
The process of salvaging and restoring vital information systems following disruptive events, such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, or hardware failures, ensures business continuity. A practical example is restoring data from backups after... Read more »

A geographically separate facility houses duplicate IT infrastructure, enabling an organization to restore its critical systems and data in the event of a primary data center outage. This alternate site allows for... Read more »

Modern businesses rely heavily on robust technological infrastructure. A centralized location housing core computing and networking equipment, such as servers, storage systems, and network devices, forms the backbone of these operations. Complementing... Read more »

Protecting digital assets is paramount in today’s interconnected world. This involves implementing robust systems to ensure business continuity in the face of unforeseen events, such as hardware failures, natural disasters, or cyberattacks.... Read more »

The ability of an organization to resume vital IT operations following an unplanned outage or disruption affecting its data center constitutes a critical business function. This involves a range of strategies and... Read more »

Protecting digital assets involves two key processes: regularly copying information to a separate, secure location and having a comprehensive plan to restore functionality after unforeseen events. For example, a business might copy... Read more »
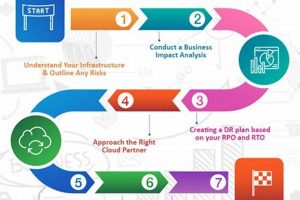
A documented process enabling the restoration of vital information systems and data following an unforeseen event, such as a natural disaster, cyberattack, or equipment failure, constitutes a cornerstone of business continuity. A... Read more »

Protecting information assets involves two key processes: routinely copying data to a separate storage location and implementing a plan to restore systems and data after an unforeseen event. For instance, a business... Read more »

A situation involving significant data loss requiring professional retrieval services exemplifies a critical failure in data management. This can range from a single hard drive crash resulting in the loss of personal... Read more »


