
A facility established following a significant disruptive event provides essential support to affected individuals and communities. These centers offer a central location for access to vital resources, including information on aid programs,... Read more »
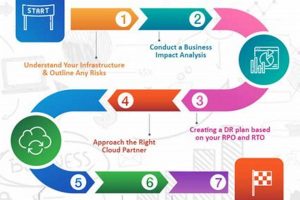
A pre-structured document provides a framework for organizations to restore their IT infrastructure and data in the event of an unforeseen disruption affecting their cloud-based systems. This framework typically includes detailed procedures,... Read more »
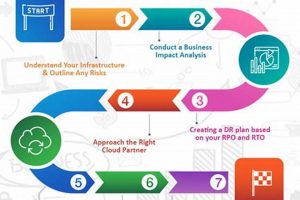
The replication and hosting of information technology (IT) infrastructure in a cloud environment to enable business continuity in the event of a disruption is a crucial aspect of modern business operations. For... Read more »
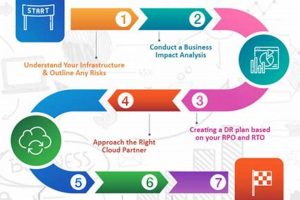
A documented strategy enabling the restoration of IT infrastructure and data housed within a cloud environment following an unplanned outage. This strategy typically involves replicating data and systems to a secondary cloud... Read more »

Restoring information technology infrastructure and operations in North Carolina after a natural or human-made disaster is a critical process. This involves a range of activities, from backing up data and developing contingency... Read more »

Maintaining operational resilience involves two key processes: preparing for disruptive events and restoring operations afterward. The former focuses on developing proactive strategies to minimize disruptions from unforeseen circumstances, such as natural disasters,... Read more »
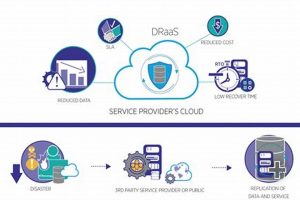
Protecting vital data and ensuring business continuity are paramount concerns for organizations of all sizes. Contingency planning for disruptive events, ranging from natural disasters to cyberattacks, requires robust solutions. Subscribing to a... Read more »
Restoring critical IT systems and operations following disruptive events involves establishing predetermined procedures and infrastructure. These might include failing over to a backup data center in another geographic location when the primary... Read more »

The process of evaluating applications and systems designed to restore data and functionality after unforeseen events like natural disasters, cyberattacks, or hardware failures is critical for business continuity. For example, a simulated... Read more »
A robust plan for business continuity and data protection in the cloud involves establishing resilient systems capable of withstanding outages and quickly restoring services. This typically encompasses a combination of infrastructure and... Read more »


