
Pinpointing the single rarest natural hazard is challenging due to complexities in defining and recording these events. Some phenomena, while individually rare, belong to broader categories (like impact events, which fall under... Read more »
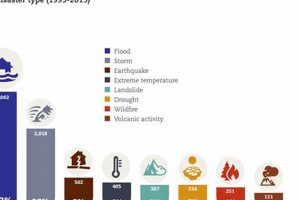
Globally, frequently occurring devastating events include floods, earthquakes, wildfires, volcanic eruptions, droughts, and severe storms such as hurricanes, cyclones, and tornadoes. These phenomena, arising from natural processes within the Earth’s systems or... Read more »

Technological or human-induced catastrophes encompass events like industrial accidents, transportation disasters, unintentional fires and explosions, and failures of infrastructure such as dams or bridges. These events often stem from human error, negligence,... Read more »

The Space Shuttle Columbia disintegrated upon re-entry into the Earth’s atmosphere on February 1, 2003, resulting in the loss of all seven crew members. During the shuttle’s launch 16 days earlier, a... Read more »

North Carolina experiences a diverse range of natural hazards, from coastal threats like hurricanes, storm surge, and coastal erosion, to inland challenges such as flooding, tornadoes, severe thunderstorms, and winter storms. Wildfires... Read more »

The African continent experiences a diverse range of natural hazards, impacting various regions with varying frequency and intensity. These events include droughts, floods, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, landslides, wildfires, and insect infestations, such... Read more »

A governmental proclamation recognizing that a specific geographic area has suffered from a calamitous event of such severity that it warrants supplemental aid beyond the capabilities of state and local resources. For... Read more »
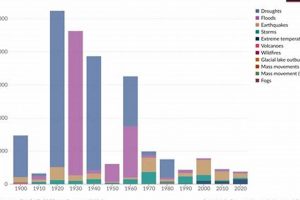
The allocation of resources following a catastrophic event, whether natural or human-caused, encompasses the processes of delivering essential supplies, personnel, and services to affected populations. For instance, following an earthquake, this might... Read more »

The term likely refers to a misconstrued or hypothetical event. There is no widely recognized or documented historical incident commonly known as an “Ohio balloon disaster.” While Ohio has a history of... Read more »

Incarcerated individuals constitute a vulnerable population during natural disasters. Their confinement restricts their ability to evacuate or take independent protective measures. Events such as earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires can compromise prison... Read more »


