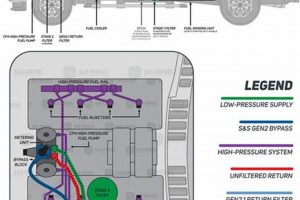
The 6.7L Power Stroke diesel engine, found in Ford Super Duty trucks from 2011 to 2022, utilizes a Bosch CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump. This pump is known for its sensitivity to contaminants in fuel, which can lead to catastrophic failure and extensive engine damage. A preventative maintenance strategy, often referred to as a “kit” approach, typically involves components and practices designed to mitigate this risk. These include upgraded fuel filtration systems, fuel additives for lubricity enhancement, and regular maintenance schedules. An example might be a combination of a high-micron fuel filter, a lift pump for improved fuel supply, and a fuel pressure regulator.
Protecting the CP4.2 pump is crucial for maintaining the longevity and reliability of these engines. The cost of repairing or replacing a failed pump, along with potential consequential damage to injectors and other engine components, can be substantial. Proactive measures offer a cost-effective solution to avoid these potentially crippling expenses. The increasing awareness of the CP4.2’s vulnerabilities has led to a growing market for preventative solutions, reflecting a demand for enhanced reliability within the diesel truck community.
This article will further explore the specific components typically included in such preventative strategies, discuss the benefits of each, and offer guidance on implementation and best practices for maintaining the 6.7L Power Stroke engine.
Preventative Maintenance for the 6.7L Power Stroke CP4.2 Fuel System
Maintaining the 6.7L Power Stroke diesel engine requires a proactive approach, especially concerning the CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump. The following tips offer guidance on mitigating the risk of fuel system failures.
Tip 1: Upgrade Fuel Filtration. Installing supplemental fuel filters with higher micron ratings helps remove contaminants before they reach the CP4.2 pump. A two-micron filter is often recommended as a secondary filter.
Tip 2: Add a Lift Pump. A lift pump improves fuel supply to the CP4.2, preventing cavitation and reducing stress on the pump. This is particularly beneficial in modified engines or those experiencing fuel starvation.
Tip 3: Use Quality Fuel Additives. Additives designed to enhance lubricity can protect the CP4.2 pump from internal wear caused by low-sulfur diesel fuel. Select additives specifically formulated for this purpose.
Tip 4: Monitor Fuel Pressure. Regularly monitoring fuel pressure can provide early warning signs of potential issues within the fuel system. Install a fuel pressure gauge for convenient monitoring.
Tip 5: Adhere to Regular Maintenance Schedules. Timely replacement of fuel filters and regular engine maintenance are essential for optimal fuel system performance and longevity. Follow manufacturer-recommended intervals.
Tip 6: Drain Water Separator Regularly. Water contamination can severely damage the CP4.2 pump. Regularly draining the water separator, often integrated into the fuel filter housing, is crucial.
Tip 7: Consider a Fuel Pressure Regulator. A fuel pressure regulator can help maintain consistent fuel pressure and prevent excessive pressure spikes that could damage the CP4.2.
By implementing these preventative measures, owners can significantly reduce the risk of CP4.2 fuel pump failure and associated engine damage, ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
These preventative measures offer significant cost savings compared to the expense of repairing or replacing a failed CP4.2 pump. Further discussion will explore the long-term implications and cost-benefit analysis of these proactive strategies.
1. Filtration
Filtration plays a critical role in preventing CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump failures in the Ford 6.7L Power Stroke diesel engine. The CP4.2 pump is highly susceptible to damage from contaminants present in diesel fuel, such as metal particles, dirt, and water. These contaminants can cause abrasive wear within the pump, leading to premature failure and potentially catastrophic engine damage. Effective filtration systems remove these harmful particles, protecting the pump and extending its lifespan. For example, incorporating a two-micron fuel filter can significantly reduce the risk of contamination-induced failure. The filtration system acts as the first line of defense, safeguarding the sensitive components of the high-pressure fuel system.
Multiple filtration stages offer increased protection. A primary filter, typically installed from the factory, provides initial filtration. However, adding a secondary filter, often with a finer micron rating, further reduces the risk of contamination. This multi-stage approach ensures that even microscopic particles are removed before reaching the CP4.2 pump. Furthermore, regular filter maintenance, including timely replacement according to manufacturer recommendations, is essential for maintaining optimal filtration efficiency. Neglecting filter changes can lead to reduced filtration capacity, increasing the risk of pump failure.
Investing in robust filtration is a cost-effective strategy for mitigating the significant expense associated with CP4.2 pump replacement. The cost of a comprehensive filtration system is minimal compared to the potential cost of a new pump, injectors, and other related repairs. Therefore, prioritizing filtration within a preventative maintenance plan offers significant long-term cost savings and ensures the reliability and longevity of the 6.7L Power Stroke engine. Addressing filtration proactively is essential for protecting this critical engine component.
2. Lubrication
Lubrication is essential for mitigating premature wear and potential failure of the CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump in the Ford 6.7L Power Stroke engine. The CP4.2 pump relies on adequate lubrication to minimize friction and heat generation within its intricate internal components. Insufficient lubrication can lead to accelerated wear, ultimately contributing to catastrophic pump failure. Therefore, maintaining proper lubrication is a crucial aspect of a comprehensive preventative maintenance strategy.
- Fuel Quality
Ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) fuel, while environmentally beneficial, contains lower levels of sulfur, which traditionally contributed to fuel lubricity. This reduction in sulfur content can lead to increased wear within the CP4.2 pump. Using high-quality ULSD fuel from reputable sources helps ensure adherence to minimum lubricity standards, minimizing potential wear issues.
- Lubricity Additives
Fuel lubricity additives are specifically formulated to enhance the lubricating properties of ULSD fuel. These additives create a protective film on the internal components of the CP4.2 pump, reducing friction and wear. Selecting additives specifically designed for diesel fuel systems and following manufacturer recommendations is essential for optimal performance and protection.
- Fuel System Components
Maintaining the integrity of fuel system components, such as injectors and fuel lines, contributes indirectly to CP4.2 lubrication. Worn or damaged components can introduce metal particles and other contaminants into the fuel stream, exacerbating wear within the pump. Regular inspection and timely replacement of these components are crucial for maintaining a clean and properly lubricated fuel system.
- Monitoring and Maintenance
Regularly monitoring fuel system performance and adhering to manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules are essential for ensuring proper lubrication. This includes routine fuel filter replacements, which help maintain fuel cleanliness and prevent contaminants from interfering with lubrication. Additionally, periodic checks for leaks or other signs of fuel system issues can help identify potential problems before they escalate and cause damage to the CP4.2 pump.
By addressing these facets of lubrication, owners of 6.7L Power Stroke engines can significantly reduce the risk of CP4.2 pump failure. Proper lubrication, combined with effective filtration and other preventative measures, ensures long-term engine reliability and avoids costly repairs associated with pump failure. A comprehensive approach to lubrication is crucial for protecting this vital engine component and maintaining optimal performance.
3. Fuel Pressure
Maintaining proper fuel pressure is paramount for the longevity and reliability of the CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump in the Ford 6.7L Power Stroke engine. Insufficient or excessive fuel pressure can contribute to premature wear, internal damage, and ultimately, catastrophic pump failure. Understanding and managing fuel pressure within the optimal range is a crucial element of preventative maintenance. Consistent and adequate fuel pressure ensures proper lubrication and cooling within the pump, mitigating the risk of damage. Conversely, fluctuations or extremes in pressure can place undue stress on the pump’s internal components, leading to accelerated wear and potential failure. This section explores the multifaceted relationship between fuel pressure and CP4.2 pump health.
- Low Fuel Pressure
Low fuel pressure can starve the CP4.2 pump of the fuel it requires for both lubrication and cooling. This starvation can lead to increased friction and heat generation within the pump, accelerating wear and potentially causing catastrophic damage. Common causes of low fuel pressure include failing lift pumps, clogged fuel filters, or restricted fuel lines. Ignoring low fuel pressure can lead to significant damage, underscoring the importance of regular monitoring and prompt corrective action.
- High Fuel Pressure
While low fuel pressure presents a clear danger, excessively high fuel pressure can also damage the CP4.2 pump. High pressure can overstress the pump’s internal components, leading to premature wear and potential failure. A faulty fuel pressure regulator is a common culprit for high fuel pressure. Excessive pressure can also strain other fuel system components, creating a cascading effect that further jeopardizes the CP4.2 pump. Therefore, maintaining fuel pressure within the manufacturer’s specified range is critical.
- Pressure Fluctuations
Rapid or significant fluctuations in fuel pressure can also negatively impact the CP4.2 pump. These fluctuations subject the pump to repeated stress cycles, contributing to fatigue and potential failure. Issues like air intrusion in the fuel lines or a malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator can cause pressure instability. Consistent fuel pressure is essential for optimal pump performance and longevity, highlighting the importance of addressing any pressure fluctuations promptly.
- Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring of fuel pressure is essential for detecting potential problems early on. Installing a fuel pressure gauge allows for real-time observation of fuel pressure, enabling prompt identification of deviations from the normal range. Regular maintenance, including fuel filter replacements and inspections of fuel system components, helps prevent pressure-related issues. Adhering to manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules is crucial for maintaining optimal fuel system health and preventing costly repairs.
Maintaining proper fuel pressure is an integral aspect of preventing CP4.2 pump failures in the 6.7L Power Stroke engine. Addressing low pressure, high pressure, and pressure fluctuations, along with diligent monitoring and maintenance, safeguards the pump from damage and ensures its long-term reliability. Integrating fuel pressure management into a comprehensive preventative maintenance strategy is essential for protecting this critical component and avoiding costly repairs. Ignoring fuel pressure issues can lead to significant and potentially irreparable engine damage, underscoring the importance of proactive management.
4. Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for preventing catastrophic CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump failures in the Ford 6.7L Power Stroke diesel engine. This pump, while delivering high performance, exhibits sensitivity to contaminants and wear, necessitating a proactive maintenance approach. Neglecting routine maintenance significantly increases the risk of pump failure, leading to substantial repair costs and potential downtime. Conversely, a disciplined maintenance schedule, incorporating key preventative measures, safeguards the CP4.2 pump and contributes to the engine’s overall longevity. This proactive approach offers a cost-effective solution compared to the substantial expense of pump replacement and associated repairs. For example, adhering to recommended fuel filter replacement intervals prevents contaminant buildup, a major contributor to CP4.2 failure. Similarly, regular checks for fuel leaks and other abnormalities allow for early detection and correction of potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
Several key maintenance practices directly impact CP4.2 pump health. Regular fuel filter replacements, often overlooked, are paramount. These filters trap contaminants that would otherwise damage the pump’s precision internal components. Using high-quality fuel filters and adhering to manufacturer-recommended replacement intervals are essential. Furthermore, routine inspections of the entire fuel system, including fuel lines, connections, and the water separator, help identify potential issues like leaks or water intrusion, both of which can compromise the CP4.2 pump. Addressing these issues promptly prevents further damage and maintains the integrity of the fuel system. Regularly draining the water separator, often integrated into the fuel filter housing, removes accumulated water, preventing corrosion and damage within the fuel system. This simple yet crucial step further protects the CP4.2 pump from water-induced failure.
Integrating these maintenance practices into a comprehensive preventative strategy provides substantial benefits. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of costly CP4.2 pump failures, extending the engine’s service life and reducing overall operating costs. The relatively minor expense of routine maintenance pales in comparison to the significant financial burden of a major fuel system repair. Furthermore, a well-maintained fuel system contributes to optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. By prioritizing maintenance, owners can avoid the inconvenience and expense associated with unexpected breakdowns, ensuring the reliable operation of their 6.7L Power Stroke engine. Therefore, a proactive maintenance schedule is not merely a recommendation but a critical investment in the long-term health and performance of the engine. It represents a cost-effective strategy for avoiding potentially crippling repair expenses and maximizing the engine’s operational life.
5. Water Separation
Water contamination in the fuel system poses a significant threat to the CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump in the Ford 6.7L Power Stroke engine. Effective water separation is therefore a critical component of any preventative maintenance strategy, often incorporated within a “kit” approach. Water, whether introduced through condensation, contaminated fuel, or other means, can cause corrosion, erode lubricity, and damage the pump’s precision internal components. Addressing water contamination proactively is essential for preserving the pump’s lifespan and avoiding costly repairs.
- Sources of Water Contamination
Water can enter the fuel system through various avenues. Condensation within the fuel tank, especially during temperature fluctuations, is a common source. Contaminated fuel from less reputable suppliers can also introduce water. Additionally, leaks in the fuel system can allow water to ingress. Understanding these sources allows for targeted preventative measures.
- Effects of Water on the CP4.2 Pump
Water in the fuel system has detrimental effects on the CP4.2 pump. It corrodes internal components, leading to premature wear and potential failure. Water also disrupts the fuel’s lubricating properties, increasing friction within the pump and exacerbating wear. Furthermore, water can cause rust and other forms of oxidation, compromising the pump’s delicate internal mechanisms. The cumulative effect of these issues can lead to catastrophic pump failure and extensive engine damage.
- Water Separation Methods
Modern diesel engines often incorporate a water separator within the fuel filter housing. This separator collects water from the fuel, preventing it from reaching the CP4.2 pump. Regularly draining the water separator is crucial for maintaining its effectiveness. Some preventative maintenance kits include upgraded water separators with increased capacity or improved filtration capabilities. These upgrades offer enhanced protection against water contamination.
- Best Practices for Water Management
Beyond relying on the water separator, several best practices further mitigate water contamination risks. Using high-quality fuel from reputable suppliers minimizes the chance of introducing contaminated fuel. Regularly inspecting the fuel system for leaks and promptly repairing any found prevents water ingress. Storing fuel in sealed containers prevents water contamination through condensation. These practices, combined with diligent water separator maintenance, contribute to a comprehensive water management strategy.
Effective water separation is an indispensable aspect of preserving the CP4.2 pump’s longevity. By understanding the sources of water contamination, its detrimental effects, and the available separation methods, owners can implement a proactive strategy to safeguard their engines. Incorporating water separation practices within a comprehensive “kit” approach to preventative maintenance offers significant long-term cost savings by preventing costly pump failures and associated repairs. Neglecting water separation can lead to substantial financial burdens and compromise the engine’s reliability.
6. Component Upgrades
Component upgrades constitute a crucial aspect of a comprehensive strategy for preventing CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump failures in the Ford 6.7L Power Stroke engine. These upgrades, often integrated into a preventative “kit” approach, address inherent vulnerabilities within the fuel system, enhancing reliability and longevity. While regular maintenance practices are essential, component upgrades provide additional layers of protection, mitigating the risk of catastrophic pump failure. These upgrades typically focus on enhancing fuel delivery, filtration, and pressure regulation, all critical factors influencing the CP4.2 pump’s operational lifespan.
One common component upgrade involves replacing the factory lift pump with a higher-flow aftermarket unit. The factory lift pump, while adequate for stock engine performance, may struggle to maintain consistent fuel supply under demanding conditions or with engine modifications. An upgraded lift pump ensures a steady and sufficient flow of fuel to the CP4.2 pump, preventing fuel starvation, a known contributor to pump failure. Another prevalent upgrade involves installing a higher-quality fuel pressure regulator. This component maintains consistent fuel pressure within the optimal range, preventing pressure spikes or drops that can stress the CP4.2 pump. Maintaining stable fuel pressure is crucial for the pump’s longevity and efficient operation.
Upgrading fuel filtration is another critical component upgrade. While stock fuel filters provide adequate filtration for normal operation, they may not effectively remove all contaminants that can damage the CP4.2 pump, especially in environments with lower fuel quality. Upgraded filtration systems, incorporating finer micron filters and multi-stage filtration, offer enhanced protection against abrasive particles that can wear down the pump’s internal components. These filtration upgrades serve as a crucial defense against contamination-induced pump failures. In conclusion, incorporating component upgrades into a preventative maintenance strategy represents a proactive and effective approach to safeguarding the CP4.2 pump. These upgrades complement regular maintenance practices, providing enhanced protection against the various factors that contribute to pump failure. While the initial investment in component upgrades might seem significant, it pales in comparison to the substantial cost of a CP4.2 pump replacement and associated engine repairs. Therefore, component upgrades offer a cost-effective solution for ensuring the long-term reliability and performance of the 6.7L Power Stroke engine.
Frequently Asked Questions
This FAQ section addresses common concerns regarding preventative measures for the CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump in the Ford 6.7L Power Stroke diesel engine.
Question 1: Is a preventative maintenance “kit” truly necessary for the 6.7L Power Stroke?
Given the CP4.2 pump’s known vulnerability to fuel contaminants and the substantial cost of repairs, preventative measures are highly recommended. While not strictly mandatory, the long-term cost savings and enhanced reliability offered by preventative strategies make them a prudent investment.
Question 2: What are the most important components of a preventative maintenance strategy?
Key components include upgraded fuel filtration, a lift pump, lubricity additives, and a fuel pressure regulator. Regular maintenance, including fuel filter replacements and water separator draining, is also essential.
Question 3: How often should fuel filters be replaced in a 6.7L Power Stroke?
Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals is crucial. However, more frequent filter changes may be necessary in environments with dusty conditions or if using fuel from less reputable sources. Consulting a qualified diesel mechanic is advisable for specific recommendations.
Question 4: Can using fuel additives completely eliminate the risk of CP4.2 failure?
While fuel additives enhance lubricity and reduce wear, they do not guarantee complete immunity from CP4.2 failure. A comprehensive preventative approach, including filtration upgrades and other measures, is essential for maximizing protection.
Question 5: What are the signs of a failing CP4.2 pump?
Symptoms may include hard starting, rough running, decreased power, and metal shavings in the fuel filter. If any of these signs are observed, immediate inspection by a qualified diesel mechanic is crucial to prevent further engine damage.
Question 6: Are these preventative measures applicable to all model years of the 6.7L Power Stroke?
While the CP4.2 pump is present in 6.7L Power Stroke engines from 2011 to 2022, specific preventative measures and recommendations may vary slightly depending on the model year. Consulting a diesel mechanic familiar with the specific model year is recommended for tailored guidance.
Proactive maintenance offers a cost-effective strategy for protecting the 6.7L Power Stroke engine from costly CP4.2 fuel pump failures. Addressing fuel contamination, lubrication, and pressure through regular maintenance and component upgrades significantly reduces the risk of catastrophic damage.
The subsequent section will provide further details on specific product recommendations and installation procedures for implementing a comprehensive preventative maintenance plan.
Protecting the 6.7L Power Stroke
Maintaining the reliability and longevity of the Ford 6.7L Power Stroke diesel engine requires a proactive approach to fuel system maintenance. Strategies focused on preventing CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump failures are paramount. This involves addressing critical aspects such as fuel filtration, lubrication, pressure regulation, water separation, and implementing key component upgrades. A comprehensive approach, often referred to as a preventative maintenance “kit” strategy, combines these elements to safeguard the engine from costly repairs and potential downtime. This article has explored these critical aspects, emphasizing the importance of each in preserving the CP4.2 pump’s operational lifespan and overall engine reliability. From filtration upgrades to fuel pressure monitoring and the use of quality lubricity additives, a multi-pronged approach offers the most robust protection against the known vulnerabilities of the CP4.2 pump.
Protecting the CP4.2 pump is not merely a maintenance recommendation; it is a crucial investment in the long-term viability of the 6.7L Power Stroke engine. The potential cost of neglecting preventative measures far outweighs the investment in proactive maintenance. Owners are encouraged to adopt a comprehensive approach to fuel system maintenance, integrating the strategies and recommendations outlined in this article. The continued performance and reliability of the 6.7L Power Stroke engine hinge on the proactive implementation of these preventative measures, ensuring its continued service for years to come.