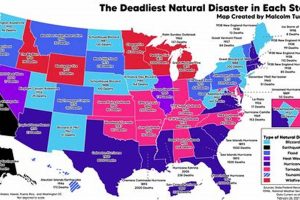
Indiana experiences a range of severe weather events, including floods, tornadoes, severe thunderstorms, and winter storms. While less frequent, earthquakes and droughts also pose risks to the state. These phenomena can cause significant damage to infrastructure, property, and agriculture, impacting communities and the economy. For example, the Great Flood of 1913 devastated numerous Indiana towns, highlighting the destructive potential of widespread flooding.
Understanding Indiana’s vulnerability to these events is crucial for effective mitigation and response strategies. Historical data, combined with ongoing meteorological and geological research, provides valuable insights into the frequency, severity, and potential impacts of various hazards. This knowledge informs community planning, building codes, emergency preparedness programs, and resource allocation decisions, aiming to minimize risks and protect lives and livelihoods.
This article will delve into the specific hazards Indiana faces, exploring their characteristics, historical impacts, and ongoing mitigation efforts. It will also examine the role of public awareness, community engagement, and technological advancements in enhancing resilience and preparedness throughout the state.
Preparedness Tips for Indiana Hazards
Effective preparation is crucial for mitigating the impact of severe weather and other hazardous events. These tips offer guidance for enhancing individual and community resilience in Indiana.
Tip 1: Develop a Family Emergency Plan: Establish a communication plan, including designated meeting points and out-of-state contacts. Outline evacuation routes and procedures, considering specific needs of household members.
Tip 2: Assemble an Emergency Kit: Prepare a kit containing essential supplies such as non-perishable food, water, first-aid supplies, medications, flashlights, batteries, and a NOAA weather radio.
Tip 3: Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and warnings through local media, NOAA weather radio, and official emergency alerts. Sign up for community notification systems to receive timely updates.
Tip 4: Understand Specific Threats: Familiarize oneself with the specific hazards prevalent in Indiana, including tornadoes, floods, and winter storms. Learn the appropriate safety procedures for each type of event.
Tip 5: Secure Property and Surroundings: Trim trees and branches near buildings, secure loose objects that could become airborne in high winds, and reinforce structures prone to flooding.
Tip 6: Participate in Community Drills and Training: Engage in community-organized drills and training exercises to practice emergency procedures and enhance preparedness levels.
Tip 7: Review Insurance Coverage: Ensure adequate insurance coverage for relevant hazards, including flood insurance, which is typically separate from standard homeowner’s policies.
By implementing these preparedness measures, individuals and communities can significantly reduce their vulnerability to the impacts of hazardous events and foster a culture of resilience.
These preparedness measures, while essential, are only part of a broader strategy for mitigating risk. The following section will explore the role of community-level planning and infrastructure development in enhancing overall resilience.
1. Flooding
Flooding represents a significant natural hazard in Indiana, posing substantial risks to both urban and rural communities. The state’s varied topography, combined with intense rainfall events and seasonal snowmelt, contributes to the frequency and severity of flood events. Understanding the different types of flooding and their potential impacts is crucial for effective mitigation and response strategies.
- Riverine Flooding
Riverine flooding occurs when rivers and streams overflow their banks due to excessive rainfall, snowmelt, or ice jams. The Wabash River, for example, has a history of significant flood events, impacting communities along its course. These floods can inundate large areas, causing widespread damage to infrastructure, homes, and businesses.
- Flash Flooding
Flash floods are characterized by rapid and unexpected rises in water levels, often triggered by intense localized rainfall. Urban areas with impervious surfaces are particularly susceptible, as pavement and buildings prevent water absorption. These sudden events can be extremely dangerous, posing immediate threats to life and property.
- Ice Jam Flooding
During the winter months, ice formations on rivers and streams can restrict water flow, leading to upstream flooding. As ice melts and breaks up, the sudden release of water can create powerful surges, exacerbating flood conditions. This type of flooding can be unpredictable and challenging to manage.
- Localized Flooding
Localized flooding often results from inadequate drainage systems or localized intense rainfall exceeding the capacity of storm drains. While typically affecting smaller areas, these events can still cause significant disruption and damage to property.
These various forms of flooding contribute significantly to the overall impact of natural disasters in Indiana. The frequency and intensity of flood events underscore the need for comprehensive flood management strategies, including infrastructure improvements, land-use planning, and public awareness campaigns, to enhance community resilience and minimize the devastating consequences of flooding across the state.
2. Tornadoes
Tornadoes represent a significant threat within the spectrum of natural disasters impacting Indiana. The state’s location within the “Tornado Alley” region of the United States places it at elevated risk for these violent atmospheric phenomena. The flat terrain and confluence of warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico and cool, dry air from Canada create favorable conditions for tornado formation, particularly during the spring and summer months. The significant damage paths caused by tornadoes can result in devastating consequences, including loss of life, injuries, and widespread destruction of property and infrastructure. The Tri-State Tornado of 1925, which tragically impacted portions of Indiana, Illinois, and Missouri, serves as a stark reminder of the destructive potential of these events.
Understanding the processes leading to tornado formation is critical for effective forecasting and warning systems. Meteorological advancements, including Doppler radar technology and improved storm prediction models, have enhanced the ability to detect and track developing tornadoes, providing crucial time for communities to seek shelter and mitigate potential impacts. Public awareness campaigns emphasizing tornado safety procedures, such as identifying safe rooms and practicing emergency drills, play a vital role in reducing casualties and promoting community resilience. Analyzing historical tornado data helps to identify high-risk areas and inform building codes and land-use planning decisions, further strengthening mitigation efforts.
The impact of tornadoes extends beyond immediate damage, affecting long-term community recovery and economic stability. Rebuilding damaged infrastructure, providing support for displaced residents, and restoring essential services require significant resources and coordination. The psychological impact on affected communities can also be substantial, highlighting the need for comprehensive disaster preparedness and recovery planning that addresses both the physical and emotional needs of those impacted. Continued research into tornado dynamics and improved warning systems remains essential for minimizing the devastating consequences of these powerful natural hazards in Indiana.
3. Severe thunderstorms
Severe thunderstorms represent a significant component of natural disasters affecting Indiana. These storms, characterized by high winds, hail, frequent lightning, and heavy rainfall, pose substantial risks to life, property, and infrastructure. The combination of atmospheric instability, moisture, and wind shear creates conditions conducive to severe thunderstorm development, particularly during the spring and summer months. The damaging effects of these storms can range from localized flooding due to intense rainfall to widespread power outages caused by downed trees and power lines. Large hail can damage crops, vehicles, and buildings, while powerful straight-line winds can rival the destructive force of tornadoes, uprooting trees and causing structural damage.
One notable example of the destructive potential of severe thunderstorms in Indiana occurred in June 2008, when a derecho, a widespread and long-lived windstorm associated with a fast-moving band of severe thunderstorms, swept across the state. The storm produced wind gusts exceeding 80 miles per hour, resulting in widespread damage, including downed trees, power outages affecting hundreds of thousands of residents, and significant agricultural losses. Such events highlight the vulnerability of communities to the destructive forces of severe thunderstorms and the importance of preparedness and mitigation strategies.
Understanding the meteorological factors contributing to severe thunderstorm development is crucial for accurate forecasting and timely warnings. Advancements in radar technology and weather modeling have improved the ability to predict and track these storms, providing critical lead time for communities to take protective actions. Public awareness campaigns emphasizing safety measures during severe weather, such as seeking sturdy shelter and avoiding contact with downed power lines, contribute significantly to minimizing casualties and property damage. Furthermore, incorporating severe thunderstorm risk assessments into building codes and land-use planning decisions can enhance community resilience and reduce the long-term impacts of these powerful storms across Indiana.
4. Winter Storms
Winter storms constitute a significant natural hazard in Indiana, posing substantial risks to infrastructure, transportation, and public safety. These storms, characterized by heavy snowfall, freezing rain, strong winds, and extreme cold, can disrupt daily life, causing power outages, road closures, and hazardous travel conditions. The accumulation of heavy snow can lead to roof collapses, while freezing rain can coat surfaces with ice, creating treacherous conditions for pedestrians and motorists. Strong winds associated with winter storms can exacerbate these hazards, leading to downed power lines and blizzard conditions, further reducing visibility and hampering rescue efforts. The extreme cold accompanying these storms presents significant health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those without adequate heating.
The January 2005 North American blizzard serves as a notable example of the disruptive potential of winter storms in Indiana. This storm brought heavy snowfall and blizzard conditions across much of the state, resulting in widespread power outages, school closures, and significant travel disruptions. The storm’s impact underscored the vulnerability of communities to severe winter weather and the importance of preparedness and mitigation strategies. The economic consequences of such storms can be substantial, impacting businesses, transportation networks, and agricultural operations. The indirect costs associated with healthcare needs, lost productivity, and infrastructure repairs contribute to the overall economic burden of winter storms.
Effective preparation and response to winter storms require coordinated efforts among government agencies, utility companies, and community organizations. Accurate weather forecasting and timely public warnings are critical for allowing residents to take necessary precautions, such as stocking up on essential supplies, ensuring adequate heating, and avoiding unnecessary travel. Investing in resilient infrastructure, including robust power grids and efficient snow removal equipment, can minimize disruptions and enhance community preparedness. Public awareness campaigns emphasizing winter weather safety measures, such as proper attire for cold weather and safe driving practices during icy conditions, contribute significantly to reducing risks and enhancing community resilience during winter storms in Indiana.
5. Earthquakes
While less frequent than other natural hazards, earthquakes represent a potential threat within the landscape of natural disasters in Indiana. The state’s proximity to the Wabash Valley Seismic Zone and the New Madrid Seismic Zone places it at risk for seismic activity. These zones, though not as active as those on the West Coast, have produced significant earthquakes in the past, demonstrating the potential for future events. The 1811-1812 New Madrid earthquakes, for example, caused widespread damage and were felt as far away as the East Coast. While Indiana does not experience frequent large-magnitude earthquakes, smaller tremors occur regularly and have the potential to cause damage to infrastructure and disrupt essential services, especially in areas with older buildings or vulnerable infrastructure.
Understanding the geological context of earthquake activity in Indiana is crucial for effective mitigation and preparedness. Ongoing research into seismic activity, fault lines, and ground motion helps to refine risk assessments and inform building codes and infrastructure design. Implementing seismic design principles in new construction and retrofitting existing structures can enhance their resistance to ground shaking and minimize potential damage. Public awareness campaigns educating residents about earthquake safety procedures, such as “Drop, Cover, and Hold On,” empower individuals to take appropriate actions during an earthquake, potentially reducing injuries and enhancing survivability. Developing emergency response plans that address the specific challenges posed by earthquakes, including potential disruptions to communication and transportation networks, is essential for ensuring a coordinated and effective response.
The potential for earthquakes in Indiana, though less frequent than other hazards, underscores the importance of incorporating seismic considerations into disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies. Continued research, enhanced building codes, and public education initiatives are essential for minimizing the impact of these events and fostering community resilience. Integrating earthquake preparedness into broader disaster management frameworks ensures a comprehensive approach to mitigating risks and protecting communities from the diverse range of natural hazards that impact Indiana.
6. Droughts
Droughts, while often less visually dramatic than other natural disasters, pose a significant threat to Indiana’s agricultural economy, water resources, and ecosystem health. Extended periods of below-average precipitation can lead to a cascade of negative impacts, affecting various sectors and requiring comprehensive mitigation and adaptation strategies. The severity and duration of droughts can vary significantly, ranging from short-term dry spells to multi-year periods of extreme water scarcity, each with distinct consequences for the state.
- Agricultural Impacts
Agriculture, a vital component of Indiana’s economy, is particularly vulnerable to drought conditions. Reduced crop yields, livestock stress, and increased irrigation costs can strain farm operations and impact food prices. The 2012 drought, for instance, significantly reduced corn and soybean yields across the state, demonstrating the vulnerability of the agricultural sector to prolonged periods of water scarcity. Drought-resistant crop varieties and improved irrigation practices can help mitigate these impacts, but long-term solutions require addressing water conservation and management strategies.
- Water Resource Stress
Droughts place significant stress on Indiana’s water resources, impacting both surface water supplies and groundwater levels. Reduced stream flows and declining reservoir levels can lead to water shortages for municipalities, industries, and agricultural operations. Competition for limited water resources can exacerbate tensions among different user groups, highlighting the need for comprehensive water management plans and drought contingency strategies. Protecting and restoring wetlands and implementing water conservation measures are crucial for enhancing water resource resilience in the face of drought conditions.
- Ecosystem Disruption
Droughts can disrupt ecosystem functions, impacting wildlife populations, forest health, and water quality. Reduced water availability can stress vegetation, increasing susceptibility to pests and diseases. Declining water levels in rivers and lakes can harm aquatic life and alter habitat conditions. The cumulative effects of drought on ecosystems can lead to long-term ecological changes, impacting biodiversity and ecosystem services. Protecting and restoring riparian corridors and promoting sustainable land management practices can enhance ecosystem resilience to drought conditions.
- Wildfire Risk
Dry vegetation caused by prolonged drought increases the risk of wildfires, posing threats to forests, grasslands, and human settlements. While not as common as in some western states, Indiana has experienced significant wildfires, particularly during periods of drought. These fires can damage property, threaten air quality, and disrupt ecosystem processes. Implementing fire prevention measures, such as prescribed burns and community wildfire protection plans, is essential for minimizing wildfire risks during drought conditions.
The multifaceted impacts of droughts in Indiana necessitate a comprehensive and integrated approach to drought management. This includes developing drought monitoring and early warning systems, implementing water conservation measures, promoting drought-resistant agricultural practices, and enhancing public awareness about drought preparedness. Integrating drought planning into broader disaster management frameworks ensures a coordinated response and strengthens the state’s resilience to this recurring natural hazard. Recognizing the interconnectedness of drought impacts across various sectors is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate the economic, environmental, and social consequences of drought in Indiana.
7. Extreme Heat
Extreme heat events represent a significant and growing concern within the spectrum of natural disasters impacting Indiana. Prolonged periods of excessively high temperatures and humidity pose substantial risks to human health, stressing infrastructure and impacting various sectors of the economy. Urban areas, with their high concentration of heat-absorbing surfaces like asphalt and concrete, can experience amplified heat effects, creating “urban heat islands” where temperatures are significantly higher than surrounding rural areas. This phenomenon exacerbates the health risks associated with extreme heat, particularly for vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and those with pre-existing health conditions. The 1995 Chicago heat wave, which also impacted parts of Indiana, serves as a stark reminder of the potentially devastating consequences of extreme heat, resulting in numerous heat-related illnesses and fatalities. The increasing frequency and intensity of heat waves, driven in part by climate change, necessitates heightened awareness and proactive mitigation strategies.
The impacts of extreme heat extend beyond immediate health concerns, affecting various sectors of society. Increased energy demand for cooling can strain power grids, leading to potential brownouts or blackouts. Heat stress can reduce worker productivity, impacting industries such as construction and agriculture. Elevated water temperatures can stress aquatic ecosystems and impact water quality. Recognizing the interconnectedness of these impacts is crucial for developing comprehensive heat preparedness and adaptation strategies. Implementing urban heat island mitigation measures, such as increasing green spaces and using reflective roofing materials, can help reduce temperatures in urban areas. Public awareness campaigns emphasizing heat safety precautions, such as staying hydrated and seeking cool environments during peak heat hours, are essential for protecting vulnerable populations. Developing heat action plans that coordinate resources and communication across various agencies and community organizations can enhance community resilience during extreme heat events.
Addressing the challenges posed by extreme heat requires a multi-faceted approach that integrates public health interventions, infrastructure adaptations, and community engagement. Continued research into the health impacts of extreme heat, improved heat forecasting and early warning systems, and enhanced urban planning strategies are essential for minimizing the risks associated with these events. Incorporating extreme heat preparedness into broader disaster management frameworks ensures a comprehensive approach to mitigating the diverse range of natural hazards impacting Indiana and protecting the health and well-being of its residents in a changing climate.
Frequently Asked Questions about Natural Hazards in Indiana
This section addresses common questions regarding the range of natural hazards impacting Indiana, providing concise and informative responses to enhance public understanding and preparedness.
Question 1: How often do tornadoes occur in Indiana?
Indiana experiences an average of 22 tornadoes annually, most frequently during the spring and summer months. However, tornadoes can occur any time of year.
Question 2: What are the primary flood risks in Indiana?
Major river flooding, flash flooding, and ice jam flooding pose significant risks. Localized flooding due to inadequate drainage systems also occurs. Understanding the specific flood risks in one’s area is crucial for preparedness.
Question 3: Does Indiana experience earthquakes?
While less frequent than other hazards, Indiana is at risk due to its proximity to the Wabash Valley and New Madrid Seismic Zones. Smaller tremors occur regularly, and larger earthquakes, though historically infrequent, are possible.
Question 4: How can I prepare for a winter storm in Indiana?
Assemble an emergency kit, monitor weather forecasts, ensure adequate heating, avoid unnecessary travel, and familiarize oneself with winter weather safety procedures. Preparing homes and vehicles for winter conditions is also essential.
Question 5: What are the signs of an approaching severe thunderstorm?
Darkening skies, strong winds, large hail, frequent lightning, and a sudden drop in temperature can indicate an approaching severe thunderstorm. Staying informed through weather alerts and seeking shelter promptly are crucial safety measures.
Question 6: How can I protect my property from drought impacts?
Implementing water conservation practices, such as efficient irrigation and drought-tolerant landscaping, can minimize the effects of drought on property. Understanding local water restrictions and community drought management plans is also important.
Preparedness and mitigation are key to reducing the impact of natural hazards. Staying informed, developing emergency plans, and understanding specific risks are vital steps in protecting life and property.
For further information and resources on specific hazards, consult official sources such as the Indiana Department of Homeland Security and the National Weather Service.
Natural Disasters in Indiana
This exploration of Indiana’s vulnerability to natural hazards has highlighted the diverse range of threats facing the state, from the destructive force of tornadoes and floods to the insidious impacts of droughts and extreme heat. Understanding the unique characteristics of each hazard, coupled with awareness of historical events and ongoing research, provides crucial context for effective mitigation and response strategies. The interconnectedness of these hazards underscores the need for comprehensive preparedness planning that integrates individual actions, community-level initiatives, and statewide coordination.
While the potential for natural disasters in Indiana remains a constant, proactive measures can significantly reduce their impact. Continued investment in resilient infrastructure, advancements in forecasting and warning systems, and ongoing public education efforts are essential for fostering a culture of preparedness and mitigating the economic, environmental, and social consequences of these events. The collective responsibility to build resilient communities, informed by scientific understanding and driven by a commitment to safety and well-being, represents the most effective defense against the inevitable challenges posed by natural disasters in Indiana.