A governmental organization dedicated to preparing for, mitigating, responding to, and recovering from natural and human-caused disasters plays a vital role in safeguarding a nation’s populace and infrastructure. Such bodies typically coordinate resources, provide training and public education, and collaborate with other agencies at local, regional, and international levels. For example, a coordinated response involving evacuation procedures, search and rescue operations, and the provision of shelter and medical assistance can significantly reduce the impact of a major earthquake.
The existence of a robust, well-funded organization focused on disaster preparedness and response is crucial for minimizing casualties, economic losses, and societal disruption. Historically, nations lacking such structured systems have experienced significantly greater devastation and slower recovery following major events. Proactive measures like early warning systems, vulnerability assessments, and community resilience initiatives are essential for mitigating the impact of future disasters and fostering a culture of preparedness.
This understanding of the critical role played by such organizations provides a foundation for exploring key topics related to disaster management, including risk assessment, emergency response protocols, community engagement, and the integration of technology in disaster mitigation and recovery efforts.
Disaster Preparedness Tips
Preparedness is crucial for minimizing the impact of disasters. These tips offer guidance on how individuals and communities can enhance their resilience and response capabilities.
Tip 1: Develop a Family Emergency Plan: Establish a communication plan including contact information for family members, meeting points, and out-of-area contacts. Practice the plan regularly.
Tip 2: Build an Emergency Kit: Assemble a kit containing essential supplies such as water, non-perishable food, first-aid supplies, medications, a flashlight, and a radio. Ensure the kit is readily accessible.
Tip 3: Know Your Risks: Understand the specific hazards that threaten your area, whether floods, earthquakes, wildfires, or other potential disasters. This knowledge informs appropriate preparedness measures.
Tip 4: Stay Informed: Monitor weather reports and official alerts through local media and designated communication channels. Timely information is crucial for effective response.
Tip 5: Secure Your Property: Implement measures to protect your home or business from potential damage. This might include reinforcing structures, installing shutters, and trimming trees near buildings.
Tip 6: Get Involved in Community Preparedness: Participate in local initiatives, such as volunteer programs or training sessions, to strengthen community-wide resilience and response capabilities.
Tip 7: Learn Basic First Aid and CPR: Acquiring these skills can be invaluable in emergency situations, enabling individuals to provide immediate assistance to those in need.
By taking these proactive steps, individuals and communities can significantly enhance their safety and resilience in the face of disasters. Preparedness empowers effective response, minimizes disruption, and fosters a culture of safety.
These preparedness measures form the foundation for a comprehensive approach to disaster management, which encompasses response, recovery, and mitigation efforts.
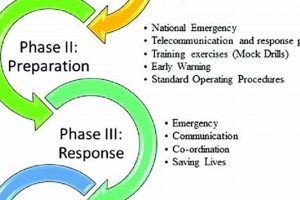
1. Preparedness
Preparedness, a cornerstone of effective disaster management, represents the proactive measures undertaken by a national disaster management agency to anticipate, mitigate, and respond to potential hazards. It forms the foundation upon which resilient communities and nations are built, minimizing the impact of disasters on lives, livelihoods, and infrastructure. This proactive approach is essential for optimizing resource allocation, coordinating inter-agency collaborations, and ensuring a swift and effective response when disaster strikes.
- Risk Assessment and Planning
Comprehensive risk assessments identify potential hazards and vulnerabilities. This analysis informs the development of detailed disaster preparedness plans, outlining specific actions, resource allocation, and communication protocols for various scenarios. For example, agencies in earthquake-prone regions develop plans that address building codes, evacuation routes, and post-disaster shelter provisions. This meticulous planning is crucial for a coordinated and effective response.
- Community Education and Engagement
Educating the public about potential risks and appropriate safety measures empowers communities to prepare and respond effectively. Public awareness campaigns, training programs, and community drills play a crucial role in fostering a culture of preparedness. For instance, educating coastal communities about hurricane preparedness measures, including evacuation procedures and emergency supply kits, can significantly reduce casualties and property damage.
- Early Warning Systems
Establishing reliable early warning systems provides critical time for communities to prepare and evacuate before a disaster strikes. These systems utilize advanced technologies, such as weather monitoring and seismic sensors, to detect impending threats and disseminate timely alerts. The effectiveness of tsunami warning systems in the Pacific Ocean, for example, has demonstrably saved lives by providing advance notice, allowing coastal populations to seek higher ground.
- Resource Management and Logistics
Effective resource management is essential for ensuring adequate supplies, equipment, and personnel are available during a disaster. This includes stockpiling essential goods, establishing logistical networks for distribution, and training specialized response teams. The strategic positioning of emergency supplies, medical equipment, and search and rescue teams before a hurricane makes landfall, for example, can significantly enhance the effectiveness of the immediate response.
These facets of preparedness highlight the crucial role of a national disaster management agency in building resilient communities. By proactively addressing potential risks, engaging with communities, and investing in robust systems, these agencies minimize the impact of disasters and contribute significantly to national safety and security. The ability to anticipate, prepare for, and mitigate the effects of disasters through these focused efforts strengthens a nation’s ability to withstand and recover from such events, underscoring the vital importance of preparedness in the broader context of disaster management.
2. Response
A national disaster management agency’s response phase is the immediate, coordinated action taken during and immediately following a disaster. This phase is critical in saving lives, minimizing damage, and initiating the recovery process. Effective response hinges on pre-existing preparedness measures, including established communication protocols, trained personnel, and strategically positioned resources. The speed and efficiency of the response directly impact the severity of a disaster’s consequences. For example, the rapid deployment of search and rescue teams following an earthquake can significantly increase the number of survivors. Conversely, a delayed or disorganized response can exacerbate the impact, leading to greater loss of life and increased economic burden.
Response encompasses a multitude of activities tailored to the specific disaster. These may include search and rescue operations, the establishment of emergency shelters, the provision of medical assistance, and the restoration of essential infrastructure such as communication networks and transportation routes. The coordination of these activities is paramount, requiring clear lines of communication and command between various agencies and stakeholders. Following a major hurricane, for instance, a coordinated response involves the collaboration of multiple agencies to provide shelter, food, medical care, and debris removal. Effective resource allocation and logistical planning are essential to ensure aid reaches those in need efficiently and equitably. Challenges in response can arise from unforeseen circumstances, overwhelmed infrastructure, and logistical complexities, highlighting the importance of flexible and adaptable response strategies.
The effectiveness of a national disaster management agency’s response is a direct reflection of its preparedness and planning. While response itself focuses on immediate action, it is underpinned by prior investment in training, resource allocation, and the development of robust operational frameworks. Successful response mitigates the immediate impacts of a disaster, setting the stage for recovery and long-term rebuilding efforts. Understanding the critical role of response within the broader context of disaster management emphasizes the need for continuous improvement in preparedness strategies, training programs, and inter-agency coordination mechanisms. This continuous refinement of response capabilities contributes significantly to a nation’s resilience and its capacity to effectively manage the multifaceted challenges posed by disasters.
3. Recovery
Recovery, a crucial component of a national disaster management agency’s mandate, encompasses the long-term process of restoring normalcy and rebuilding communities following a disaster. This phase extends beyond immediate relief efforts, focusing on reconstructing infrastructure, revitalizing economies, and providing psychosocial support to affected populations. Recovery operations are inherently complex, often requiring substantial resources, extensive planning, and sustained commitment from various stakeholders. The effectiveness of recovery efforts directly influences a community’s ability to rebound from a disaster and mitigate the long-term social, economic, and environmental consequences. For example, following a major earthquake, recovery may involve rebuilding damaged homes and businesses, restoring essential services like water and electricity, and providing long-term support for individuals experiencing psychological trauma. The failure to adequately address these needs can impede a community’s recovery trajectory, leading to prolonged hardship and increased vulnerability to future disasters.
A national disaster management agency plays a central role in coordinating and facilitating recovery efforts. This includes assessing damage, developing recovery plans, allocating resources, and collaborating with government agencies, non-governmental organizations, and international partners. Effective recovery strategies incorporate a holistic approach, addressing both the physical and psychosocial needs of affected communities. For instance, rebuilding infrastructure to higher standards of resilience can mitigate the impact of future disasters. Similarly, providing mental health services and supporting community-based recovery initiatives fosters social cohesion and accelerates the healing process. Challenges in recovery can arise from funding limitations, logistical complexities, and the long-term nature of rebuilding efforts, highlighting the need for sustained commitment and adaptive management strategies. The Indian Ocean tsunami of 2004, for instance, underscored the enormous scale and complexity of post-disaster recovery, requiring a coordinated international response and sustained investment over many years.
The recovery phase, while often extending over years, is integral to a nation’s ability to build back better. Successful recovery not only restores pre-disaster conditions but also strengthens community resilience and reduces vulnerability to future hazards. Understanding the interconnectedness of preparedness, response, and recovery within the framework of a national disaster management agency’s mission emphasizes the importance of long-term planning, community engagement, and sustained investment in disaster risk reduction. Effective recovery strategies contribute not only to restoring communities but also to fostering sustainable development and enhancing national security in the face of evolving disaster risks.
4. Mitigation
Mitigation, a core function of a national disaster management agency, encompasses sustained actions taken to reduce or eliminate long-term disaster risks. Unlike response and recovery, which address immediate needs, mitigation focuses on proactive measures to minimize the impact of future hazards. This forward-looking approach involves a range of strategies, from implementing building codes and land-use planning regulations to investing in infrastructure improvements and ecosystem restoration. Mitigation efforts require comprehensive risk assessments, interagency collaboration, and community engagement. For example, enforcing stringent building codes in earthquake-prone areas can significantly reduce structural damage and casualties during seismic events. Similarly, constructing flood defenses or restoring coastal wetlands can mitigate the impact of floods and storm surges. Effective mitigation reduces the frequency and severity of disasters, saving lives and minimizing economic losses.
A national disaster management agency plays a crucial role in developing and implementing mitigation strategies. This includes conducting vulnerability assessments, developing mitigation plans, advocating for policy changes, and providing technical assistance to communities. These agencies often collaborate with scientific institutions, engineering firms, and local governments to identify cost-effective mitigation measures. For instance, agencies may work with researchers to model flood risks and identify optimal locations for flood control infrastructure. They also provide guidance to communities on implementing mitigation measures, such as retrofitting buildings to withstand earthquakes or developing community-based evacuation plans. Successful mitigation requires sustained investment, political will, and community buy-in. Challenges can arise from competing priorities, funding limitations, and the long-term nature of mitigation projects, requiring agencies to prioritize actions based on risk assessments and cost-benefit analyses.
Mitigation represents a critical investment in long-term disaster risk reduction. While often less visible than response and recovery efforts, mitigation measures yield substantial benefits by reducing the frequency, intensity, and consequences of disasters. A robust mitigation strategy, implemented and championed by a national disaster management agency, strengthens community resilience, protects critical infrastructure, and contributes to sustainable development. Understanding the importance of mitigation within the broader disaster management framework requires recognizing its proactive nature and its essential contribution to reducing long-term risks. Integrating mitigation into all aspects of planning and development is crucial for building safer, more resilient communities and nations.
5. Coordination
Coordination, a critical function of a national disaster management agency, ensures the seamless integration and efficient operation of diverse stakeholders during all phases of disaster managementpreparedness, response, recovery, and mitigation. Effective coordination minimizes duplication of effort, maximizes resource utilization, and facilitates timely and appropriate action. This intricate process involves establishing clear communication channels, defining roles and responsibilities, and fostering collaborative relationships among government agencies, non-governmental organizations, international partners, and the private sector. For example, during the response phase of a major hurricane, coordination ensures that search and rescue teams, medical personnel, and logistics providers work together seamlessly to deliver aid to affected populations. A lack of coordination can lead to delays, confusion, and gaps in service delivery, hindering the effectiveness of disaster management efforts. The success of disaster response often hinges on the pre-existing relationships and communication protocols established through proactive coordination efforts.
A national disaster management agency serves as the central coordinating body, facilitating communication and collaboration among various stakeholders. This involves developing comprehensive disaster preparedness plans, conducting regular training exercises, and establishing clear lines of authority. The agency plays a crucial role in information sharing, resource allocation, and logistical support. In the aftermath of a large-scale earthquake, for instance, the agency coordinates the deployment of search and rescue teams, the establishment of temporary shelters, and the distribution of essential supplies. This coordinated approach ensures a rapid and effective response, maximizing the chances of saving lives and minimizing suffering. Practical challenges in coordination can arise from differing organizational cultures, communication barriers, and competing priorities, emphasizing the need for strong leadership, adaptable strategies, and robust communication systems. The experience of responding to the 2010 Haiti earthquake, for example, highlighted the challenges of coordinating international aid efforts in a complex and rapidly evolving disaster environment.
Effective coordination is essential for maximizing the impact of disaster management efforts. It amplifies the effectiveness of individual agencies, optimizes resource allocation, and facilitates a unified, coherent response. By fostering collaboration and communication, a national disaster management agency strengthens a nations capacity to prepare for, respond to, and recover from disasters, ultimately reducing human suffering and economic losses. Investing in robust coordination mechanisms, including communication systems, training programs, and joint planning exercises, is a critical component of building resilient communities and nations. The ability to effectively coordinate diverse actors and resources during times of crisis is a hallmark of a well-prepared and resilient nation, underscoring the fundamental role of coordination in comprehensive disaster management.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the role and function of a national disaster management agency, providing concise and informative responses.
Question 1: How does a national disaster management agency differ from local emergency services?
A national-level organization focuses on strategic planning, coordination, resource allocation, and policy development at the national level. Local emergency services, such as fire departments and emergency medical services, provide immediate, on-the-ground response within their specific jurisdictions. The national agency supports and coordinates the efforts of local agencies during large-scale events.
Question 2: What role does the public play in national disaster management efforts?
Public participation is crucial. Individual preparedness, including developing family emergency plans and assembling emergency kits, significantly enhances community resilience. Active involvement in community-based preparedness initiatives and adherence to official guidance during emergencies contributes to effective disaster management.
Question 3: How does a national disaster management agency address the needs of vulnerable populations during disasters?
Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, individuals with disabilities, and low-income communities, receive prioritized attention. Disaster preparedness plans incorporate specific strategies to address their unique needs, including accessible communication channels, specialized evacuation procedures, and targeted resource allocation.
Question 4: How are resources allocated during a disaster response?
Resource allocation follows established protocols based on need and impact assessments. Priority is given to life-saving activities, such as search and rescue, medical assistance, and the provision of essential supplies like food, water, and shelter. Resource distribution is continuously monitored and adjusted as the situation evolves.
Question 5: What measures are taken to mitigate the economic impact of disasters?
Economic mitigation strategies encompass pre-disaster planning, including business continuity planning and insurance coverage, as well as post-disaster support programs, such as financial assistance for businesses and individuals affected by the event. These measures aim to minimize economic disruption and facilitate recovery.
Question 6: How does a national disaster management agency collaborate with international partners?
International collaboration is essential for effective disaster management. Agencies routinely engage in knowledge sharing, joint training exercises, and mutual assistance agreements with international counterparts. This collaboration enhances response capabilities, particularly during large-scale disasters that require international support.
Understanding the role and responsibilities of a national disaster management agency is crucial for informed participation in disaster preparedness and response efforts. Community awareness and proactive engagement contribute significantly to building resilient nations.
This FAQ section provides a foundational understanding of disaster management principles. The following sections will explore specific disaster scenarios and delve deeper into the intricacies of each phase of disaster management.
Conclusion
Organizations dedicated to disaster management serve a crucial function in safeguarding communities and nations. From proactive mitigation efforts to immediate response and long-term recovery operations, these entities provide essential services that protect lives, minimize economic losses, and foster societal resilience. Effective disaster management requires a comprehensive approach encompassing preparedness planning, community engagement, robust infrastructure development, and interagency coordination. Investing in these capacities represents a critical investment in national security and sustainable development.
The increasing frequency and intensity of disasters globally underscores the vital importance of robust disaster management frameworks. Continued investment in research, technology, and capacity building is essential to effectively address evolving disaster risks. Strengthening international cooperation and fostering a culture of preparedness at all levelsindividual, community, and nationalwill be paramount in mitigating the impacts of future disasters and building a more resilient world.