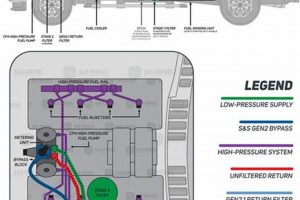
The Bosch CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump, commonly used in 2011-2016 Ford 6.7L Powerstroke diesel engines (such as those found in the 2015 F-250), has a known vulnerability to fuel contamination. Because even microscopic contaminants can damage the precisely machined components within the CP4.2, leading to catastrophic failure, preventative measures are crucial. A proactive approach typically involves a combination of strategies, including enhanced fuel filtration, regular fuel system maintenance, and the use of fuel additives designed to lubricate and protect the pump. These strategies, when implemented together, function as a safeguard against potential fuel system issues.
Protecting the fuel system in these trucks is paramount. The CP4.2 pump is a critical component, and its failure can result in costly repairs, extensive downtime, and potential damage to other engine parts. A proactive maintenance approach significantly reduces the risk of such failure, preserving the engine’s longevity and reliability. Given the known vulnerability of this particular pump, a comprehensive preventative strategy provides substantial peace of mind and long-term cost savings for owners of affected vehicles. Preventing these issues is significantly more cost-effective than addressing a major failure after it occurs.
This article will explore the various components of a comprehensive preventative maintenance plan for the 6.7L Powerstroke engine, including detailed information on fuel filtration options, recommended maintenance schedules, effective fuel additives, and diagnostic procedures. It will also delve into the specific vulnerabilities of the CP4.2 pump and the mechanics of its failure, offering a thorough understanding of the importance of preventative care.
Preventative Maintenance Tips for the 6.7L Powerstroke CP4.2 Fuel System
Maintaining the fuel system in a 2011-2016 6.7L Powerstroke diesel engine requires diligence and a proactive approach. The following tips offer guidance on preventing catastrophic fuel system failures.
Tip 1: Upgrade Fuel Filters. Installing high-quality aftermarket fuel filters with enhanced filtration capabilities is critical. These filters offer improved protection against the microscopic contaminants that can damage the CP4.2 pump. Look for filters with a lower micron rating for superior particle removal.
Tip 2: Adhere to a Strict Fuel Filter Replacement Schedule. Regular filter changes are essential. Consult the owner’s manual for recommended intervals, but consider more frequent changes, especially in dusty or harsh operating environments.
Tip 3: Use Quality Fuel Additives. Fuel additives designed for diesel engines can provide added lubrication and protection for the CP4.2 pump. Select additives that specifically address lubricity improvement and deter the formation of harmful deposits.
Tip 4: Monitor Fuel Pressure Regularly. Consistent monitoring of fuel pressure can provide early warning signs of potential issues within the fuel system. Low fuel pressure could indicate a failing pump or clogged filters.
Tip 5: Drain Water Separator Frequently. The water separator in the fuel filter housing should be drained regularly to remove accumulated water, which can contribute to corrosion and fuel system damage.
Tip 6: Keep the Fuel Tank Full. Maintaining a full fuel tank can help prevent condensation from forming inside the tank, which can introduce water into the fuel system.
Tip 7: Choose Reputable Fuel Sources. Whenever possible, refuel at reputable fuel stations known for providing clean, high-quality diesel fuel. Avoid stations with suspected fuel contamination issues.
By following these preventative maintenance tips, owners can significantly reduce the risk of CP4.2 fuel pump failure and associated engine damage, preserving the longevity and reliability of their 6.7L Powerstroke diesel engine. Proactive maintenance represents a far more cost-effective approach than addressing a major failure.
This discussion now transitions to addressing frequently asked questions regarding CP4.2 fuel system maintenance and common concerns.
1. Fuel Filtration
Fuel filtration plays a critical role in preventing CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump failures in 2015 Ford F-250 trucks equipped with the 6.7L Powerstroke diesel engine. The CP4.2 pump is highly susceptible to damage from even microscopic contaminants present in diesel fuel. These contaminants, including dirt, rust, and metal particles, can erode the precisely machined components within the pump, leading to premature wear, reduced performance, and ultimately, catastrophic failure. Effective filtration removes these harmful particles before they reach the pump, acting as the first line of defense.
Consider a scenario where a 2015 F-250 is fueled with diesel containing microscopic metal shavings. Without adequate filtration, these shavings can circulate through the fuel system and reach the CP4.2 pump. The tight tolerances within the pump are easily compromised by these abrasive particles. Over time, this can lead to scoring of the pump’s internal components, increased friction, and a significant reduction in fuel pressure, ultimately resulting in complete pump failure. Installing high-quality aftermarket fuel filters with a lower micron rating than the factory filter can significantly reduce the risk of such failures. These filters trap smaller particles, providing enhanced protection for the sensitive CP4.2 pump. Regular filter replacement is equally crucial, as a clogged filter can restrict fuel flow and compromise pump performance.
Investing in robust fuel filtration is a crucial aspect of preventing CP4.2 pump failures in 2015 F-250 trucks. This proactive measure minimizes the risk of costly repairs and extended downtime associated with pump replacement. While other preventative measures, such as the use of lubricity additives, are important, effective fuel filtration remains the foundation of a comprehensive CP4.2 disaster prevention strategy. By effectively removing harmful contaminants from the fuel, robust filtration safeguards the pump, ensures optimal engine performance, and extends the lifespan of the entire fuel system.
2. Water Separation
Water contamination in the fuel system poses a significant threat to the CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump in 2015 Ford F-250 trucks equipped with the 6.7L Powerstroke diesel engine. Effective water separation is, therefore, a critical component of a comprehensive prevention strategy. Water can enter the fuel system through condensation in the fuel tank, contaminated fuel sources, or even through leaks in the fuel system itself. Once present, water can cause corrosion within the fuel system components, including the CP4.2 pump, leading to premature wear and potential failure. Furthermore, water can disrupt the lubrication properties of the diesel fuel, increasing friction within the pump and exacerbating wear. Efficient water separation mitigates these risks.
- Fuel Filter Water Separators:
Most modern diesel fuel filters incorporate a water separator. This device collects water that has accumulated in the fuel, preventing it from reaching the engine. Regular draining of the water separator is essential for maintaining its effectiveness. Neglecting this crucial maintenance step can lead to water bypassing the separator and entering the CP4.2 pump, potentially causing damage.
- Additional Water Separator Systems:
In addition to the fuel filter’s water separator, supplemental systems can provide enhanced protection. These systems typically employ a coalescing filter media that effectively captures and removes even small water droplets from the fuel. Such secondary systems provide an additional layer of defense, further reducing the risk of water-induced damage to the CP4.2 pump.
- Fuel Additives:
Certain fuel additives can help to emulsify small amounts of water in the fuel, allowing it to be burned harmlessly during combustion. While not a replacement for effective water separation, these additives can provide supplemental protection against small amounts of water contamination, further mitigating risk.
- Regular Fuel Tank Draining:
Periodically draining the fuel tank can remove any accumulated water that has settled at the bottom. This proactive measure helps prevent water from being drawn into the fuel system and reaching the sensitive CP4.2 pump. This is especially important in environments with high humidity or temperature fluctuations, where condensation is more likely to occur.
By prioritizing these water separation strategies, owners of 2015 Ford F-250 trucks with the 6.7L Powerstroke engine can significantly reduce the risk of CP4.2 pump failure due to water contamination. Coupled with other preventative measures like quality fuel filtration and the use of lubricity additives, effective water separation forms an integral part of a comprehensive maintenance plan, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the fuel system and protecting against costly repairs.
3. Lubricity Additives
The CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump, found in the 2015 Ford F-250’s 6.7L Powerstroke engine, requires adequate fuel lubricity for optimal performance and longevity. Ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) fuel, while environmentally beneficial, often lacks the necessary lubricity to protect the precisely machined components within the CP4.2 pump. Lubricity additives play a crucial role in supplementing this deficiency, mitigating the risk of premature wear and catastrophic failure. They form an essential part of a comprehensive “2015 f250 cp4 disaster prevention kit,” protecting the pump from the damaging effects of friction and wear.
- Friction Reduction:
Lubricity additives create a protective film on the metal surfaces within the CP4.2 pump, reducing friction between moving parts. This protective layer minimizes wear and tear, extending the pump’s operational life. Without adequate lubrication, these metal surfaces can rub against each other, leading to scoring, pitting, and eventual failure. This friction reduction is crucial for maintaining the pump’s efficiency and preventing costly repairs.
- Protection Against ULSD Fuel:
ULSD fuel, while cleaner-burning, often lacks the lubricating properties of traditional diesel fuel. This reduced lubricity can accelerate wear on the CP4.2 pump. Lubricity additives compensate for this deficiency, providing the necessary lubrication to protect the pump from the potentially damaging effects of ULSD fuel. This is particularly important in older engines designed for higher-sulfur fuels.
- Additive Types and Selection:
Various lubricity additives are available, each with different chemical compositions and performance characteristics. Selecting the appropriate additive is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness. Some common types include two-stroke oil, specially formulated diesel fuel additives, and even certain biodiesels. Consulting reputable sources and adhering to manufacturer recommendations is crucial for choosing the right additive for a specific application.
- Integration with Preventative Maintenance:
Lubricity additives are not a standalone solution but rather a crucial component of a broader preventative maintenance strategy. Their effectiveness is amplified when combined with other preventative measures, such as regular fuel filter changes, water separation, and the use of quality diesel fuel. This integrated approach provides comprehensive protection for the CP4.2 pump, minimizing the risk of failure and ensuring the long-term health of the fuel system.
By incorporating appropriate lubricity additives into a comprehensive maintenance plan, owners of 2015 Ford F-250 trucks with the 6.7L Powerstroke engine can significantly reduce the risk of CP4.2 pump failure. This proactive approach, combined with other preventative measures, ensures the longevity and reliability of the fuel system, protecting against costly repairs and downtime. The use of lubricity additives represents a cost-effective investment in preserving the health and performance of the CP4.2 pump.
4. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is paramount in preventing catastrophic failure of the CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump in the 2015 Ford F-250 6.7L Powerstroke diesel engine. A proactive maintenance schedule, encompassing several key areas, forms the backbone of a comprehensive prevention strategy. Neglecting these routine procedures significantly increases the risk of pump failure, leading to extensive repairs and downtime.
- Fuel Filter Replacement
Regular fuel filter changes are essential for preventing CP4.2 pump failure. Contaminants accumulate in the fuel filter over time, restricting fuel flow and potentially introducing harmful particles into the pump. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended replacement intervals, or even shorter intervals in harsh operating conditions, ensures optimal filtration and minimizes the risk of contamination-induced pump damage. For example, operating in dusty environments may necessitate more frequent filter changes than highway driving. Consistent filter replacement is a fundamental aspect of preventative maintenance.
- Water Separator Draining
Regularly draining the water separator, typically located in the fuel filter housing, is crucial for removing accumulated water from the fuel system. Water can corrode internal components and compromise the lubricating properties of diesel fuel, leading to increased wear on the CP4.2 pump. Draining the separator prevents water from reaching the pump, mitigating these risks. This simple procedure, often overlooked, can significantly extend the life of the pump. Failing to drain the separator can negate the benefits of other preventative measures, such as fuel filtration and additive use.
- Fuel System Inspections
Regular visual inspections of the entire fuel system can identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems. Checking for leaks, damaged lines, or loose connections can prevent fuel contamination and pressure loss, both of which can negatively impact the CP4.2 pump. For instance, a small fuel leak, if left unaddressed, can introduce contaminants and reduce fuel pressure, increasing the strain on the pump. Thorough inspections are a cost-effective way to identify and address minor issues before they cause significant damage.
- Fuel Pressure Monitoring
Regularly monitoring fuel pressure provides valuable insights into the health of the fuel system and the CP4.2 pump. Low fuel pressure can indicate a failing pump, clogged filters, or other issues within the fuel system. Consistent monitoring allows for early detection of these problems, enabling timely intervention before significant damage occurs. Using a fuel pressure gauge or monitoring the fuel pressure through diagnostic tools allows for proactive maintenance, preventing catastrophic failures and costly repairs. Sudden drops in fuel pressure warrant immediate investigation.
These regular maintenance procedures, when implemented diligently, form a robust defense against CP4.2 pump failure in the 2015 Ford F-250. Combined with the use of quality fuel, appropriate additives, and a proactive approach to fuel system management, regular maintenance significantly reduces the risk of costly repairs and ensures the long-term reliability of the fuel system. Ignoring these routine tasks undermines the effectiveness of other preventative measures and substantially increases the likelihood of experiencing a catastrophic pump failure.
5. Fuel Pressure Monitoring
Fuel pressure monitoring is a critical component of a comprehensive strategy for preventing CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump failures in the 2015 Ford F-250 6.7L Powerstroke diesel engine. Consistent monitoring provides valuable data, enabling early detection of potential issues that could lead to catastrophic pump failure. This proactive approach allows for timely intervention and preventative maintenance, minimizing the risk of extensive repairs and downtime. Fuel pressure acts as a key indicator of the overall health of the fuel system, providing crucial insights into the CP4.2 pump’s operating condition.
- Real-Time Diagnostics
Monitoring fuel pressure in real-time provides immediate feedback on the performance of the CP4.2 pump and the fuel system as a whole. A sudden drop in fuel pressure, for instance, could indicate a failing pump, a clogged fuel filter, or a leak in the fuel lines. This real-time information allows for swift diagnosis and corrective action, preventing further damage and mitigating the risk of a complete pump failure. Specialized gauges, installed within the vehicle’s cabin, or diagnostic software connected to the vehicle’s onboard computer, can facilitate this continuous monitoring. Such real-time data is invaluable for averting costly repairs.
- Trend Analysis
Analyzing fuel pressure trends over time provides a broader perspective on the health of the fuel system. A gradual decline in fuel pressure, even within seemingly acceptable limits, could signal the onset of pump wear or other developing issues. Recognizing these subtle changes allows for proactive maintenance, addressing potential problems before they escalate into major failures. Logging fuel pressure data at regular intervals, either manually or through data logging software, enables this trend analysis. This long-term perspective is crucial for maximizing the lifespan of the CP4.2 pump.
- Correlation with Other Parameters
Fuel pressure data, when correlated with other engine parameters such as engine speed, load, and temperature, provides a more comprehensive understanding of the fuel system’s behavior. For example, observing low fuel pressure under high load conditions could pinpoint a specific issue with the pump’s ability to meet demand. This multifaceted analysis enables more accurate diagnosis and targeted repairs. Modern diagnostic tools facilitate this correlation, offering a holistic view of engine performance and enabling more effective troubleshooting.
- Preventative Maintenance Trigger
Deviations from normal fuel pressure readings can serve as a trigger for preventative maintenance. Consistently low fuel pressure, even if not yet critical, warrants investigation and potential intervention. This proactive approach prevents minor issues from escalating into catastrophic pump failures. For example, a slightly lower than normal fuel pressure could prompt a fuel filter change or a closer inspection of the fuel lines, preventing potential contamination or pressure loss that could damage the CP4.2 pump. Fuel pressure monitoring, therefore, plays a key role in triggering timely preventative maintenance.
Integrating fuel pressure monitoring into a comprehensive maintenance plan for the 2015 Ford F-250 6.7L Powerstroke diesel engine significantly reduces the risk of CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump failure. By providing real-time diagnostics, enabling trend analysis, correlating with other engine parameters, and triggering preventative maintenance, fuel pressure monitoring acts as an early warning system, allowing for timely intervention and protecting against costly repairs. This proactive approach is essential for maximizing the lifespan and reliability of the CP4.2 pump and the entire fuel system. Combined with other preventative measures like regular filter changes, water separation, and the use of quality fuel and additives, diligent fuel pressure monitoring forms a crucial part of a robust CP4.2 disaster prevention strategy.
6. Quality Diesel Fuel
Quality diesel fuel plays a crucial role in preventing CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump failures in 2015 Ford F-250 trucks. The CP4.2 pump, known for its sensitivity to contamination, relies on clean, properly formulated diesel fuel for optimal performance and longevity. Substandard fuel, often containing excessive water, sediment, or microbial growth, can introduce harmful contaminants into the fuel system. These contaminants can erode the precisely machined components within the CP4.2 pump, leading to premature wear, reduced efficiency, and ultimately, catastrophic failure. Furthermore, low-quality fuel may lack the necessary lubricity to protect the pump’s internal components, exacerbating wear and tear. For instance, fuel contaminated with abrasive particles can score the pump’s plungers and barrels, leading to increased friction and metal shavings, which further contaminate the fuel system and accelerate pump failure. Similarly, fuel with high water content can corrode internal components, compromising the pump’s structural integrity and leading to leaks or complete failure. In contrast, high-quality diesel fuel, free from contaminants and formulated with appropriate lubricity, ensures smooth operation and extends the pump’s lifespan.
Consider a scenario where two identical 2015 F-250 trucks are operated under similar conditions, but one consistently uses high-quality diesel fuel from reputable suppliers, while the other frequently refuels at stations known for lower fuel standards. The truck using substandard fuel is significantly more likely to experience premature CP4.2 pump failure. The accumulated contaminants and reduced lubricity in the lower-quality fuel will gradually degrade the pump’s internal components, leading to costly repairs and extended downtime. The truck using high-quality fuel, on the other hand, benefits from enhanced pump protection, minimizing the risk of failure and ensuring long-term reliability. This real-world example illustrates the direct impact of fuel quality on the lifespan and performance of the CP4.2 pump.
Understanding the critical link between fuel quality and CP4.2 pump health is essential for preventing costly repairs and ensuring the longevity of the 2015 Ford F-250’s fuel system. Prioritizing the use of high-quality diesel fuel from reputable sources, along with other preventative measures such as regular filter changes and water separator draining, forms a comprehensive strategy for protecting the CP4.2 pump and minimizing the risk of failure. While the initial cost of premium diesel fuel might be slightly higher, the long-term savings from avoiding major repairs far outweigh this marginal expense. Therefore, consistent use of quality diesel fuel represents a crucial investment in protecting the CP4.2 pump and ensuring the reliable operation of the 2015 Ford F-250.
7. Contamination Awareness
Contamination awareness is paramount for preventing CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump failures in 2015 Ford F-250 trucks. Understanding potential contamination sources and implementing preventative measures are crucial for protecting this sensitive component. Contamination can occur at various points in the fuel supply chain, from refinery to fuel tank. Proactive measures, driven by contamination awareness, are essential for mitigating these risks and ensuring the longevity of the fuel system. This awareness forms a critical element of a comprehensive “2015 f250 cp4 disaster prevention kit,” safeguarding the pump from the detrimental effects of contaminants.
- Fuel Storage Practices
Proper fuel storage practices play a vital role in preventing contamination. Storing diesel fuel in clean, sealed containers, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures, minimizes the risk of water ingress, microbial growth, and particulate contamination. For instance, storing fuel in rusty or open containers exposes it to environmental contaminants, increasing the risk of CP4.2 pump damage. Diligent storage practices are fundamental for maintaining fuel quality and protecting the pump.
- Fuel Transfer Procedures
Careful fuel transfer procedures minimize the introduction of contaminants during refueling. Using clean transfer equipment, such as designated fuel hoses and funnels, prevents the ingress of dirt, debris, and other foreign particles. For example, using a contaminated funnel to refuel can introduce harmful particles directly into the fuel tank, potentially damaging the CP4.2 pump. Meticulous attention to transfer procedures is crucial for maintaining fuel cleanliness.
- Fuel Source Selection
Choosing reputable fuel sources significantly reduces the risk of contamination. Reputable fuel suppliers adhere to strict quality control measures, minimizing the likelihood of contaminated fuel reaching the consumer. Refueling at stations known for questionable fuel quality or neglecting fuel storage best practices increases the risk of CP4.2 pump damage. Selecting reliable fuel sources is a crucial preventative measure.
- Regular Fuel System Inspections
Regularly inspecting the fuel system for signs of contamination or damage is essential. Checking for leaks, damaged fuel lines, or compromised seals can prevent contaminants from entering the system and causing pump failure. For example, a small leak in a fuel line can introduce air and contaminants into the system, potentially damaging the CP4.2 pump. Diligent inspections are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the fuel system.
Cultivating contamination awareness and implementing preventative measures are essential for protecting the CP4.2 pump in 2015 Ford F-250 trucks. By understanding potential contamination sources and adopting best practices for fuel storage, transfer, source selection, and system inspection, owners can significantly reduce the risk of pump failure. This proactive approach, driven by contamination awareness, complements other preventative measures, such as regular maintenance and the use of quality fuel and additives, forming a comprehensive “2015 f250 cp4 disaster prevention kit” that ensures the longevity and reliability of the fuel system.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common concerns regarding CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump failure prevention in 2015 Ford F-250 trucks equipped with the 6.7L Powerstroke diesel engine. Understanding these frequently asked questions can empower owners to make informed decisions regarding preventative maintenance and fuel system management.
Question 1: How often should fuel filters be replaced to prevent CP4.2 failure?
Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended replacement schedule is crucial. However, more frequent changes, such as every 10,000 to 15,000 miles or even sooner in dusty or severe operating conditions, offer enhanced protection for the CP4.2 pump. Shorter intervals ensure optimal filtration and minimize the risk of contamination-induced damage.
Question 2: Are aftermarket fuel filters more effective than OEM filters in protecting the CP4.2 pump?
Certain aftermarket filters offer superior filtration capabilities compared to OEM filters. Look for filters with a lower micron rating, indicating their ability to trap smaller particles. These enhanced filtration capabilities can provide additional protection for the CP4.2 pump. Thorough research and selection of reputable brands are essential.
Question 3: What role do lubricity additives play in CP4.2 pump protection?
Lubricity additives compensate for the reduced lubricity of ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) fuel. They form a protective film on the pump’s internal components, reducing friction and wear. This added lubrication is crucial for mitigating the risk of premature pump failure and extending its operational lifespan. Proper selection and usage of additives are crucial.
Question 4: Can water in the fuel system damage the CP4.2 pump, and how can this be prevented?
Water contamination can cause corrosion and reduce the lubricating properties of diesel fuel, leading to accelerated wear and potential CP4.2 pump failure. Regularly draining the water separator in the fuel filter housing and using quality fuel from reputable sources minimize the risk of water contamination. Additional water separator systems offer further protection.
Question 5: How does regular fuel system maintenance contribute to CP4.2 pump longevity?
Regular maintenance, including fuel filter replacements, water separator draining, and fuel system inspections, is essential for preventing CP4.2 pump failure. These procedures minimize contamination, maintain optimal fuel pressure, and allow for early detection of potential issues, preventing catastrophic damage. Consistent maintenance is crucial for long-term pump health.
Question 6: What are the signs of a failing CP4.2 pump, and what steps should be taken if these signs are observed?
Symptoms of a failing CP4.2 pump can include low fuel pressure, rough engine operation, hard starting, and metallic debris in the fuel filter. If any of these signs are observed, immediate diagnosis and repair by a qualified diesel mechanic are crucial. Continuing to operate the vehicle with a failing pump can lead to extensive and costly engine damage.
Implementing the preventative measures discussed above significantly reduces the risk of CP4.2 pump failure. Proactive maintenance and informed decision-making are essential for protecting this critical component and ensuring the longevity of the fuel system.
The following section delves into case studies of CP4.2 pump failures, providing real-world examples of the importance of preventative maintenance.
Protecting the 2015 F-250 6.7L Powerstroke
Maintaining the fuel system’s integrity in the 2015 Ford F-250 equipped with the 6.7L Powerstroke diesel engine requires a comprehensive and proactive approach. This article explored crucial elements of a preventative strategy, emphasizing the importance of quality fuel filtration, diligent water separation, the use of appropriate lubricity additives, adherence to a strict maintenance schedule, consistent fuel pressure monitoring, selection of reputable fuel sources, and cultivating an overall awareness of potential contamination. Each element plays a vital role in safeguarding the CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump, a component known for its sensitivity to contamination and the potential for costly failures. By addressing these key areas, owners can significantly reduce the risk of catastrophic pump failure and the associated downtime and expenses.
The long-term reliability of the 2015 F-250 6.7L Powerstroke’s fuel system hinges on a commitment to preventative maintenance and informed decision-making. While the CP4.2 pump presents a known vulnerability, proactive measures can effectively mitigate the risk of failure. Investing in preventative maintenance represents a cost-effective strategy compared to the substantial expense of addressing a major fuel system failure. Through diligent adherence to the strategies outlined in this article, owners can safeguard their investment and ensure the continued performance and reliability of their trucks.