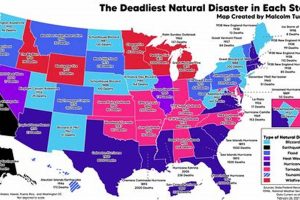
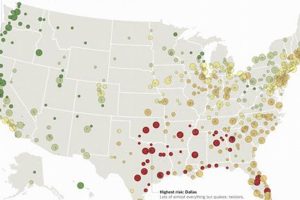
Depictions of earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, floods, wildfires, and other calamitous natural events, created through various artistic mediums such as sketching, painting, or digital illustration, serve as powerful visual records. These illustrations can range from realistic portrayals of specific events to symbolic representations of the destructive forces of nature. For example, a woodblock print might capture the devastation of a historical earthquake, while a charcoal sketch could depict the swirling chaos of a tornado.
Visualizations of these events hold significant value in communicating the impact and scale of such phenomena. They can serve as educational tools, providing insights into the geological and meteorological processes involved. Historically, artistic representations were a crucial means of documenting and disseminating information about these events before the advent of photography and videography. Moreover, such imagery can raise public awareness, fostering empathy and prompting discussions about preparedness and mitigation strategies. Art also offers a unique lens through which to explore the emotional and psychological impact of these events on individuals and communities.
This exploration delves further into specific categories of these impactful depictions, examining their roles in documentation, education, and emotional expression. Subsequent sections will analyze specific examples, discuss the diverse artistic techniques employed, and consider the evolving role of technology in visualizing and understanding the power of nature.
Tips for Depicting Natural Disasters in Art
Creating compelling and informative visualizations of natural disasters requires careful consideration of several factors. The following tips offer guidance for effectively conveying the power and impact of these events through artistic representation.
Tip 1: Research Thoroughly: Understanding the specific characteristics of the chosen disaster is crucial. Research the science behind the event, including its causes, progression, and typical effects. This knowledge will inform accurate and impactful depictions.
Tip 2: Focus on Composition: Effective use of perspective, scale, and balance can enhance the visual narrative. Leading lines, focal points, and the arrangement of elements within the artwork can draw the viewer’s attention and emphasize the scale of the disaster.
Tip 3: Utilize Value and Contrast: Strategic use of light and shadow can create dramatic effects, highlighting the devastation and conveying the intensity of the event. Strong contrasts can emphasize the destructive forces at play.
Tip 4: Consider Color Palette: Color choices can evoke specific emotions and enhance the overall impact. Muted tones might convey the somber aftermath, while vibrant hues could represent the raw energy of the disaster itself.
Tip 5: Emphasize Human Impact: Including human figures or elements of human presence (e.g., buildings, vehicles) can provide scale and underscore the consequences of the disaster on individuals and communities.
Tip 6: Explore Different Mediums: Experiment with various artistic media to find the best approach for capturing the specific qualities of the chosen disaster. Charcoal might be suitable for depicting wildfires, while watercolor could effectively portray floods.
Tip 7: Observe Real-World References: Studying photographs, videos, and firsthand accounts of natural disasters can provide valuable visual information and inspire authentic representations.
By considering these guidelines, artists can create powerful and informative visualizations that communicate the impact of natural disasters effectively, fostering understanding and empathy.
These tips provide a starting point for artistic exploration of natural disasters. The following section will offer concluding thoughts on the significance of this form of visual communication.
1. Visual Storytelling
Visual storytelling plays a crucial role in depictions of natural disasters, offering a powerful means of conveying complex narratives and emotional experiences. Unlike written or verbal accounts, visual narratives can transcend language barriers, communicating the impact of these events directly and viscerally. A single image can capture the sheer scale of destruction, the human suffering, and the resilience of communities in the face of adversity. For example, a drawing of a flooded village might depict not only the submerged homes but also the expressions of despair and hope on the faces of the survivors. This ability to convey multiple layers of meaning makes visual storytelling a vital component of understanding and responding to natural disasters.
The effectiveness of visual storytelling in this context relies on several factors. Composition, color palette, and the use of symbolism all contribute to the narrative’s impact. A carefully chosen perspective can emphasize the vastness of a wildfire, while somber tones can convey the gravity of the situation. Symbolic elements, such as a lone tree standing amidst debris, can represent resilience and hope. The historical context also plays a significant role. For instance, woodblock prints of the Great Kanto Earthquake of 1923 provide invaluable insights into the destruction and social upheaval of that era. These visual narratives serve as historical records, preserving the memory of these events for future generations.
Understanding the principles of visual storytelling is crucial for both creators and interpreters of disaster-related artwork. Artists can leverage these techniques to create compelling and impactful narratives, while viewers can gain a deeper understanding of the human experience of these events. Visual storytelling bridges the gap between factual documentation and emotional resonance, offering a unique and powerful lens through which to explore the complex relationship between humanity and the forces of nature. The challenges lie in balancing accurate representation with artistic interpretation and ensuring that the narrative respects the experiences of those affected. Nevertheless, visual storytelling remains a potent tool for raising awareness, fostering empathy, and promoting dialogue around natural disasters.
2. Emotional Impact
Depictions of natural disasters possess a unique capacity to evoke profound emotional responses. These visual representations transcend factual documentation, offering visceral insights into the human experience of loss, fear, resilience, and hope in the face of overwhelming natural forces. Examining the emotional impact of such artwork reveals its power to foster empathy, raise awareness, and promote dialogue around disaster preparedness and response.
- Fear and Anxiety
Images of impending or unfolding disasters can trigger immediate feelings of fear and anxiety. The depiction of turbulent storm surges, raging wildfires, or collapsing buildings can viscerally convey the imminent threat to life and property. These depictions often tap into primal fears associated with loss of control and vulnerability to powerful natural forces. For instance, a painting depicting individuals fleeing a volcanic eruption can evoke a sense of panic and desperation in the viewer, even if they have never experienced such an event firsthand. This emotional response can be a catalyst for increased awareness and preparedness.
- Grief and Loss
Artwork depicting the aftermath of a disaster often focuses on themes of grief and loss. Images of ruined landscapes, destroyed homes, and displaced communities can evoke a sense of profound sadness and empathy for those affected. For example, a photograph of a child searching through the rubble of their home can convey the devastating personal impact of such events. These depictions serve as poignant reminders of the human cost of natural disasters, fostering compassion and motivating support efforts.
- Resilience and Hope
While acknowledging the devastation caused by natural disasters, many artistic representations also highlight the resilience of the human spirit. Images of communities rebuilding, individuals helping one another, and signs of life returning to ravaged landscapes can inspire hope and optimism. A mural depicting a community garden flourishing in the aftermath of a flood can symbolize the capacity for renewal and the enduring strength of the human spirit. These depictions offer a counterpoint to the despair often associated with disasters, reminding viewers of the potential for recovery and growth.
- Collective Trauma and Memory
Artistic representations serve as powerful tools for processing collective trauma and preserving the memory of significant disaster events. By externalizing experiences of fear, loss, and recovery, art provides a platform for communities to grieve, heal, and rebuild. A memorial sculpture commemorating the victims of an earthquake can become a focal point for collective remembrance and a symbol of community strength. These artistic expressions contribute to the ongoing narrative of a community’s experience, shaping its identity and resilience in the face of future challenges.
By exploring these diverse emotional responses, artistic depictions of natural disasters offer valuable insights into the human experience of these events. They serve not only as historical records but also as powerful tools for fostering empathy, promoting dialogue, and strengthening community resilience. The exploration of these emotional impacts underscores the importance of art as a means of processing trauma, inspiring hope, and ultimately, building a more prepared and resilient future.
3. Scientific Accuracy
Scientific accuracy plays a crucial role in depictions of natural disasters, particularly when the objective is to educate or inform. Accurately portraying the geological or meteorological processes underlying these events enhances the educational value of the artwork, allowing viewers to grasp the forces at play. For example, illustrating the tectonic plate movements involved in an earthquake or the formation of a hurricane’s eye can provide valuable insights into these phenomena. A scientifically informed depiction can clarify misconceptions and promote a deeper understanding of the science behind natural disasters. Consider a drawing of a tsunami. If the wave’s height and speed are exaggerated for dramatic effect, it could mislead viewers about the true nature of these events. However, a scientifically accurate portrayal, informed by wave mechanics and coastal topography, can effectively communicate the destructive potential of a tsunami while remaining true to the scientific principles governing its behavior. The cause-and-effect relationship between atmospheric pressure, wind speed, and storm surge becomes clearer when depicted accurately, leading to a more informed public.
Furthermore, incorporating scientific accuracy strengthens the credibility of the artwork, making it a more effective tool for communication and advocacy. A scientifically grounded visualization can lend weight to discussions about disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies. For instance, illustrations depicting the effectiveness of different building techniques in earthquake-prone areas can inform policy decisions and promote safer construction practices. Similarly, accurate depictions of floodplains can aid in urban planning and development, minimizing the risk to human settlements. The practical significance of this understanding lies in its ability to inform public discourse, influence policy, and ultimately, contribute to more resilient communities.
Scientific accuracy, while crucial, must be balanced with artistic expression. The challenge lies in conveying complex scientific information in a visually engaging and accessible manner. Oversimplification can lead to inaccuracies, while excessive detail might obscure the core message. Ultimately, the goal is to create artwork that is both scientifically sound and aesthetically compelling, effectively communicating the power and complexity of natural disasters while inspiring informed action and promoting a deeper understanding of the natural world.
4. Educational Value
Illustrations of natural disasters offer significant educational value, serving as powerful tools for conveying complex information about these events in an accessible and engaging manner. Visualizations can clarify scientific principles, highlight geographical vulnerabilities, and demonstrate the impact of human activities on disaster risk. For example, diagrams illustrating the formation of tornadoes can explain the interplay of atmospheric conditions, while maps depicting historical flood zones can inform urban planning decisions. Cross-sectional drawings of buildings demonstrating earthquake-resistant construction techniques can educate the public about effective mitigation strategies. The impact of deforestation on landslide risk can be powerfully conveyed through before-and-after illustrations of a hillside. These visual aids bridge the gap between abstract scientific concepts and tangible real-world consequences, promoting deeper understanding.
Furthermore, such depictions provide valuable context for historical events, allowing audiences to grasp the scale and impact of past disasters. Illustrations of the 1906 San Francisco earthquake and fire, for instance, can convey the devastation more effectively than written descriptions alone. Similarly, visualizations of the 1883 eruption of Krakatoa can illustrate the global reach of its atmospheric effects. By combining scientific accuracy with artistic expression, these illustrations offer valuable learning opportunities, promoting informed discussion and contributing to a greater appreciation of the historical context of disaster events. This understanding can motivate preventative measures, inform policy decisions, and encourage community-level preparedness.
The educational value of these depictions lies in their capacity to translate complex information into readily understandable visuals, fostering engagement and promoting knowledge retention. The challenge lies in balancing scientific rigor with artistic interpretation, ensuring the accuracy of the information while maintaining visual appeal. By effectively leveraging the power of visual communication, these illustrations can play a crucial role in educating the public about natural disasters, fostering a culture of preparedness, and ultimately, contributing to more resilient communities.
5. Artistic Mediums
The choice of artistic medium significantly influences the portrayal and perception of natural disasters in visual art. Different mediums offer unique expressive possibilities, affecting the depiction of texture, movement, scale, and emotional impact. Understanding the characteristics of various mediums provides valuable insight into the artist’s intent and the overall effectiveness of the artwork in conveying the complex realities of these events.
- Drawing
Drawing, encompassing techniques like sketching, charcoal, and pen and ink, offers precision and detail, allowing artists to capture the intricate textures of devastated landscapes or the nuanced expressions of human suffering. Charcoal’s ability to create dramatic contrasts of light and shadow makes it particularly effective in depicting the aftermath of fires or the darkness of a volcanic eruption. Pen and ink drawings can meticulously render the structural damage of buildings or the intricate patterns of debris fields. A crosshatched pen drawing might capture the intricate details of cracked earth following an earthquake, while a charcoal sketch could evoke the smoky atmosphere of a wildfire.
- Painting
Painting, with its diverse range of pigments and techniques, allows for a broader exploration of color and texture. Watercolors can evoke the fluidity of floods or the ethereal quality of atmospheric phenomena. Acrylics and oils offer greater control over texture and layering, enabling artists to depict the viscous flow of lava or the build-up of storm clouds. The impasto technique, applying thick layers of paint, can effectively portray the textures of debris or the churning waters of a tsunami. A watercolor painting might capture the translucent quality of floodwaters, while an oil painting could depict the rich, earthy tones of a landslide.
- Printmaking
Printmaking techniques, such as woodblock printing, etching, and lithography, enable the reproduction of images, facilitating wider dissemination of information about disasters. Woodblock prints, historically used to document earthquakes and tsunamis in Japan, offer bold lines and stark contrasts, effectively conveying the scale and impact of these events. Etching and lithography allow for finer details and tonal variations, capturing the subtleties of atmospheric effects or the emotional nuances of human responses. A woodblock print might depict the stylized waves of a tsunami, while an etching could capture the fine details of a damaged cityscape.
- Digital Media
Digital media, encompassing photography, digital painting, and 3D modeling, offer new possibilities for visualizing and understanding natural disasters. Photography captures the immediate aftermath of events, providing valuable documentation for scientific analysis and humanitarian response. Digital painting allows artists to combine traditional painting techniques with digital tools, offering greater flexibility and control. 3D modeling enables the creation of realistic simulations of disasters, aiding in predicting their impact and developing mitigation strategies. A photograph might document the devastation of a hurricane, while a 3D model could simulate the spread of a wildfire.
The interplay between subject matter and artistic medium shapes the viewer’s understanding and emotional response to depictions of natural disasters. The chosen medium influences not only the visual representation but also the overall narrative conveyed by the artwork. By considering the specific qualities of each medium, viewers can gain a deeper appreciation for the artist’s choices and the complex interplay of factors that contribute to the power and impact of disaster-related art. This understanding enhances the communicative power of the artwork, fostering empathy, promoting education, and encouraging dialogue about the complex relationship between humanity and the forces of nature.
6. Historical Context
Understanding the historical context surrounding depictions of natural disasters provides crucial insights into their creation, purpose, and impact. Historical context informs the artistic choices, reflects societal attitudes towards these events, and reveals how interpretations of natural disasters have evolved over time. Examining this context enriches comprehension of the artwork’s significance and its role in shaping cultural memory and understanding of these phenomena.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping
Historically, artistic representations served as crucial records of natural disasters before the advent of photography and other recording technologies. These depictions, often created by eyewitnesses or based on firsthand accounts, offer valuable glimpses into past events, documenting the extent of destruction, the impact on communities, and the immediate responses. For instance, woodblock prints of the 1755 Lisbon earthquake provide visual evidence of the devastation and the subsequent rebuilding efforts. These historical records offer valuable data for researchers studying past events, informing present-day disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies.
- Cultural and Religious Interpretations
The historical context also reveals how different cultures and religious traditions interpreted natural disasters. In some societies, these events were attributed to divine wrath or viewed as omens, influencing artistic representations that emphasized symbolic and allegorical meanings. Medieval European art often depicted disasters as punishments from God, reflecting the prevailing religious beliefs of the time. Conversely, some indigenous cultures viewed natural disasters as part of a natural cycle, reflected in artwork that emphasized balance and harmony within the natural world. Analyzing these cultural interpretations provides insights into the societal values and beliefs surrounding natural disasters in different historical periods.
- Evolution of Scientific Understanding
The historical context also reflects the evolution of scientific understanding of natural disasters. As scientific knowledge progressed, artistic representations shifted from mythological or symbolic interpretations to more realistic depictions based on observation and data. The development of geology and meteorology, for example, led to more accurate portrayals of earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and weather phenomena in art. Comparing artistic depictions across different eras reveals how evolving scientific understanding shaped visual representations of these events. This progression highlights the interplay between scientific advancements and artistic expression in shaping public perception of natural disasters.
- Social and Political Commentary
Artistic representations of natural disasters often serve as vehicles for social and political commentary. Artists have used these depictions to critique government responses, highlight social inequalities exacerbated by disasters, or advocate for policy changes. For example, artwork depicting the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina in New Orleans often focuses on themes of social injustice and the disproportionate impact of the disaster on marginalized communities. Analyzing this artwork within its historical context reveals the social and political dimensions of disaster representation, highlighting the role of art in raising awareness and advocating for change.
By considering these facets of historical context, analysis of depictions of natural disasters gains depth and nuance. Understanding the historical circumstances surrounding the creation of these artworks provides crucial insights into their meaning, purpose, and impact on society. This contextual awareness enhances appreciation for the role of art in documenting, interpreting, and responding to natural disasters throughout history, ultimately contributing to a richer understanding of the complex relationship between humanity and the forces of nature.
7. Social Commentary
Depictions of natural disasters often serve as powerful vehicles for social commentary, offering critiques of societal structures, political systems, and human behavior in the face of crisis. These visual narratives can expose underlying social inequalities exacerbated by disasters, challenge official narratives, and advocate for policy changes. The relationship between social commentary and depictions of natural disasters is complex and multifaceted, reflecting the intricate interplay between natural phenomena and human societies. For example, artistic representations of the Great Famine in Ireland not only depict the suffering caused by the potato blight but also critique the British government’s response and the social structures that contributed to the widespread starvation. Similarly, artwork depicting the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina in New Orleans often highlights the racial and economic disparities that amplified the disaster’s impact on marginalized communities. These works move beyond mere documentation of the event, serving as critiques of social injustice and calls for systemic change. The practical significance of this understanding lies in its potential to raise awareness, foster dialogue, and mobilize action towards addressing the root causes of vulnerability and building more equitable and resilient communities.
The effectiveness of social commentary within disaster-related artwork relies on several factors. The artist’s choice of subject matter, composition, and artistic style can all contribute to the message conveyed. A focus on marginalized communities struggling to recover can highlight systemic inequalities, while the use of symbolic imagery can reinforce the critique of societal structures. The historical context surrounding the artwork also plays a crucial role in shaping its interpretation. For example, artwork created in the immediate aftermath of a disaster might focus on the immediate suffering and resilience of survivors, while works created years later might offer a more nuanced reflection on the long-term social and political consequences. Furthermore, the intended audience and the platform for dissemination influence the impact of the social commentary. Artwork displayed in a museum might reach a different audience and generate different conversations than artwork shared through social media or community spaces. Navigating these complexities is crucial for artists seeking to engage in meaningful social commentary through their work.
Social commentary embedded within depictions of natural disasters adds a crucial layer of meaning to these works, transforming them from mere documentation into powerful tools for social critique and change. By exposing injustices, challenging assumptions, and prompting dialogue, these artistic expressions can contribute to a deeper understanding of the complex relationship between natural events and human societies. The challenge lies in balancing artistic expression with responsible representation, ensuring that the voices and experiences of those affected are respected and that the commentary contributes constructively to addressing the underlying social issues. Ultimately, the goal is to use art as a catalyst for positive change, promoting greater awareness, empathy, and action towards building more just and resilient communities in the face of future disasters.
Frequently Asked Questions about Depictions of Natural Disasters
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the creation, interpretation, and significance of artistic representations of natural disasters.
Question 1: How can artistic depictions of natural disasters contribute to disaster preparedness?
Visualizations can effectively communicate complex information about disaster risks, preparedness measures, and evacuation procedures. Illustrations demonstrating safe building practices or the proper use of emergency supplies can enhance public awareness and preparedness levels.
Question 2: What is the role of symbolism in artistic representations of natural disasters?
Symbolism can convey deeper meanings related to resilience, loss, hope, and the cyclical nature of natural processes. A recurring motif, such as a phoenix rising from ashes, can represent the capacity for renewal and recovery after devastation.
Question 3: How do historical depictions of natural disasters differ from contemporary ones?
Historical depictions often reflect the limited scientific understanding of the time, sometimes attributing these events to supernatural forces. Contemporary artwork tends to incorporate more scientific accuracy, reflecting advancements in our understanding of natural phenomena. Modern works may also focus on the social and political dimensions of disasters.
Question 4: Can artistic representations of natural disasters be considered a form of historical documentation?
Especially in periods predating photography, artistic depictions served as valuable records of disaster events. These visual accounts provide insights into the extent of damage, the impact on communities, and the responses undertaken. They offer valuable historical data for researchers and inform current understanding of disaster impacts.
Question 5: How can artistic mediums influence the interpretation of natural disasters in art?
Different mediums offer unique expressive possibilities. A watercolor painting might emphasize the fluidity and chaos of a flood, while a charcoal drawing could highlight the stark devastation of a wildfire. The chosen medium shapes the viewer’s emotional response and understanding of the event.
Question 6: What is the ethical responsibility of artists depicting natural disasters?
Artists bear a responsibility to represent these events with sensitivity and respect for those affected. Avoiding sensationalism and prioritizing accurate portrayal over dramatic exaggeration are crucial ethical considerations. Engaging with affected communities can ensure authenticity and avoid misrepresentation.
Understanding these aspects of disaster-related art allows for deeper engagement with the complex interplay between human experience and natural phenomena. These depictions offer valuable insights into societal responses, cultural interpretations, and the ongoing efforts to understand and mitigate the impact of natural disasters.
This FAQ section provides a foundation for further exploration of the complex relationship between art and natural disasters. The following section will offer concluding thoughts on the significance of this form of visual communication.
Conclusion
Exploration of depictions of natural disasters reveals their significance as potent tools for communication, education, and social commentary. Visual representations transcend the limitations of language, conveying the impact of these events on human lives, landscapes, and societal structures. From historical woodblock prints documenting earthquakes to contemporary digital art visualizing climate change impacts, these depictions serve as invaluable records, educational resources, and catalysts for social change. Examination of artistic mediums, historical context, and emotional impact underscores the multifaceted role these visualizations play in shaping understanding and response to natural disasters. Scientific accuracy, balanced with artistic interpretation, enhances the educational value, informing disaster preparedness strategies and promoting informed decision-making. The power of visual storytelling lies in its ability to bridge the gap between scientific understanding and human experience, fostering empathy and inspiring action.
Continued exploration of disaster representation through art remains crucial for fostering informed public discourse, promoting disaster risk reduction efforts, and building more resilient communities. Supporting artists engaged in this work, promoting access to these powerful visual narratives, and critically analyzing their messages are essential steps toward a future where societies are better equipped to understand, prepare for, and mitigate the impact of natural disasters. These depictions hold the potential to shape not only individual perceptions but also collective responses, contributing to a future where humanity and nature coexist more harmoniously.