intense heat and thick, toxic smoke generated by the burning foam trapped occupants and contributed significantly to the high number of casualties. This tragedy highlighted the critical role that flammable materials play in accelerating fire spread and underscores the importance of using fire-resistant materials in public venues.
The disaster served as a catalyst for stricter fire codes and regulations regarding the use of flammable materials in public spaces. Many jurisdictions subsequently banned or restricted the use of certain types of foam insulation and mandated the installation of sprinkler systems and other fire suppression measures. The lessons learned from this tragedy emphasize the crucial need for careful consideration and regulation of flammable materials in building design and construction to ensure public safety.
3. Overcrowding
Overcrowding played a critical role in the devastating consequences of the 2003 nightclub fire. The venue’s legal capacity was significantly exceeded on the night of the fire, hindering safe evacuation and contributing to the high number of casualties. Understanding the factors contributing to overcrowding, its impact on escape routes, and the subsequent regulatory changes is crucial for comprehending the magnitude of this tragedy.
- Exceeding Legal Capacity
The nightclub was operating well beyond its legal occupancy limit on the night of the fire. Estimates suggest the crowd size was nearly double the permitted capacity, creating a dangerously congested environment. This severe overcrowding made orderly evacuation nearly impossible once the fire broke out.
- Obstructed Escape Routes
The excessive number of people inside the club significantly obstructed available escape routes. Narrow doorways and limited exits became bottlenecks as panicked patrons attempted to flee the burning building. The overcrowding intensified the chaos and hampered efforts to escape quickly and safely.
- Impact on Emergency Response
Overcrowding also complicated emergency response efforts. First responders faced difficulty accessing the building and navigating the dense crowd to reach those trapped inside. The sheer volume of people requiring assistance overwhelmed initial rescue attempts.
- Regulatory Changes and Enforcement
Following the tragedy, stricter regulations regarding occupancy limits and enforcement were implemented in many jurisdictions. Increased emphasis on fire safety inspections and penalties for exceeding capacity aimed to prevent similar disasters. The disaster underscored the crucial role of occupancy limitations in ensuring public safety.
The overcrowding in the nightclub significantly exacerbated the consequences of the fire, transforming a dangerous situation into a catastrophic tragedy. The lessons learned from this event emphasize the vital importance of adhering to occupancy limits and maintaining clear escape routes in public venues. The subsequent regulatory changes and increased enforcement highlight the ongoing efforts to prevent similar tragedies and prioritize public safety.
4. Inadequate Exits
The insufficient number, size, and accessibility of exits at the nightclub proved tragically inadequate for the large crowd present on the night of the fire, directly contributing to the high casualty count. The configuration of exits, coupled with the rapid spread of fire and smoke, created a deadly bottleneck, trapping many patrons inside. Analyzing the specific shortcomings of the exit arrangements is critical to understanding the extent of the disaster.
- Limited Number of Exits
The nightclub had far too few exits for its maximum occupancy, let alone for the overcrowded conditions on the night of the fire. This limited number of escape routes funneled fleeing patrons into a congested crush, hindering rapid evacuation and increasing panic.
- Inaccessible or Blocked Exits
Some exits were either poorly marked, locked, or obstructed by furniture and equipment, further complicating escape efforts. Patrons unfamiliar with the layout wasted precious time searching for usable exits, while others became trapped behind obstacles.
- Exit Size and Design
The available exits were not designed to accommodate the rapid egress of a large crowd. Narrow doorways and hallways created choke points, slowing down evacuation and increasing the risk of trampling and injury.
- Lack of Emergency Lighting
Insufficient emergency lighting within the club further hampered evacuation efforts in the smoke-filled environment. The lack of clear visibility added to the confusion and panic, making it difficult for patrons to find their way to safety.
The combination of these factors limited exits, inaccessible escape routes, inadequate exit design, and poor emergency lighting created a perfect storm for tragedy. The inadequate exits directly contributed to the high number of fatalities and injuries, demonstrating the critical importance of proper egress planning and design in public venues. The disaster served as a harsh lesson in the devastating consequences of inadequate emergency preparedness and spurred significant changes in fire safety codes and regulations nationwide.
5. Failed Safety Regulations
The 2003 nightclub fire serves as a stark example of the devastating consequences of failed safety regulations. Multiple regulatory failures contributed to the magnitude of the tragedy, highlighting systemic issues within fire safety enforcement and oversight. The absence of proper inspections, inadequate fire code enforcement, and a lack of clear guidelines regarding pyrotechnics and flammable materials all played a crucial role in the disaster.
The venue lacked a mandatory sprinkler system, which could have significantly suppressed the fire’s rapid spread. Existing fire codes required sprinklers, but inadequate enforcement and grandfathering clauses allowed the club to operate without this essential safety feature. Similarly, the use of highly flammable polyurethane foam for soundproofing violated existing fire codes, yet went unaddressed due to insufficient inspections and enforcement. Furthermore, the band’s use of pyrotechnics inside the venue was illegal under state law, yet no mechanisms were in place to prevent such violations.
This confluence of regulatory failures created a dangerous environment ripe for disaster. The absence of adequate fire suppression systems, coupled with the presence of highly flammable materials and the illegal use of pyrotechnics, resulted in a rapidly spreading fire that overwhelmed the limited exit capacity. The tragic outcome underscores the critical importance of robust fire safety regulations, rigorous inspections, and stringent enforcement to protect public safety. The disaster prompted widespread reforms in fire safety codes and enforcement practices nationwide, aiming to prevent similar tragedies from occurring in the future.
6. Legal Ramifications
The legal ramifications of the 2003 nightclub fire were extensive and complex, involving criminal charges, civil lawsuits, and significant changes to fire safety regulations. The disaster exposed critical gaps in regulatory oversight and enforcement, leading to legal action against multiple parties, including the club owners, the band, and town officials. This legal fallout underscores the importance of accountability and the far-reaching consequences of negligence in public safety.
Criminal charges were brought against the club owners and the band’s tour manager for involuntary manslaughter. The owners were ultimately convicted and sentenced to prison, while the tour manager received probation and community service. Numerous civil lawsuits were filed by victims and their families against the club owners, the band, the manufacturers of the flammable foam, and the town. These lawsuits resulted in substantial financial settlements and spurred significant changes in fire safety regulations and enforcement practices.
The legal battles that followed the nightclub fire had a profound impact on fire safety regulations and enforcement practices nationwide. The tragedy exposed the inadequacy of existing regulations and enforcement mechanisms, leading to stricter codes regarding occupancy limits, sprinkler systems, and the use of flammable materials. The legal ramifications also highlighted the importance of thorough inspections and proactive enforcement to prevent future disasters. The case serves as a significant legal precedent, underscoring the responsibility of venue owners, operators, and public officials to ensure the safety of occupants.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common questions about the 2003 nightclub fire, aiming to provide clear and accurate information about this tragic event.
Question 1: What caused the fire?
Pyrotechnics used by the band Great White ignited flammable polyurethane foam used for soundproofing within the club. This combination of an ignition source and highly flammable material resulted in a rapidly spreading fire.
Question 2: How many people died or were injured?
One hundred individuals perished in the fire, and over 200 sustained injuries.
Question 3: Were there any violations of fire codes?
Yes, several fire code violations contributed to the disaster. The club lacked sufficient exits and a required sprinkler system, and the use of pyrotechnics inside the venue violated state law.
Question 4: What legal actions resulted from the fire?
Criminal charges were filed against the club owners and the band’s tour manager. Numerous civil lawsuits were also filed against various parties, including the club owners, the band, and manufacturers of the flammable foam.
Question 5: What changes were made to fire safety regulations after the tragedy?
The disaster led to stricter fire codes nationwide, including requirements for sprinkler systems, improved exit designs, and restrictions on the use of flammable materials in public spaces.
Question 6: What lessons can be learned from this event?
The nightclub fire underscores the critical importance of fire safety awareness, stringent adherence to fire codes, and proactive enforcement of safety regulations to prevent similar tragedies.
Understanding the circumstances surrounding this tragedy and its aftermath emphasizes the need for continued vigilance and proactive safety measures in public venues.
Further resources and in-depth information on the fire can be found through various reputable sources dedicated to documenting this event and its impact on fire safety standards.
Conclusion
The Station Nightclub fire remains a profound tragedy, underscoring the devastating consequences of inadequate fire safety measures and regulatory oversight. The combination of pyrotechnics, highly flammable materials, overcrowding, insufficient exits, and failed safety regulations culminated in a catastrophic loss of life. The event’s legal ramifications led to significant changes in fire codes and enforcement practices, highlighting the importance of accountability and proactive safety measures.
This disaster serves as a sobering reminder of the continuous need for vigilance in public safety. Continued education, stringent adherence to fire codes, and robust enforcement are crucial to preventing future tragedies. Remembering the lives lost compels ongoing efforts to improve fire safety standards and cultivate a culture of proactive prevention in public spaces. The legacy of this event must be a sustained commitment to ensuring safer environments for all.