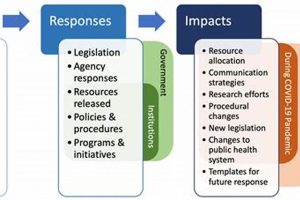
The allocation of resources during the COVID-19 pandemic encompassed a wide range of essential supplies and services. This included medical equipment like ventilators and personal protective equipment (PPE), as well as the... Read more »

Identifying the single “worst” natural disaster in United States history presents a complex challenge. Disasters vary significantly in terms of measurable impacts like fatalities, economic damage, and long-term societal disruption. While the... Read more »

Withdrawals from retirement accounts, like 401(k)s and IRAs, made specifically due to federally declared disasters are often referred to as hardship withdrawals related to qualified disasters. These withdrawals can provide individuals with... Read more »
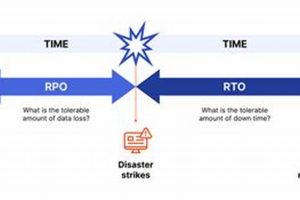
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) are two crucial metrics used in disaster recovery planning. RTO defines the maximum acceptable duration for a system to be offline following a... Read more »

Puerto Rico’s location in the Caribbean renders it vulnerable to a range of natural hazards. The island lies within the Atlantic hurricane belt and is also prone to earthquakes, tsunamis, landslides, and... Read more »

Maryland, while not typically associated with large-scale catastrophic events, faces a range of potential hazards. These include severe storms such as hurricanes and tornadoes, flooding from heavy rainfall and coastal surges, winter... Read more »

Identifying the single “worst” natural disaster in United States history presents a complex challenge. Disasters vary significantly in terms of measurable impacts like fatalities, economic damage, and long-term societal disruption. While the... Read more »

An exclamation expressing a calamitous event or situation, often characterized by widespread destruction, significant loss, or substantial disruption. For instance, a widespread power outage following a hurricane can be described using this... Read more »

The fundamental goal of such a plan is to ensure business continuity in the face of disruptive events. This involves outlining procedures to restore critical IT infrastructure and business processes, minimizing downtime... Read more »



