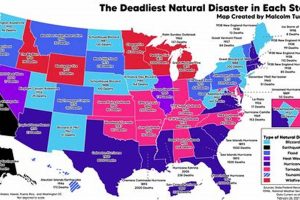
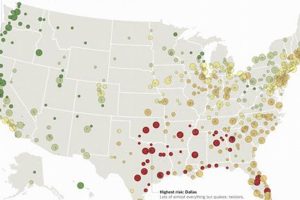
Houston, Texas, experiences a range of severe weather events due to its geographical location and subtropical climate. These include hurricanes, floods, droughts, tornadoes, and severe thunderstorms. Hurricane Harvey in 2017, which caused catastrophic flooding, serves as a stark reminder of the city’s vulnerability. Such events can lead to significant damage to infrastructure, displacement of residents, and economic disruption.
Understanding the risks and impacts of these events is critical for residents, businesses, and emergency management agencies. Effective mitigation strategies, robust infrastructure development, and comprehensive disaster preparedness plans are essential to minimize the impact of future events and build community resilience. Historical data on these events informs urban planning and resource allocation for disaster prevention and response.
This information provides a foundation for exploring specific aspects of Houston’s vulnerability to severe weather, including detailed analyses of individual disaster types, the city’s ongoing mitigation efforts, community preparedness initiatives, and resources available to residents.
Disaster Preparedness Tips for Houston Residents
Given Houston’s susceptibility to various severe weather events, preparedness is crucial for resident safety and minimizing potential damage. The following tips offer guidance for proactive measures:
Tip 1: Develop a Family Emergency Plan: Establish a communication plan including out-of-state contacts, designated meeting points, and evacuation routes. Practice the plan regularly.
Tip 2: Assemble an Emergency Kit: Include essential supplies such as water, non-perishable food, first-aid supplies, medications, flashlights, batteries, a radio, and important documents. Replenish supplies annually.
Tip 3: Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts regularly and sign up for emergency alerts from local authorities. Familiarize oneself with official evacuation procedures.
Tip 4: Protect Property: Trim trees and shrubs near structures. Secure loose objects that could become projectiles in high winds. Consider flood insurance if residing in a flood-prone area.
Tip 5: Understand Evacuation Procedures: Know designated evacuation routes and shelter locations. Prepare vehicles for possible evacuation and ensure fuel tanks remain adequately filled.
Tip 6: Post-Disaster Safety: Avoid floodwaters and downed power lines. Report damages to appropriate authorities. Exercise caution when returning home and inspect for structural damage.
Tip 7: Community Engagement: Participate in community preparedness initiatives and volunteer with local organizations to assist with disaster relief efforts.
Proactive planning and preparation significantly enhance community resilience and individual safety during severe weather events. These measures minimize potential risks and contribute to a quicker recovery.
By understanding the specific risks and adopting appropriate preventative measures, residents contribute to a safer and more resilient Houston.
1. Hurricanes
Hurricanes pose a significant threat to Houston, Texas, due to its coastal location and proximity to the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico. These powerful storms bring intense winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surge, capable of inflicting widespread devastation and disruption.
- Storm Surge:
Storm surge, the abnormal rise of water generated by a storm’s winds, is often the most destructive aspect of a hurricane. Low-lying coastal areas, like much of Houston, are particularly vulnerable. The storm surge associated with Hurricane Ike in 2008 inundated Galveston Island and portions of the Houston metro area, causing extensive damage.
- High Winds:
Hurricane-force winds can damage buildings, uproot trees, and disrupt power lines, leading to extended power outages and communication disruptions. Hurricane Alicia in 1983 caused widespread wind damage across the Houston area, highlighting the destructive potential of these high-velocity winds.
- Heavy Rainfall and Flooding:
Intense rainfall accompanying hurricanes often overwhelms drainage systems, leading to widespread flooding. Hurricane Harvey in 2017 dumped record amounts of rain on Houston, resulting in catastrophic flooding that displaced thousands and caused billions of dollars in damage.
- Long-Term Impacts:
The impacts of hurricanes extend beyond the immediate aftermath. Disruptions to infrastructure, displacement of residents, and economic losses can have long-lasting consequences. Recovery from a major hurricane can take months or even years, impacting the community’s social and economic well-being.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of hurricane threats is crucial for effective disaster preparedness and mitigation in Houston. Comprehensive planning, robust infrastructure development, and community education are essential for minimizing the impact of future hurricanes and enhancing the city’s resilience to these powerful storms.
2. Flooding
Flooding is a significant and recurring natural disaster threat to Houston, Texas. The city’s flat topography, clay-rich soils, rapid urbanization, and proximity to major waterways contribute to its vulnerability. Understanding the various factors influencing flood events is critical for effective mitigation and response.
- Bayou Overflow:
Houston’s extensive bayou system plays a vital role in drainage, but during periods of intense rainfall, these bayous can overflow their banks, inundating surrounding areas. The Addicks and Barker Reservoirs, designed for flood control, can also reach capacity, necessitating controlled releases that exacerbate downstream flooding.
- Coastal Flooding:
Storm surge associated with hurricanes and tropical storms can push seawater inland, causing significant flooding in coastal communities. Hurricane Ike in 2008 demonstrated the devastating impact of coastal flooding on the Houston-Galveston region.
- Flash Flooding:
Intense, localized rainfall can overwhelm drainage systems and quickly lead to flash flooding, particularly in urban areas with impervious surfaces. These rapid-onset floods pose immediate threats to life and property, requiring swift emergency response.
- Urban Development Impact:
Rapid urbanization, coupled with the expansion of impervious surfaces like concrete and asphalt, reduces the ground’s ability to absorb rainfall. This increased runoff contributes to higher flood peaks and more frequent flood events in developed areas.
Addressing Houston’s flood challenges requires a comprehensive approach encompassing improved infrastructure, updated drainage systems, responsible urban planning, and effective flood warning systems. Mitigation efforts must consider the interplay of natural factors and human development to enhance the city’s resilience to flooding and protect its residents and infrastructure.
3. Tornadoes
While hurricanes and flooding often dominate discussions of natural disasters in Houston, Texas, tornadoes also pose a significant, albeit less frequent, threat. Understanding the characteristics and potential impact of tornadoes is crucial for comprehensive disaster preparedness in the region.
- Tornado Formation and Characteristics
Tornadoes in the Houston area typically form during severe thunderstorms, often associated with larger weather systems such as squall lines or supercells. These violently rotating columns of air can vary significantly in size and intensity, with wind speeds exceeding 200 miles per hour in the most extreme cases. The Enhanced Fujita Scale (EF Scale) categorizes tornadoes based on estimated wind speeds and the damage they inflict.
- Seasonal and Geographic Factors
While tornadoes can occur any time of year in Southeast Texas, they are most common during the spring and fall months. The flat coastal plain offers few natural barriers to impede tornado development or dissipate their energy, making the Houston area susceptible to these destructive storms.
- Impact and Damage Potential
Tornadoes can cause significant damage due to their high wind speeds and the debris they carry. Damage can range from minor structural damage to complete destruction of buildings, trees, and infrastructure. The unpredictability of tornado paths makes early warning and preparedness essential for mitigating their impact.
- Tornado Preparedness and Safety Measures
Effective tornado preparedness involves having a plan in place for seeking shelter during a tornado warning. Identified safe rooms, sturdy interior rooms on the lowest level of a building away from windows, or underground shelters provide the best protection. Monitoring weather forecasts and heeding tornado warnings are critical for personal safety during these events.
Including tornadoes within the broader context of natural disaster preparedness in Houston is vital. While less frequent than hurricanes or floods, the potential for destructive impact necessitates awareness, planning, and community education to mitigate risks and enhance resilience to these powerful atmospheric events.
4. Droughts
While Houston, Texas, is often associated with flooding and hurricanes, droughts represent a significant natural disaster threat with far-reaching consequences. Extended periods of abnormally low rainfall can strain water resources, impact agriculture and ecosystems, and increase the risk of wildfires. Understanding the complexities of droughts in the context of Houston’s climate and urban environment is crucial for effective mitigation and adaptation.
- Water Resource Depletion
Droughts directly impact water availability, stressing surface water supplies like reservoirs and lakes, and depleting groundwater aquifers. This scarcity can lead to mandatory water restrictions, impacting residential, commercial, and industrial water use. The drought of 2011, one of the most severe in Texas history, significantly reduced water levels in Lake Houston and other regional reservoirs, highlighting the vulnerability of the city’s water supply.
- Impact on Agriculture and Ecosystems
Reduced rainfall during drought periods negatively impacts agricultural production, stressing crops and livestock. This can lead to reduced yields and economic losses for farmers and ranchers in the surrounding regions. Droughts also disrupt natural ecosystems, stressing native vegetation and wildlife, increasing the risk of wildfires, and altering habitat conditions.
- Increased Wildfire Risk
Dry vegetation becomes highly flammable during prolonged droughts, significantly increasing the risk of wildfires. While not as common in the immediate Houston area, wildfires can threaten surrounding counties and impact air quality within the city. The combination of drought conditions and high winds can rapidly spread wildfires, posing a threat to life and property.
- Economic and Social Impacts
The economic consequences of droughts can be substantial, affecting agriculture, tourism, and other industries reliant on water resources. Water restrictions can disrupt businesses and impact daily life. Social tensions can arise due to competition for limited water resources, particularly during prolonged and severe droughts.
Integrating drought preparedness into Houston’s overall disaster management strategy is essential. Water conservation measures, efficient irrigation practices, drought-resistant landscaping, and public awareness campaigns are crucial for mitigating the impact of future droughts and ensuring the long-term sustainability of the region’s water resources. Understanding droughts as a component of the complex tapestry of natural disasters affecting Houston is critical for building a more resilient and prepared community.
5. Extreme Heat
Extreme heat is a significant component of natural disasters affecting Houston, Texas. The city’s subtropical climate, combined with the urban heat island effect, results in prolonged periods of high temperatures and humidity, posing substantial risks to human health and stressing critical infrastructure. The urban heat island effect, driven by dense concrete and asphalt surfaces absorbing and retaining heat, exacerbates naturally occurring high temperatures, creating significantly hotter conditions within the city compared to surrounding rural areas.
Prolonged periods of extreme heat contribute to heat-related illnesses such as heat exhaustion and heatstroke, particularly among vulnerable populations like the elderly, young children, and those with pre-existing health conditions. The 2011 Texas drought, accompanied by record-breaking temperatures, resulted in a surge of heat-related illnesses and fatalities, underscoring the severity of this threat. Heat waves also place a strain on the power grid as demand for air conditioning increases, potentially leading to rolling blackouts and further compromising the ability of residents to cool their homes. The increased energy demand can also exacerbate air pollution, posing additional health risks.
Addressing the challenges posed by extreme heat requires a multifaceted approach. Implementing urban planning strategies that incorporate green spaces and reflective surfaces can mitigate the urban heat island effect. Public awareness campaigns focused on heat safety measures, access to cooling centers, and community support systems are essential for protecting vulnerable populations during heat waves. Integrating extreme heat considerations into the city’s overall disaster preparedness and response plans is crucial for minimizing its impact and enhancing community resilience to the growing threat of extreme heat events in a changing climate.
6. Infrastructure Impact
Natural disasters significantly impact Houston’s infrastructure, affecting essential services and posing long-term recovery challenges. The interconnected nature of infrastructure systems amplifies the cascading effects of disruptions. Hurricane Harvey in 2017 exemplifies this vulnerability, as widespread flooding overwhelmed drainage systems, inundated wastewater treatment plants, and disrupted transportation networks. The resulting damage led to prolonged service outages, displacement of residents, and economic disruption.
Damage to transportation infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and airports, disrupts supply chains, hinders evacuation efforts, and impedes access for emergency responders. Power outages, caused by damage to power generation and distribution facilities, affect essential services such as hospitals, communication networks, and water treatment plants. Compromised water and wastewater systems pose public health risks, while damage to communication infrastructure hinders emergency communication and coordination. Furthermore, the economic consequences of infrastructure damage can be substantial, requiring significant investment for repairs and reconstruction, impacting businesses and livelihoods.
Building resilient infrastructure is crucial for mitigating the impact of future natural disasters. Investing in robust drainage systems, strengthening building codes, and hardening critical facilities enhances community preparedness and reduces the long-term consequences of these events. Integrating infrastructure resilience into urban planning and development decisions is essential for creating a more sustainable and disaster-resistant Houston. Understanding the interconnectedness of infrastructure systems and their vulnerability to natural hazards informs effective mitigation strategies, strengthens community resilience, and promotes long-term economic stability.
7. Community Preparedness
Community preparedness plays a vital role in mitigating the impact of natural disasters in Houston, Texas. Given the city’s vulnerability to hurricanes, floods, and other severe weather events, proactive planning and collective action are crucial for minimizing risks, protecting lives, and facilitating efficient recovery. A prepared community demonstrates enhanced resilience and recovers more effectively from the disruptions caused by natural disasters.
- Early Warning Systems
Effective early warning systems are fundamental for community preparedness. Timely and accurate dissemination of weather alerts and emergency notifications enables residents to take proactive measures, such as evacuating vulnerable areas or securing their properties. Integration of multiple communication channels, including mobile alerts, social media, and traditional broadcast media, ensures broad reach and accessibility of critical information during emergencies. Real-time updates on evolving conditions empower residents to make informed decisions, enhancing personal safety and community-wide coordination.
- Evacuation Planning and Coordination
Well-defined evacuation plans are essential for minimizing casualties and facilitating safe and efficient movement of people away from hazardous areas. Designated evacuation routes, clearly marked shelters, and readily available transportation resources facilitate timely evacuations. Coordination among local authorities, transportation agencies, and community organizations streamlines the evacuation process, ensuring effective communication and resource allocation. Regular drills and exercises enhance preparedness and refine evacuation procedures, addressing potential logistical challenges and improving responsiveness.
- Public Education and Awareness
Educating the public about potential hazards and promoting awareness of appropriate safety measures are crucial components of community preparedness. Disseminating information on disaster-specific risks, preparedness guidelines, and available resources empowers individuals to take proactive steps to protect themselves and their families. Community workshops, educational materials, and outreach programs build community resilience by fostering a culture of preparedness and promoting individual responsibility in disaster situations.
- Resource Management and Distribution
Effective resource management ensures the availability of essential supplies and services during and after a disaster. Stockpiling critical resources such as food, water, medical supplies, and temporary shelter materials strengthens the community’s ability to respond effectively to immediate needs. Establishing clear distribution channels and logistics plans facilitates efficient allocation of resources to affected areas. Collaboration among government agencies, non-profit organizations, and private sector partners enhances resource mobilization and ensures equitable distribution based on need.
These interconnected facets of community preparedness contribute significantly to mitigating the impact of natural disasters in Houston. By fostering a culture of preparedness, investing in resilient infrastructure, and promoting effective communication and coordination, Houston enhances its ability to withstand and recover from these inevitable events, minimizing disruptions and protecting the well-being of its residents.
Frequently Asked Questions about Natural Disasters in Houston, Texas
This FAQ section addresses common inquiries regarding the diverse range of natural disasters affecting Houston, Texas, offering concise and informative responses to enhance community understanding and preparedness.
Question 1: What types of natural disasters are most common in Houston?
Houston is susceptible to hurricanes, floods, tornadoes, droughts, and extreme heat events. Flooding, often exacerbated by hurricanes, poses a particularly significant threat due to the city’s flat topography and extensive bayou system.
Question 2: How does the urban environment influence Houston’s vulnerability to natural disasters?
Rapid urbanization and extensive impervious surfaces contribute to increased runoff and exacerbate flooding. The urban heat island effect intensifies extreme heat events within the city. Dense development can also amplify the impact of high winds during hurricanes and tornadoes.
Question 3: What resources are available to Houston residents during a natural disaster?
The City of Houston Office of Emergency Management provides resources and information regarding evacuation procedures, shelter locations, and disaster assistance programs. The Harris County Office of Homeland Security & Emergency Management offers similar services at the county level. Numerous non-profit organizations, such as the American Red Cross, also provide disaster relief and support.
Question 4: How can residents prepare for a hurricane in Houston?
Hurricane preparedness includes developing a family emergency plan, assembling an emergency kit, staying informed about weather forecasts, and understanding evacuation procedures. Protecting property by securing loose objects and trimming trees can also minimize potential damage.
Question 5: What steps can be taken to mitigate flood risks in Houston?
Flood mitigation involves improving drainage infrastructure, implementing responsible urban planning practices that consider floodplains, and promoting public awareness about flood safety. Individuals can take steps such as purchasing flood insurance and elevating critical infrastructure within their homes.
Question 6: How does extreme heat impact Houston, and what precautions can residents take?
Extreme heat poses health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations. Precautions include staying hydrated, avoiding strenuous outdoor activities during peak heat hours, seeking air-conditioned environments, and checking on neighbors and relatives who may be at higher risk.
Understanding the specific natural disaster risks affecting Houston and taking proactive preparedness measures enhances community resilience and minimizes the potential impact of these events. Accessing available resources and staying informed empowers residents to protect themselves, their families, and their properties.
For further information and resources, consult official government websites and established disaster relief organizations. The following sections provide additional details on specific disaster types and preparedness strategies.
Natural Disasters Houston Texas
This exploration of natural disasters affecting Houston, Texas, has highlighted the city’s vulnerability to a range of hazards, including hurricanes, floods, tornadoes, droughts, and extreme heat. The interplay of geographical factors, rapid urbanization, and a changing climate contributes to the complexity of these challenges. Understanding the specific characteristics of each hazard, their potential impact on infrastructure and communities, and the importance of preparedness is crucial for mitigating risks and enhancing resilience.
Effective disaster management in Houston requires a multifaceted approach encompassing robust infrastructure development, comprehensive preparedness planning, community education, and ongoing research. Investing in resilient infrastructure, promoting community-wide awareness, and fostering collaboration among government agencies, non-profit organizations, and residents are essential for minimizing the impact of future events and building a more sustainable and disaster-resistant city. Continued focus on these critical areas will be paramount for safeguarding Houston’s future in the face of evolving environmental challenges.