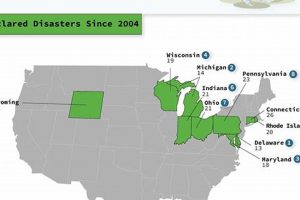
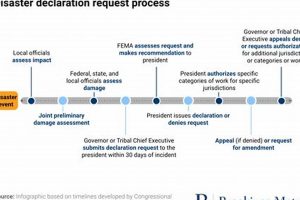
Catastrophic events stemming from environmental forces have profoundly impacted global communities recently. Examples include seismic activity resulting in widespread destruction, extreme weather events causing extensive flooding and displacement, and wildfires consuming vast tracts of land. These occurrences often lead to significant loss of life, infrastructure damage, and long-term economic consequences.
Understanding the patterns, frequency, and intensity of such events is crucial for disaster preparedness, mitigation efforts, and resource allocation. Studying recent occurrences provides valuable data for developing predictive models, improving early warning systems, and implementing effective strategies for community resilience. Historical analysis reveals an increasing trend in both the frequency and intensity of certain types of events, highlighting the urgency for proactive measures.
The following sections will explore specific categories of these events in greater detail, analyzing their causes, impacts, and the ongoing efforts to address the challenges they present. We will examine case studies of individual events, analyze the effectiveness of various response strategies, and discuss the role of scientific advancements in predicting and mitigating future occurrences.
Disaster Preparedness Tips
Recent catastrophic events underscore the importance of proactive preparedness measures. The following recommendations offer guidance for enhancing individual and community resilience.
Tip 1: Develop an Emergency Plan: Establish a comprehensive plan that includes evacuation routes, communication protocols, and designated meeting points. This plan should account for the specific needs of all household members, including pets and individuals with disabilities.
Tip 2: Assemble an Emergency Kit: Gather essential supplies such as non-perishable food, water, first-aid supplies, medications, and a battery-powered radio. Ensure the kit is readily accessible and regularly replenished.
Tip 3: Stay Informed: Monitor weather alerts and official communications from local authorities. Familiarize oneself with early warning systems and evacuation procedures specific to the geographic location.
Tip 4: Secure Property: Take preventative measures to protect homes and businesses from potential damage. This may include reinforcing structures, clearing drainage systems, and trimming trees near power lines.
Tip 5: Understand Insurance Coverage: Review existing insurance policies to ensure adequate coverage for potential disaster-related losses. Document valuables and consider flood insurance, even in areas not traditionally considered flood-prone.
Tip 6: Community Engagement: Participate in community-based disaster preparedness initiatives. Collaboration with neighbors and local organizations can strengthen collective resilience and response capabilities.
Proactive preparation significantly enhances the ability to navigate the challenges presented by these events. By implementing these strategies, individuals and communities can mitigate risks and safeguard well-being.
The insights provided in this article aim to empower readers with the knowledge and tools necessary for effective disaster preparedness. The concluding section will reiterate key takeaways and offer resources for further information.
1. Frequency
Analysis of disaster occurrences over recent years reveals noteworthy trends in frequency. Certain types of events, such as extreme heat waves and intense rainfall events, have demonstrably increased in frequency. This rise correlates with observed changes in global climate patterns. Understanding these frequency shifts is crucial for developing predictive models and implementing effective mitigation strategies. For example, increased flooding in coastal regions necessitates improved infrastructure planning and flood defense mechanisms. Similarly, more frequent heat waves require enhanced public health measures to address heat-related illnesses.
Examining the frequency of specific disaster types allows for targeted resource allocation and preparedness efforts. Regions experiencing a surge in wildfire activity benefit from enhanced fire prevention strategies and rapid response capabilities. Areas facing more frequent and intense hurricanes require robust evacuation plans and reinforced building codes. Data-driven analysis of frequency trends empowers communities to proactively address emerging risks. For example, the increasing frequency of droughts in certain agricultural regions necessitates investments in water conservation technologies and drought-resistant crops.
The observed changes in the frequency of various catastrophic events underscore the dynamic nature of global environmental challenges. Addressing these evolving risks requires continuous monitoring, data analysis, and adaptive strategies. Further research into the underlying causes of these frequency shifts remains essential for long-term mitigation and resilience building. The insights gained from frequency analysis contribute significantly to informed decision-making and effective resource management in the face of increasing environmental pressures.
2. Geographic Distribution
Understanding the geographic distribution of recent catastrophic events is crucial for effective resource allocation, targeted preparedness strategies, and international cooperation. Analyzing spatial patterns reveals vulnerabilities specific to certain regions, informs infrastructure development, and enhances predictive capabilities.
- Coastal Regions:
Coastal areas face heightened vulnerability to a range of hazards, including hurricanes, storm surges, tsunamis, and rising sea levels. The concentration of populations and infrastructure in these areas exacerbates the potential impact of such events. For example, recent hurricanes impacting coastal communities in the Caribbean and the United States caused widespread devastation and displacement, highlighting the need for resilient infrastructure and effective evacuation plans in these vulnerable zones. The increasing frequency and intensity of such events pose significant challenges for coastal communities worldwide.
- Seismic Zones:
Regions situated along tectonic plate boundaries experience heightened seismic activity, increasing the risk of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. The devastating earthquakes in Nepal (2015), Mexico (2017), and Indonesia (2018) underscore the destructive potential of seismic events. Understanding seismic risk informs building codes, land-use planning, and early warning systems, mitigating potential losses in these vulnerable areas.
- Arid and Semi-Arid Regions:
These regions are particularly susceptible to droughts and wildfires, which can lead to desertification, crop failures, and displacement of populations. Prolonged droughts in the Horn of Africa and Australia have resulted in widespread food insecurity and humanitarian crises. Effective water management strategies and drought-resistant agricultural practices are crucial for enhancing resilience in these areas.
- High-Altitude Regions:
Mountainous regions face specific risks, including landslides, avalanches, and glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs). Climate change contributes to the instability of glaciers and permafrost, increasing the likelihood of such events. Monitoring glacial activity and implementing early warning systems are critical for protecting communities in these high-altitude zones.
The geographic distribution of recent catastrophic events highlights the interconnectedness of global environmental challenges. Analyzing spatial patterns informs targeted interventions, facilitates international cooperation, and strengthens global resilience in the face of increasing climate-related risks. This understanding is fundamental for developing comprehensive strategies that address the specific vulnerabilities of different regions and promote sustainable development in a changing world.
3. Intensity Variations
Observed intensity variations in recent catastrophic events present significant challenges for disaster preparedness and mitigation. Several factors contribute to these fluctuations, including climate change, natural climate variability, and changes in land use. The increasing intensity of hurricanes, for example, correlates with rising sea surface temperatures, a key indicator of climate change. More intense storms generate higher wind speeds, increased storm surge, and heavier rainfall, leading to more extensive damage and greater loss of life. Understanding the drivers of intensity variations is crucial for developing effective adaptation strategies.
Examples of increased intensity across various hazard types underscore the practical significance of this phenomenon. The 2017 Atlantic hurricane season witnessed several exceptionally intense storms, including Hurricanes Harvey, Irma, and Maria, which caused widespread devastation across the Caribbean and the United States. Similarly, the increasing intensity of wildfires, as observed in recent events in California and Australia, poses significant threats to ecosystems, human lives, and infrastructure. These heightened intensities challenge existing disaster management frameworks and necessitate innovative approaches to preparedness and response.
Addressing the challenges posed by intensity variations requires a multifaceted approach. Investing in resilient infrastructure, developing advanced early warning systems, and implementing effective land-use planning are crucial steps. Furthermore, international cooperation and data sharing play a vital role in enhancing global capacity to predict and respond to increasingly intense catastrophic events. Recognizing the complex interplay of factors contributing to intensity variations remains essential for developing effective long-term mitigation strategies and building resilient communities in a changing climate.
4. Economic Consequences
Catastrophic events occurring within the last five years have induced substantial economic consequences, impacting diverse sectors globally. These consequences manifest as direct costs, such as physical damage to infrastructure and property, and indirect costs, including business interruption, supply chain disruptions, and reduced agricultural output. The overall economic impact of a specific event depends on its severity, geographic location, and the resilience of affected communities. For example, the 2023 Turkey-Syria earthquake resulted in billions of dollars in damages, impacting not only the immediate region but also global supply chains reliant on affected industries.
Analyzing the economic impact of these events reveals several key trends. Reconstruction costs following large-scale events strain public finances and necessitate international aid. Disruptions to supply chains can lead to increased prices for essential goods and services. Damage to agricultural lands and infrastructure can impact food security, particularly in vulnerable regions. The tourism sector, often a significant contributor to local economies, can suffer prolonged setbacks following major events. For instance, the 2019-2020 Australian bushfires significantly impacted tourism, leading to substantial revenue losses. Understanding these economic consequences is crucial for developing effective disaster risk reduction strategies and promoting sustainable economic recovery.
Addressing the economic fallout of these events requires a multi-pronged approach. Investing in resilient infrastructure, diversifying economies, and developing comprehensive insurance mechanisms are key strategies for mitigating future economic losses. Furthermore, international cooperation and financial assistance play a critical role in supporting recovery efforts in affected regions. Accurate and timely economic impact assessments are essential for informing policy decisions and ensuring effective resource allocation. The long-term economic consequences of these events underscore the need for proactive measures that prioritize disaster resilience and sustainable development.
5. Humanitarian Crises
Recent catastrophic events have triggered significant humanitarian crises, characterized by widespread displacement, food insecurity, water scarcity, and public health emergencies. These crises often exacerbate existing vulnerabilities within affected populations, disproportionately impacting marginalized communities. The scale and complexity of humanitarian needs following a major disaster necessitate rapid and coordinated responses from governments, international organizations, and non-governmental agencies. For example, the 2023 Turkey-Syria earthquake resulted in a massive humanitarian crisis, displacing millions and requiring extensive international aid to address urgent needs such as shelter, food, and medical care.
The connection between these crises and recent disasters is multifaceted. Extreme weather events can destroy crops and livestock, leading to food insecurity and malnutrition. Floods and earthquakes can damage or destroy essential infrastructure, disrupting access to clean water and sanitation, increasing the risk of waterborne diseases. Displacement due to disasters creates overcrowded living conditions in temporary shelters, increasing the risk of infectious disease outbreaks. Moreover, disruptions to healthcare systems can limit access to essential medical services, exacerbating existing health conditions and increasing mortality rates. The 2020 Cyclone Amphan in India and Bangladesh exemplified these challenges, causing widespread displacement and disrupting access to essential services in a densely populated region.
Addressing the humanitarian consequences of these events requires a comprehensive and coordinated approach. Rapid needs assessments, efficient logistics for aid delivery, and effective coordination among humanitarian actors are crucial for minimizing suffering and promoting recovery. Strengthening community-level preparedness and resilience is essential for mitigating the impact of future events. Furthermore, addressing the underlying drivers of vulnerability, such as poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation, is fundamental for building more resilient societies. Understanding the complex interplay between disasters and humanitarian crises is critical for developing effective strategies that prioritize human well-being and promote sustainable development in a world facing increasing climate-related risks.
6. Technological Advancements in Prediction
Advancements in predictive technologies have played a crucial role in mitigating the impact of catastrophic events over recent years. These advancements, spanning improved monitoring systems, sophisticated modeling techniques, and enhanced communication networks, offer increasingly accurate and timely predictions, enabling more effective preparedness and response efforts. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of these technologies is essential for maximizing their effectiveness in disaster risk reduction.
- Improved Monitoring Systems:
Deployment of advanced sensor networks, satellite imagery, and remote sensing technologies provides real-time data on environmental conditions, enabling more precise monitoring of potential hazards. For example, advancements in radar technology and satellite-based precipitation measurement enhance the ability to track and predict the trajectory and intensity of hurricanes. Similarly, improved seismic monitoring networks provide critical data for earthquake early warning systems, enabling timely alerts to potentially affected populations. These advancements in monitoring capabilities contribute significantly to enhanced situational awareness and informed decision-making during disaster events.
- Sophisticated Modeling Techniques:
Development of sophisticated computer models, incorporating vast datasets and advanced algorithms, enhances the ability to predict the behavior of complex natural systems. These models incorporate factors such as atmospheric conditions, topography, and land use to generate more accurate predictions of events such as floods, wildfires, and landslides. Improved modeling of hurricane intensity and storm surge, for example, informs evacuation planning and coastal defense strategies. Advancements in wildfire modeling contribute to more effective fire suppression efforts and resource allocation. The increasing sophistication of these models enhances the precision and reliability of disaster predictions.
- Enhanced Communication Networks:
Reliable and timely communication is crucial for effective disaster response. Advancements in communication technologies, including mobile networks, social media platforms, and early warning systems, enable rapid dissemination of information to affected populations and emergency responders. Mobile phone alerts, for example, play a vital role in disseminating timely warnings about impending hazards. Social media platforms facilitate real-time information sharing during disaster events, enabling rapid assessment of needs and coordination of response efforts. These enhanced communication networks contribute significantly to improved situational awareness and coordinated action during emergencies.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into disaster prediction is rapidly evolving. AI and ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from diverse sources, identifying patterns and anomalies that may indicate an impending event. These technologies can enhance the accuracy and speed of predictions, particularly in complex and rapidly evolving situations. For example, AI-powered systems are being developed to predict the likelihood and location of landslides based on real-time rainfall data and terrain analysis. The application of AI and ML in disaster prediction holds significant promise for enhancing preparedness and response capabilities.
These interconnected technological advancements have significantly improved the capacity to predict and respond to catastrophic events within the last five years. While challenges remain in terms of data availability, model accuracy, and communication infrastructure in certain regions, the ongoing development and integration of these technologies offer significant potential for further enhancing disaster risk reduction efforts globally. Continued investment in research and development, coupled with international cooperation and data sharing, will be crucial for maximizing the benefits of these advancements and building more resilient communities in the face of increasing climate-related risks.
7. Global Cooperation for Disaster Relief
The increasing frequency and intensity of catastrophic events observed within the last five years underscore the critical importance of global cooperation for disaster relief. Effective disaster response often exceeds the capacity of individual nations, necessitating coordinated international efforts to provide timely and effective assistance. Global cooperation manifests in various forms, including the sharing of resources, expertise, and financial aid, as well as collaborative efforts in search and rescue operations, medical assistance, and the provision of shelter and essential supplies. The 2023 Turkey-Syria earthquake, for example, highlighted the vital role of international assistance in providing critical support to affected populations, with numerous countries contributing personnel, equipment, and financial aid to the relief effort. This cooperative approach is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of disaster response and minimizing human suffering.
Several factors drive the need for enhanced global cooperation in disaster relief. The interconnected nature of global systems means that disasters in one region can have cascading effects on others, impacting supply chains, trade, and migration patterns. Climate change is projected to exacerbate the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, increasing the demand for international disaster assistance. Furthermore, many countries lack the resources and infrastructure to effectively manage large-scale disasters independently, making international support crucial for saving lives and rebuilding communities. The 2020 Beirut port explosion demonstrated the need for international cooperation not only in immediate disaster response but also in longer-term recovery and reconstruction efforts, with countries providing technical expertise and financial aid to support Lebanon’s rebuilding process. The COVID-19 pandemic further highlighted the importance of international collaboration in addressing global crises, including the sharing of medical supplies, research data, and best practices for pandemic management.
Effective global cooperation in disaster relief requires robust coordination mechanisms, clear communication channels, and pre-arranged agreements for resource sharing. International organizations, such as the United Nations and the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, play a crucial role in facilitating coordination and mobilizing resources during disaster events. Strengthening partnerships between governments, international organizations, and non-governmental organizations is essential for enhancing the effectiveness of disaster response. Furthermore, investing in disaster preparedness and risk reduction measures at the national and regional levels is critical for minimizing the impact of future events and reducing the demand for international assistance. While challenges remain in ensuring equitable access to aid and navigating complex geopolitical dynamics, the interconnected nature of disaster risk necessitates continued efforts to strengthen global cooperation for disaster relief, promoting resilience and minimizing human suffering in the face of increasing environmental challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding catastrophic events observed globally within the last five years.
Question 1: How has climate change influenced the frequency and intensity of recent catastrophic events?
Scientific evidence suggests a strong correlation between climate change and the increased frequency and intensity of certain types of events, particularly extreme weather phenomena such as hurricanes, heatwaves, and droughts. Rising global temperatures contribute to increased atmospheric energy, leading to more intense storms and prolonged periods of extreme heat. Changes in precipitation patterns can exacerbate both droughts and floods. Further research continues to refine the understanding of these complex interactions.
Question 2: What role does human activity play in exacerbating the impact of natural disasters?
Human activities, such as deforestation, urbanization, and greenhouse gas emissions, can exacerbate the impact of natural disasters. Deforestation increases the risk of landslides and flooding. Urbanization can lead to increased surface runoff and localized flooding. Greenhouse gas emissions contribute to climate change, which intensifies extreme weather events. Sustainable land management practices and emissions reductions are crucial for mitigating these impacts.
Question 3: How can communities enhance their resilience to natural disasters?
Building community resilience involves a multi-faceted approach that includes developing comprehensive disaster preparedness plans, investing in resilient infrastructure, strengthening early warning systems, and promoting community education and awareness. Engaging vulnerable populations and incorporating local knowledge are essential for effective resilience building.
Question 4: What are the most significant challenges in providing effective disaster relief in remote or underserved areas?
Logistical challenges, limited infrastructure, communication barriers, and security concerns can impede effective disaster relief efforts in remote or underserved areas. Coordination among humanitarian agencies, leveraging local resources, and utilizing innovative technologies, such as drones and mobile communication platforms, are essential for overcoming these challenges.
Question 5: What are the long-term consequences of natural disasters on public health?
Natural disasters can have long-lasting impacts on public health, including increased rates of infectious diseases, mental health issues, chronic illnesses, and disabilities. Disruptions to healthcare systems, displacement, and environmental contamination contribute to these health challenges. Addressing these long-term health consequences requires sustained investment in healthcare infrastructure, mental health services, and environmental remediation.
Question 6: How does international cooperation contribute to effective disaster risk reduction?
International cooperation plays a vital role in disaster risk reduction by facilitating the sharing of knowledge, resources, and best practices. Collaborative efforts in research, technology development, and capacity building enhance global preparedness and response capabilities. International frameworks, such as the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction, provide guidance and promote collaborative action for reducing disaster risk.
Understanding the complex dynamics of catastrophic events and their impacts is crucial for informing effective mitigation strategies and building more resilient communities. Continued research, technological advancements, and international cooperation are essential for addressing these global challenges.
The following section will explore specific case studies of recent natural disasters, providing detailed analysis of their causes, consequences, and the lessons learned.
Conclusion
Analysis of catastrophic events occurring within the last five years reveals a complex interplay of factors influencing their frequency, intensity, and geographic distribution. From intensified hurricanes and widespread wildfires to devastating earthquakes and prolonged droughts, these events underscore the growing impact of both climate change and human activities on the global landscape. The economic consequences, humanitarian crises, and public health challenges resulting from these events necessitate proactive and comprehensive strategies for disaster risk reduction. Technological advancements in prediction and monitoring offer crucial tools for enhancing preparedness and response capabilities, while global cooperation remains essential for effective disaster relief and long-term recovery.
The increasing frequency and intensity of these events present a profound challenge to global communities. Addressing this challenge requires a fundamental shift towards proactive mitigation strategies, resilient infrastructure development, and a renewed commitment to international cooperation. Investing in scientific research, strengthening early warning systems, and empowering vulnerable communities are essential steps towards building a more resilient and sustainable future. The lessons learned from recent catastrophic events serve as a stark reminder of the urgent need for collective action to mitigate risks and safeguard human well-being in a world facing increasing environmental pressures.